INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
- A comprehensive study of the structure and quality of commit messages encompassed data collection from GitHub repositories and preliminary data cleansing.
- The research involved text vectorization of commit messages and evaluation of semantic similarity between the first sentences and full texts of messages using cosine similarity.
- The comparative analysis of message quality in the collected dataset and several analogous datasets used classification based on the CodeBERT model.
Objectives. In contemporary software development practice, version control systems are often used to manage the development process. Such systems allow developers to track changes in the codebase and convey the context of these changes through commit messages. The use of such messages to provide relevant and high-quality descriptions of the changes generally requires a high level of competence and time commitment from the developer. However, modern machine learning methods can enable the automation of this task. Therefore, the work sets out to provide a statistical and comparative analysis of the collected data sample with sets of changes in the program code and their descriptions in natural language.
Methods. In this study, a comprehensive approach was used, including data collection from popular GitHub repositories, preliminary data processing and filtering, as well as statistical analysis and natural language processing method (text vectorization). Cosine similarity was used as a means of assessing the semantic proximity between the first sentence and the full text of commit messages.
Results. A comprehensive study of the structure and quality of commit messages encompassed data collection from GitHub repositories and preliminary data cleansing. The research involved text vectorization of commit messages and evaluation of semantic similarity between the first sentences and full texts of messages using cosine similarity. The comparative analysis of message quality in the collected dataset and several analogous datasets used classification based on the CodeBERT model.
Conclusions. The analysis revealed a low level of cosine similarity (0.0969) between the first sentences and full texts of commit messages, indicating a weak semantic relationship between them and refuting the hypothesis that first sentences serve as summaries of message content. The low proportion of empty messages in the collected dataset at 0.0007% was significantly lower than expected, indicating high-quality data collection. The results of classification analysis showed that the proportion of messages categorized as “poor” in the collected dataset was 16.82%, substantially lower than comparable figures in other datasets, where this percentage ranged from 34.75% to 54.26%. This fact underscores the high quality of the collected dataset and its suitability for further application in automatic commit message generation systems.
- Ontological modeling is shown to be applicable only to related models or to models between which there is a commonality.
- A technology of ontological modeling is proposed, in which version information retrieval is the initial part, while the second option involves the use of cluster analysis technology.
- Since ontological modeling uses qualitatively quantitative transitions, the proposed variant can be used to extract implicit knowledge.
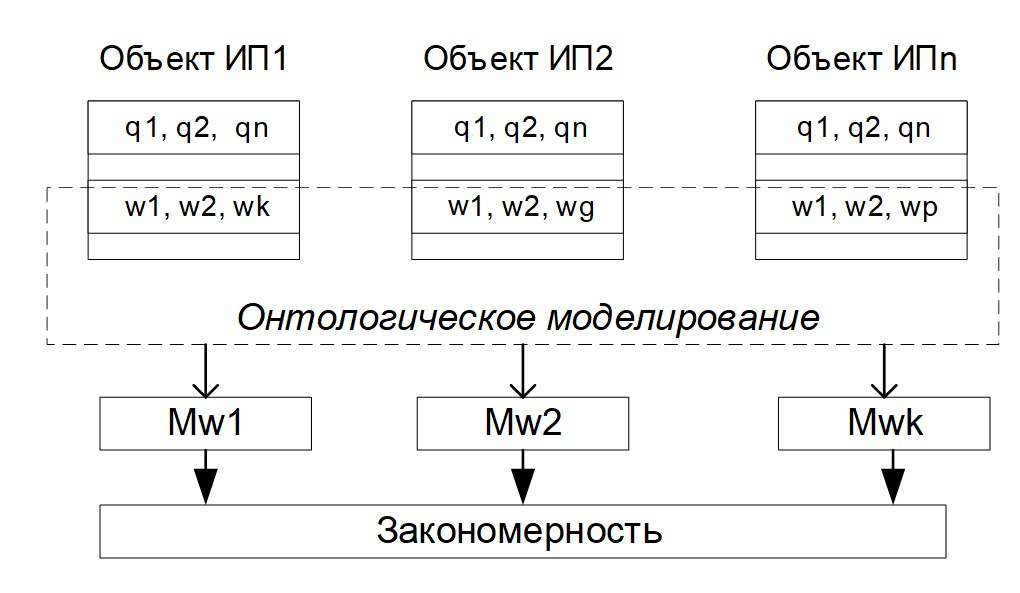
Objectives. Despite the wide application of the term “ontology” in philosophy and social sciences, ontological modeling in the fields of computer science and information theory remains poorly studied. The purpose of the work is to develop a methodology for the ontological modeling of information and to clarify the theory of information retrieval technology both in a broad sense and as part of ontological modeling. Relevant problems in ontological modeling include the necessity of demonstrating the difference between regularity and functional dependence.
