MULTIPLE ROBOTS (ROBOTIC CENTERS) AND SYSTEMS. REMOTE SENSING AND NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
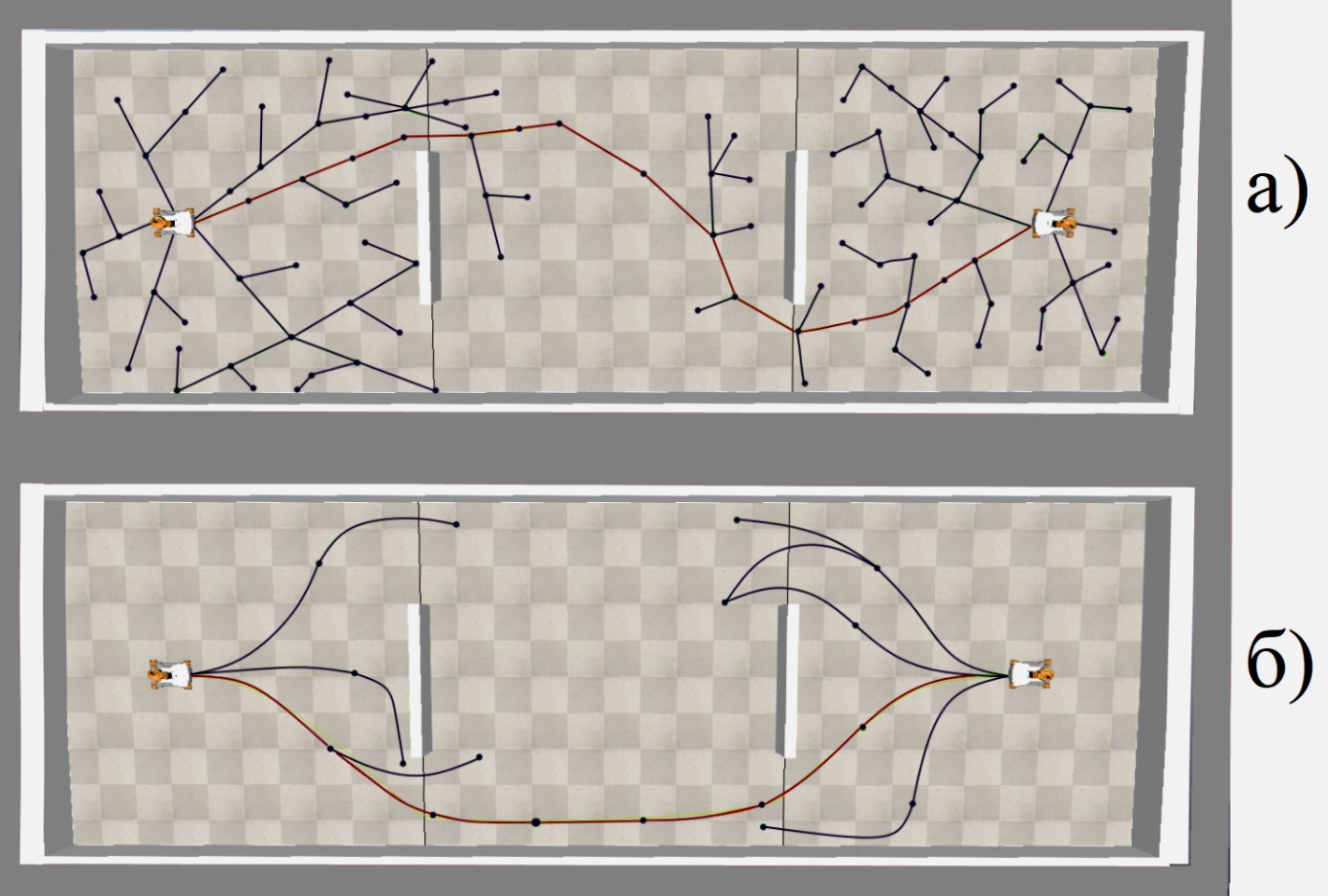
- The study analyzed the features of automatic docking as one of the tasks of group control of autonomous robots. This is part of multi-agent systems, capable of reconfiguring structures for purposeful changes to the existing set of functional properties and application possibilities.
- The study also proposes a decentralized modification of the counter-growth RRT method. This allows the movements of autonomous mobile robots in the course of their mutual approach and subsequent docking to be planned.
- A set of software-algorithmic tools was developed to automate the docking of autonomous robots.
- A series of model and full-scale experiments were carried out to confirm the effectiveness of the approach developed herein.
Objectives. The article substantiates the relevance of automatic docking of autonomous mobile robots. Specific examples show that the implementation of the automatic docking functions of autonomous robots reveals the potential for creating multi-agent systems with a transformable structure. The aim of the work is to develop means for automatic docking of autonomous mobile robots in complex scenarios and an uncertain environment.