Methods. To achieve the stated goal, a logically structural approach is used, including the construction of conceptual schemes and their description in terms of logical formalism. The logically structural approach includes the construction of conceptual schemes that serve to apply logical formalism. The basis of logical modeling involves the selection of related models. The extended information retrieval technology proposed for this purpose searches not for individual objects, but for groups of objects. Since ontological research is based on a transition from qualitative to quantitative description, the methods used include quantitative-qualitative transitions.
Results. A new concept of ontological modeling of information is introduced. The conditions of ontological modeling are substantiated. Relationships between the concepts of regularity and functionality are investigated. On this basis, an interpretation of regularity and functional dependence is given. Structural and formal differences between information modeling, information retrieval technologies, and ontological modeling are demonstrated. Three information retrieval tasks are described, of which the second and third tasks involving the search for a group of related objects and the search for relationships or connections within a group of related objects, respectively, are solved using ontological modeling. Formal schemes of ontological modeling are provided. The transition from relations to connections in the case of ontological modeling is demonstrated.
Conclusions. Ontological modeling is shown to be applicable only to related models or to models between which there is a commonality. A technology of ontological modeling is proposed, in which version information retrieval is the initial part, while the second option involves the use of cluster analysis technology. Since ontological modeling uses qualitatively quantitative transitions, the proposed variant can be used to extract implicit knowledge.
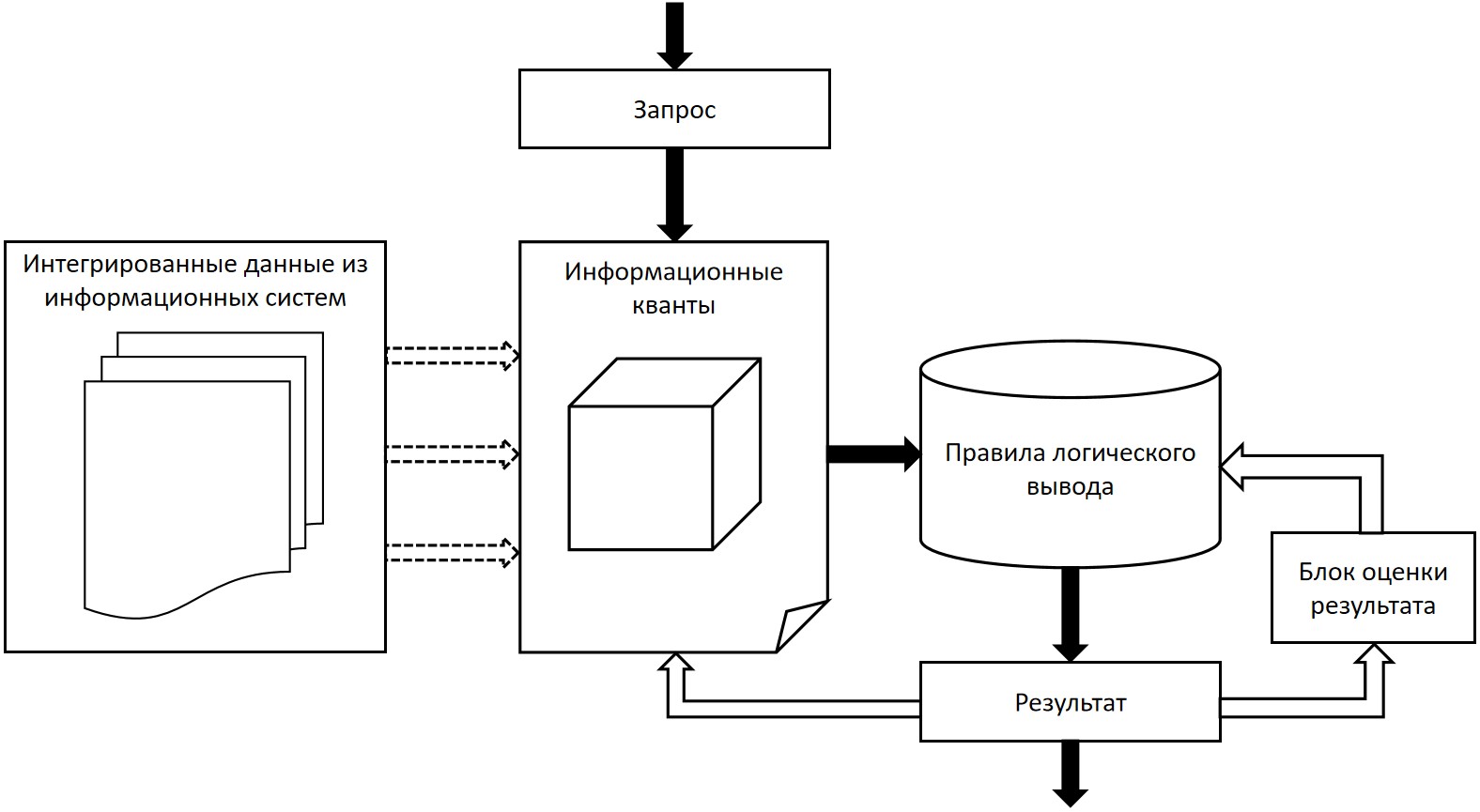
- Issues and challenges involved in the integration of information systems (IS) in large organizations are considered in terms of integration methods based on physical and logical principles.
- The proposed scheme for the logical integration of IS includes an algebraic method for quantitatively assessing the topological significance of integration.
- Methods based on learning expert systems, which represent a fundamental solution for organizing the logical integration of IS for intelligent data analysis, are reviewed.
Objectives. The study set out to develop fundamental methodological principles for the logical integration of information systems (IS) in organizations and to quantitatively assess the topological significance of the IS integration process.
Methods. Methods based on expert systems were used for the logical integration of information in conjunction with data-mining approaches based on various IS. In order to quantitatively assess the topological significance of the IS integration procedure, graph theory methods were used. Discrete topology methods were also employed for calculating the topological invariants of the IS interconnection topology.
Results. Issues and challenges involved in the integration of IS in large organizations are considered in terms of integration methods based on physical and logical principles. While IS integration approaches based on logical principles offer distinct advantages over physical integration approaches, new problems arising in the context of logical integration approaches require innovative solutions. The proposed scheme for the logical integration of IS includes an algebraic method for quantitatively assessing the topological significance of integration, comprising an important numerical indicator in the logical integration of IS. Methods based on learning expert systems, which represent a fundamental solution for organizing the logical integration of IS for intelligent data analysis, are reviewed.
Conclusions. When integrating IS in organizations, it is advisable to use a logical integration approach that preserves the logic of existing information systems. The application of logical integration enables intelligent data analysis using various IS. The use of expert systems in logical integration enables the creation of a new logical layer for providing decision support within the organization.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- An experimental test bench of the Zeta topology DC/DC converter was designed and built using coupled chokes based on the TPS40200 driver.
- The results of the study showed a high correlation of both its load characteristics and its DC and AC components of currents flowing through the choke windings and capacitor voltages from the input voltage at two load resistances of 50 and 100 Ohm obtained by experimental, computational, and modeling methods.
Objectives. The study set out to investigate typical characteristics of a Zeta converter developed by the authors based on the TPS40200 driver under various input voltages and loads and compare the experimental characteristics of the Zeta converter with those obtained through SPICE1 simulation in the Multisim computer-aided design (CAD) system, as well as with the results derived from a continuous-time mathematical model.