Methods. The proposed approach to automating autonomous mobile robot docking is reduced to a modification of the counter-growth rapidly-exploring random tree (RRT) method. It is based on the parallel execution of a decentralized route planning algorithm with mutual coordination of distributed computing processes. The effectiveness of the complex of algorithmic and software tools developed was evaluated using computer and natural simulation methods. The final series of full-scale experiments was carried out on the example of JetBot AI kit Nvidia platforms for automatic docking of autonomous robots. This was performed using the means and methods of intelligent control, visual navigation, technical vision and wireless network communication.
Results. The study analyzed the features of automatic docking as one of the tasks of group control of autonomous robots. This is part of multi-agent systems, capable of reconfiguring structures for purposeful changes to the existing set of functional properties and application possibilities. The study also proposes a decentralized modification of the counter-growth RRT method. This allows the movements of autonomous mobile robots in the course of their mutual approach and subsequent docking to be planned. A set of software-algorithmic tools was developed to automate the docking of autonomous robots. A series of model and full-scale experiments were carried out to confirm the effectiveness of the approach developed herein.
Conclusions. The modification presented herein of the counter-growth RRT method, traditionally used for planning the movements of manipulators and mobile platforms, is complementary to the tasks it resolves. This enables the docking of autonomous robots to be automated. The results obtained open up the potential for universal schedulers with extended functionality for autonomous robot control systems to be designed.
- Simulation of the acoustic signal propagation in multilayer printed circuit boards in serviceable and faulty (with a rectangular defect in the form of delamination) states was carried out to show the difference in the received signals at the sensor installation point.
- Experimental studies were conducted to examine the acoustic emission method applicability for detecting defects of various sizes and quantities.
Objectives. Defects in the form of layering may occur during lamination in the production of multilayer printed circuit boards (MPCB). These defects cannot be detected by optical and electrical methods of output control. However, they can lead to breaches of the mechanical mode of operation and failures while running radioelectronic devices. In order to detect such defects, the acoustic emission (AE) method is proposed. This is based on the occurrence and propagation of acoustic waves in MPCBs caused by the presence of defects. The aim of this study is to investigate the possibility of using the AE method to detect defects in multilayer printed circuit boards. These defects can occur, in particular, in the lamination process.
Methods. A mechanical processes modeling program (for research on the MPCB model) and various samples of two-layer printed circuit boards with pre-introduced defects (for experimental studies) were used to study the propagation of acoustic signals in the MPCB in the presence of defects. A solenoid mounted on the MPCB was used as a source of acoustic signals, while a piezoelectric sensor was used to receive signals. Data processing was carried out by comparing AE signals obtained for a serviceable MPCB sample and for MPCB samples with defects.
Results. Simulation of the acoustic signal propagation in MPCBs in serviceable and faulty (with a rectangular defect in the form of delamination) states was carried out to show the difference in the received signals at the sensor installation point. Experimental studies were also conducted to examine the AE method applicability for detecting defects of various sizes and quantities.
Conclusions. The studies demonstrated that the AE method allows the presence of defects in MPCB occurring during the lamination process to be detected effectively and reliably. This study proposes a new approach to non-destructive testing of MPCB using the AE method. This method significantly increases the reliability of MPCBs and the efficiency of their production processes.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- The software architecture of a multifunctional audio module based on the ADAU1701 audio digital signal processor for testing and debugging media devices in a given spectral-dynamic and spectral-temporal ranges was designed.
- Balanced routing allows the effect of noise induced into the audio channel to be reduced 20-fold, thus enabling calibration of pickup audio devices.
Objectives. The aim of this study is to develop and analyze parameters for a multifunctional audio module based on the ADAU1701 audio digital signal processor in the SigmaStudio environment. This will be used for testing audio devices in the following modes: routing of balanced and unbalanced audio channels according to the differential scheme Di-Box/R Di-Box; spatiotemporal and dynamic audio processing; three-band monochannel cross-separation with independent equalization; and correction of the frequency response of the audio channel with tracking notch auto-suppression of electro-acoustic positive feedback in a given spectral band.
Methods. Visual-graphical architectural programming of audio modules in the SigmaStudio and Flowstone, as well as algorithms for real-time signal audio measurements and analysis of experimental data in the REW and Soundcard Oscilloscope are used.
Results. The characteristics of the Di-Box/R Di-Box circuit were studied, in order to estimate the effect of differential signal conversion on the signal-to-noise ratio in the audio signal path. The characteristics of the reverberation and saturation submodules were established. Furthermore, the effect of equalization modes on the frequency response correction of a studio audio monitor was determined. The paper also studied the effect of an audio compressor on the dynamic range and the level of the output signal. The experimental results of the submodule for compensating the frequency response of an audio monitor using matched filtering were established, and the spectral characteristics of the submodule for automatic suppression of electro-acoustic positive feedback were obtained.