Methods. A continuous-time mathematical model of the Zeta converter and the Multisim CAD system were used. The schematic diagram of the converter was developed according to the TPS40200 driver circuit design methodology presented in its datasheet. The printed circuit board layout was created using the Altium Designer CAD system.
Results. An experimental test bench of the Zeta topology DC/DC converter was designed and built using coupled chokes based onthe TPS40200driver. The results ofthe study showed ahigh correlation ofboth its load characteristics and its DC and AC components of currents flowing through the choke windings and capacitor voltages from the input voltage at two load resistances of 50 and 100 Ohm obtained by experimental, computational, and modeling methods.
Conclusions. The continuous-time mathematical model of the converter, along with the calculation method based on it, forms a foundation for the design of DC/DC converters using the Zeta topology. The experiment confirms the validity of both the mathematical model and the calculation method. The proposed design methods takes the magnetic coupling and the active resistance of inductors into account. The magnetic coupling permits a two-fold reduction of inductor values while maintaining the same ripple or a reduction in the ripple by up to half with unchanged inductor values.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
- Analytical expressions were obtained for the operator of the concentration of the temperature field strength on the surface of the inclusion taking the form of a thin disk of multilayer graphene in a matrix composite. The expressions take into account inclusion anisotropy, the position of the point on the inclusion surface, the volume fraction of inclusions in the material, and the inclusion orientation.
- Two types of inclusion orientation distributions were considered: equally oriented inclusions and uniform distribution of inclusion orientations.
- In the case of graphene multilayer inclusions, it is shown that the field strength at points on their edges can exceed the applied field strength by several orders of magnitude.
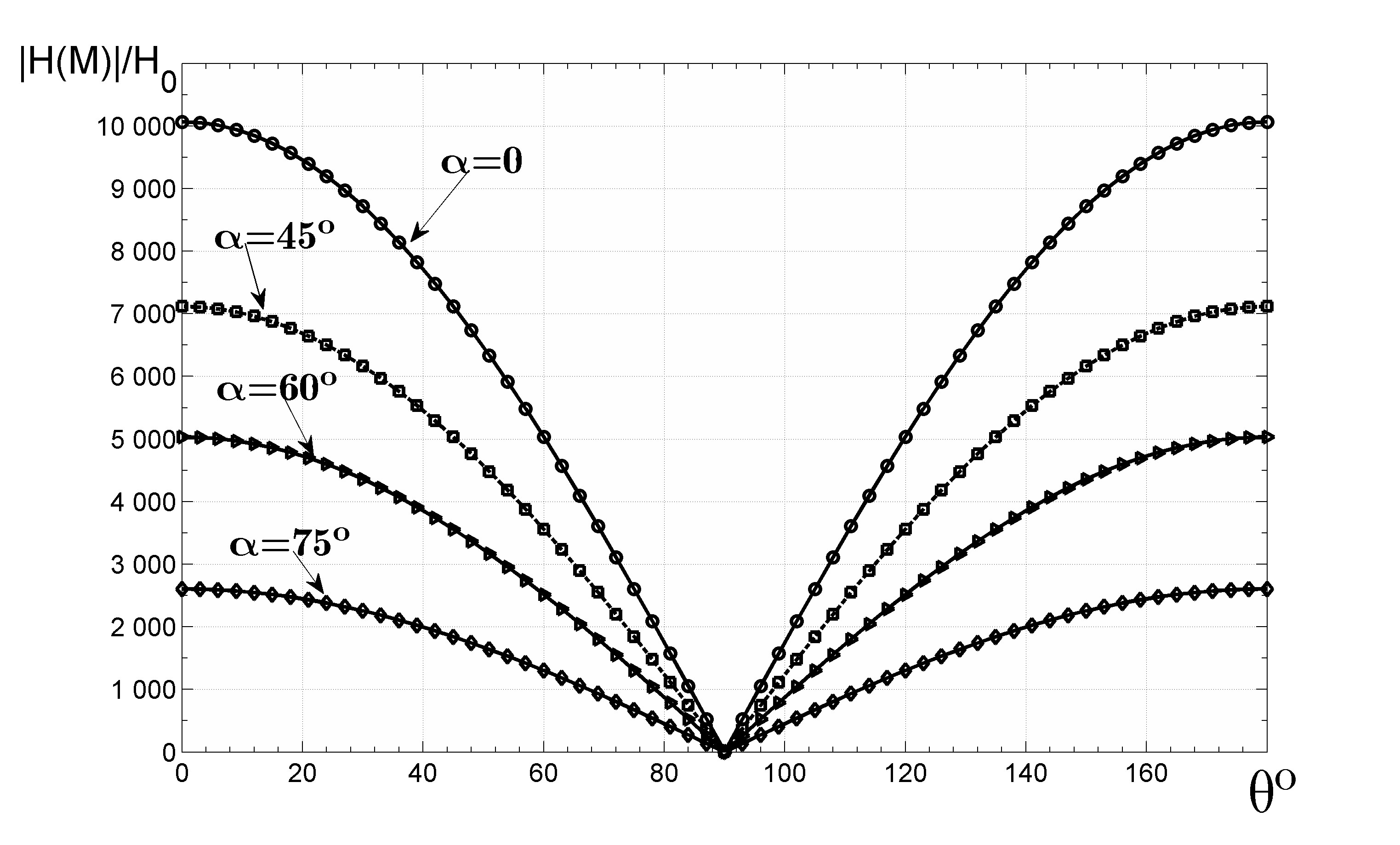
Objectives. The study sets out to obtain an analytical expression for the distribution of the temperature field strength on the surfaces of anisotropic graphene inclusions taking the form of thin disks in the matrix composite and to use the obtained expressions to predict the strength of the temperature field on the surface of inclusions from the matrix side.
Methods. An inclusion taking the form of a thin circular disk represents a special limit case of an ellipsoidal inclusion. To obtain the corresponding analytical expressions, the authors use their previously derived more general expression for the operator of the concentration of the electric field strength on the surface of ellipsoidal inclusion. The approach is justified by the mathematical equivalence of problems of finding the electrostatic and temperature field in the stationary case. The operator relates the field strength on the inclusion surface from the matrix side to the average field strength in the composite sample; the corresponding expression is obtained in a generalized singular approximation.
Results. Analytical expressions were obtained for the operator of the concentration of the temperature field strength on the surface of the inclusion taking the form of a thin disk of multilayer graphene in a matrix composite. The expressions take into account inclusion anisotropy, the position of the point on the inclusion surface, the volume fraction of inclusions in the material, and the inclusion orientation. Two types of inclusion orientation distributions were considered: equally oriented inclusions and uniform distribution of inclusion orientations. Model calculations of the value for the temperature field strength at the points of the inclusion disk edge as a function of the angle between the radius vector of this point and the direction of the applied field strength were carried out. Conclusions. In the case of graphene multilayer inclusions, it is shown that the field strength at points on their edges can exceed the applied field strength by several orders of magnitude.
- The results of the study show that strong electric fields and high specific thermal loading of high-power GaN HFETs can cause physical, polarization, piezoelectric and thermal phenomena that lead to redistribution of mechanical stresses in the active region, degradation of electrical characteristics, and a decrease in the reliability of the transistor as a whole.
- It is shown that the presence of a field-plate and a passivating SiN layer leads to a decrease in the values of mechanical stress in the gate area by 1.3–1.5 times. The effects of thermal degradation in class AB amplifiers are more pronounced than the effects of strong fields in class E amplifiers; moreover, the mean time to failure sharply decreases at GaN HFET active zone temperatures over 320–350°C.
Objectives. Gallium nitride heterostructural field-effect transistors (GaN HFET) are among the most promising semiconductor devices for power and microwave electronics. Over the past 10–15 years, GaN HFETs have firmly established their position in radio-electronic equipment for transmitting, receiving, and processing information, as well as in power electronics products, due to their significant advantages in terms of energy and thermal parameters. At the same time, issues associated with ensuring their reliability are no less acute than for devices based on other semiconductor materials. The aim of the study is to review the thermal and mechanical mechanisms of degradation in GaN HFETs due to the physicochemical characteristics of the materials used, as well as their corresponding growth and post-growth processes. Methods for preventing or reducing these mechanisms during development, production, and operation are evaluated.
Methods. The main research method consists in an analytical review of the results of publications by a wide range of specialists in the field of semiconductor physics, production technology of heteroepitaxial structures and active devices based on them, as well as the modeling and design of modules and equipment in terms of their reliable operation.
Results. As well as describing the problems of GaN HFET quality degradation caused by thermal overheating, mechanical degradation, problems with hot electrons and phonons in gallium nitride, the article provides an overview of research into these phenomena and methods for reducing their impact on transistor technical parameters and quality indicators.
Conclusions. The results of the study show that strong electric fields and high specific thermal loading of highpower GaN HFETs can cause physical, polarization, piezoelectric and thermal phenomena that lead to redistribution of mechanical stresses in the active region, degradation of electrical characteristics, and a decrease in the reliability ofthe transistor as a whole. Itis shown that the presence of a field-plate and a passivating SiN layer leads to a decrease in the values of mechanical stress in the gate area by 1.3–1.5 times. The effects of thermal degradation in class AB amplifiers are more pronounced than the effects of strong fields in class E amplifiers; moreover, the mean time to failure sharply decreases at GaN HFET active zone temperatures over 320–350°C.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- The process of hot isostatic pressing of long tubes from powder materials in metal capsules was investigated using mathematical modeling. By analyzing the stress-strain state in the areas far from the top and bottom borders in the cylindrical system of coordinates, the axial strain rate at every moment of the process can be considered to be constant through the entire volume.
- The proposed model takes all the features of this process into account depending on the system parameters.
- The possibility of using tubular samples to determine the functions included in the Green’s condition is demonstrated.
Objectives. The work set out to create a mathematical model to investigate the process of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process of long tubes from powder materials in metal capsules. By analyzing the stress-strain state in the areas far from the top and bottom borders in the cylindrical system of coordinates, the axial strain rate at every moment of the process can be considered to be constant through the entire volume.
Methods. Mathematical modeling methods were used to describe mechanical properties in the process of HIP deformation by Green’s model of porous compressible media. The HIP capsule material, which is considered to be non-compressible, is described by the ideal plasticity model. The temperature field is assumed to be uniform over the volume and constant during the time of deformation.
Results. The hypothesis of the uniform density over the cross section at each moment of the process was considered during analysis to the extent that the wall thickness of the tube is substantially less than its diameter. This hypothesis allowed us to reduce the task of determining the strain rates at every step of the process to a solution comprising two equations having two variables. When the strain rates are determined, the deformation field is built to obtain the final dimensions of the tube when the powder material is fully consolidated at the end of the HIP process.
Conclusions. The proposed model for describing the process hot isostatic pressing of long tubes from powder materials takes all the features of this process into account depending on the system parameters. The possibility of using tubular samples to determine the functions included in the Green’s condition is demonstrated.
- A dynamic model for unrestricted management of a BSF portfolio was developed.
- By presenting risky asset prices according to a tree structure, the model can be used to increase the accuracy of evaluating investments by from 2.4 to 2.7 times for the first approach and from 1.7 to 2.7 times for the second.
- The increased accuracy of evaluating investments as compared with previously proposed models is achieved by averaging prices at various vertices of the tree.
Objectives. The work compares studies on BSF portfolios consisting of a risk-free Bond (B) asset, a Stock (S), and a cash Flow (F) that represents risky asset prices in the form of a tree structure. On the basis of existing models for managing dynamic investment portfolios, the work develops a dynamic model for managing a BSF portfolio that combines risk-free and risky assets with a deposit. Random changes in the prices of a risky asset are reflected in the developed model according to a tree structure. Two approaches to portfolio formation are proposed for the study: (1) initial capital is invested in a risk-free asset, while management is conducted at the expense of a risky asset; (2) the initial capital is invested in a risky asset, but management is carried out at the expense of a risk-free asset.
Methods. A binomial model was used to predict the prices of risky assets. Changes in risky asset prices in the model are dynamically managed via a branching tree structure. A comparative analysis of modeling results reveals the optimal control method.
Results. A dynamic model for unrestricted management of a BSF portfolio has been developed. By presenting risky asset prices according to a tree structure, the model can be used to increase the accuracy of evaluating investments by from 2.4 to 2.7 times for the first approach and from 1.7 to 2.7 times for the second. The increased accuracy of evaluating investments as compared with previously proposed models is achieved by averaging prices at various vertices of the tree.
Conclusions. The results of the research suggest that the use of a dynamic management model based on a tree-like price structure can significantly increase the accuracy of evaluating investments in an investment portfolio.
- To investigate the molecular mechanisms of the direct proton transport along the water-membrane interface, we developed a model of proton movement along quasi-one-dimensional lateral domain structures in multicomponent lipid membranes.
- The results of modeling showed that the interaction between an excess proton on the membrane surface and a soliton of membrane compression leads to the proton being trapped by an acoustic soliton, followed by its transport by moving soliton.
- The developed model was applied to describe effective proton transport along the inner mitochondrial membrane and its role in the local coupling function of molecular complexes in cell bioenergetics.
Objectives. The study of proton transport in membrane structures represents a significant technological task in the development of hydrogen energy as well as a fundamental problem in bioenergetics. Investigation in this field aims at finding out the physical mechanisms of fast proton transport in the meso-porous structures in polymer electrolyte membranes, which serve as electrochemical components of hydrogen fuel cells. The objectives of the research in the field of bioenergetics are to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of effective proton transport in transmembrane channel proteins, as well as along the surface proton-conducting structures in biological membranes. To investigate the molecular mechanisms of the direct proton transport along the water-membrane interface, we developed a model of proton movement along quasi-one-dimensional lateral domain structures in multicomponent lipid membranes.
Methods. The developed approach is based on a model of collective excitations spreading along the membranes in the form of acoustic solitons, which represent the regions of local compression of polar groups and structural defects in hydrocarbon chains of lipid molecules.
Results. The results of modeling showed that the interaction between an excess proton on the membrane surface and a soliton of membrane compression leads to the proton being trapped by an acoustic soliton, followed by its transport by moving soliton. The developed model was applied to describe effective proton transport along the inner mitochondrial membrane and its role in the local coupling function of molecular complexes in cell bioenergetics.
Conclusions. The developed soliton model of proton transport demonstrated that collective excitations within lipid membranes can determine one of the factors affecting the efficiency of proton transport along interphase boundaries. Further development of the theoretical approaches, taking into account dynamic properties of polymer and biological proton-conducting membranes, can contribute to the study of a role of surface proton transport in cell bioenergetics, as well as to the investigation of transport characteristics of the proton-exchange polymer membranes developed for the hydrogen energy industry.
- A method for estimating the objective function landscape convexity in the extremum neighborhood. The proposed method, which requires no additional objective function calculations or complicated mathematical processing, relies on the data accumulated during extremum search was developed.
- The experiments confirm that the proposed method provides a reliable estimation of power index range bounds upon condition of appropriate definition of trial points and trial point pair selection parameters.
Objectives. The work set out to develop a method for estimating the objective function (OF) landscape convexity in the extremum neighborhood. The proposed method, which requires no additional OF calculations or complicated mathematical processing, relies on the data accumulated during extremum search.
Methods. Landscape convexity is characterized by the index of power approximation of the OF in the vicinity of the extremum. The estimation of this index is carried out for pairs of test points taking into account their distances to the found extremum and OF values in them. Based on the analysis of estimation errors, the method includes the selection of test points by their distances from the found extremum and the selection of pairs of test points by the angle between the directions to them from the found extremum. Test functions having different convexities, including concave, were used to experimentally validate the method. The particle swarm optimization algorithm was used as an extremum search method. The experimental results were presented in the form of statistical characteristics and histograms of distributions of the estimation values of the degree of the OF approximation index.
Results. The conductive experiments confirm that the proposed method provides a reliable estimation of power index range bounds upon condition of appropriate definition of trial points and trial point pair selection parameters.
Conclusions. The proposed method may be a part of OF landscape analysis. It is necessary to complement it with the algorithms for automatic adjustment of trial points and pairs of trial points selection parameters. Additional information may be provided by analyzing the dependencies of power index estimations and trial point distances from extrema.
- A nonlinear two-parameter function was selected from three options for approximating functions of the section profile of a laser surfacing track.
- Optimal values of the technological parameters of surfacing were obtained using regression models of these mappings to provide the maximum value of the area of the surfacing contour under restrictions on the proportion of the sub-melting area to the total cross-sectional area.
Objectives. Laser powder surfacing is a promising mechanical engineering technology used to effectively restore worn surfaces of parts and create special coatings with valuable properties. In the research and development of laser cladding technology, mathematical modeling methods are of crucial importance. The process of applying powder coating involves moving the spray head relative to the surface of the part to form a roller or spray path, whose sequential application results in the formation of coatings. The study sets out to evaluate methods of profile approximation and optimization of technological parameters in laser powder cladding processes.
Methods. In order to describe the dependencies of the profile parameters of the deposition paths during laser surfacing on the technological parameters of the process, mathematical modeling methods were used. The contours of the profiles of the surfacing section were obtained by analyzing images of microphotographs of thin sections of the cross sections of parts with applied surfacing. To approximate the curves of the section contours, methods of linear and nonlinear regression analysis were used. The dependence of the parameters of the profile contours of the surfacing section on the technological parameters of the spraying was represented by a two-factor parabolic regression equation. The search for optimal values of spraying technological parameters was carried out using the method of conditional optimization with linear approximation of the confidence region.
Results. A nonlinear two-parameter function was selected from three options for approximating functions of the section profile of a surfacing track. Technological surfacing parameters were mapped onto a set of parameters of the approximating contour line. Optimal values of the technological parameters of surfacing were obtained using regression models of these mappings to provide the maximum value of the area of the surfacing contour under restrictions on the proportion of the sub-melting area to the total cross-sectional area. The approximating function of the cross-sectional profile of the surfacing track was used to calculate the optimal pitch of the tracks that provides the most even surface.
Conclusions. The results of the study represent a technique for optimizing the technological parameters of laser surfacing with powder metals to ensure specified characteristics of the deposition track profile and select the track deposition step at which the most even deposition surface is achieved.
- The problem of restoring defocused and/or linearly blurred images using a Tikhonov-regularized inverse filter is considered.
- In the case of restoring images at the resolution limit, i.e., when the pixel size cannot be considered negligibly small compared to the details of the image, the proposed approach can slightly improve the resolution.
Objectives. The problem of restoring defocused and/or linearly blurred images using a Tikhonov-regularized inverse filter is considered. A common approach to this problem involves solving the Fredholm integral equation of the first convolution type by means of discretization based on quadrature formulas. The work sets out to obtain an expression of the point scattering function (PSF) taking into account pixel size finiteness and demonstrate its utility in application.
Methods. The research is based on signal theory and the method of digital image restoration using Tikhonov regularization.
Results. Taking into account the finiteness of the pixel size, discrete PSF formulas are obtained both for the case of a defocused image and for the case of a linearly blurred image at an arbitrary angle. It is shown that, while differences between the obtained formulas and those traditionally used are not significant under some conditions, under other conditions they can become significant.
Conclusions. In the case of restoring images at the resolution limit, i.e., when the pixel size cannot be considered negligibly small compared to the details of the image, the proposed approach can slightly improve the resolution. In addition, the derived formula for the discrete PSF corresponding to linear blur in an arbitrarily specified direction can be used to solve the problem without the need for prior image rotation and account for the blur value with subpixel accuracy. This offers an advantage in terms of improving the resolution of extremely fine details in the image, allowing the obtained formula to be used in solving the adaptive deconvolution problem, where precise adjustment of PSF parameters is required.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)