Conclusions. The software architecture of a multifunctional audio module based on the ADAU1701 audio digital signal processor for testing and debugging media devices in a given spectral-dynamic and spectral-temporal ranges was designed. Balanced routing allows the effect of noise induced into the audio channel to be reduced 20-fold, thus enabling calibration of pickup audio devices. The audio signal processing submodule provides: compression response in the dynamic range from −27 to 18.6 dB with the possibility of equalization parameterization in the range of 0.04–18 kHz; reverberation response in the range from 0.5–3000 ms; audio-channel cross-division into 3 with the ability to adjust the amplitude-frequency response in the dynamic range from −30 to 30 dB. The auto-correction submodule of the amplitude-frequency response allows the dynamic nonuniformity of the amplitude-frequency response to be reduced by 40 dB. The auto-suppression submodule of electro-acoustic positive feedback provides notch formant suppression up to −100 dB with an input dynamic range from −50 to 80 dB.
- The studies enabled us to conclude that an imbalance of the quadrature reference oscillations can lead to a significant decrease in the noise immunity of radio systems using amplitude-phase shift keyed (APSK) signals. The minimum energy loss due to imbalance of quadrature reference oscillations is achieved when the imbalance value is less than 10% in amplitude and 2°–3° in phase.
- The amplitude imbalance of quadrature reference oscillations when receiving quadrature amplitude modulation signals is more pronounced than in the case of APSK signals.
- The phase imbalance affects approximately the same.
Objectives. At the present time, amplitude-phase shift keyed (APSK) signals are actively used in satellite communication systems. In particular, they are applied in systems which operate in a limited radio frequency spectrum with increased data transmission quality requirements. Such systems use multi-channel type receivers with maximum likelihood decision on the received symbol (correlation receiver) or quadrature type receivers. The noise immunity of these receivers is directly dependent on the quality of the formation of reference oscillations. These oscillations are reference signals for correlation receivers and in-phase and quadrature components for quadrature receivers. The aim of the work is to analyze the influence of the amplitude and phase parameter spread of the in-phase and quadrature channels on the noise immunity of receiving APSK signals with a circular shape of the signal constellation.
Methods. Methods of statistical radio engineering, theory of optimal signal reception, and computer simulation are used.
Results. The study established the characteristics of noise immunity of the APSK signal reception depending on the spread of parameters of the quadrature converter. The theoretical calculations were confirmed by the results of modeling the transmission of APSK signals in a Gaussian communication channel. A comparison with systems using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) was carried out, in order to assess system stability in the presence of spread parameters among other similar systems.
Conclusions. The studies enabled us to conclude that an imbalance of the quadrature reference oscillations can lead to a significant decrease in the noise immunity of radio systems using APSK signals. The minimum energy loss due to imbalance of quadrature reference oscillations is achieved when the imbalance value is less than 10% in amplitude and 2°–3° in phase. The amplitude imbalance of quadrature reference oscillations when receiving QAM signals is more pronounced than in the case of APSK signals. The phase imbalance affects approximately the same.
- The limiting continuous mathematical model of the DC/DC converter based on SEPIC topology was developed. This model allows for an estimation of the dependence of the currents flowing through the inductor windings and the voltages across the capacitors on a number of parameters.
- Results show that the phase coordinates of the mathematical model tend towards the values of real currents and voltages of the converter at a switching frequency higher than 200 kHz.
Objectives. A DC/DC converter based on SEPIC topology is a unipolar electronic device which converts an input positive voltage into a stabilized output voltage of the same polarity. It also has the ability to regulate polarity both below and above the input voltage. The aim of the paper is to analyze the DC/DC converter in its both operation phases, as well as to draw up equivalent circuits and obtain characterizing differential equations using Kirchhoff’s rules for each phase. Each system of differential equations is reduced to Cauchy equations, in order to be further transformed into a limiting continuous mathematical model. Each system of equations is converted into a matrix form and subsequently combined into a single matrix system.
Methods. The construction of a limiting continuous mathematical model was accomplished using Kirchhoff’s rules. Multisim software was used for the computer simulation, thus enabling the calculated results of direct currents and voltages to be compared to those of the simulation.
Results. Results show that the phase coordinates of the mathematical model tend towards the values of real currents and voltages of the converter at a switching frequency higher than 200 kHz. Fairly good agreement is established between the calculated values of currents and voltages and the values obtained by simulation (with varying fill factor and switching frequency).
Conclusions. The resulting limiting continuous mathematical model of the DC/DC converter based on SEPIC topology allows for an estimation of the dependence of the currents flowing through the inductor windings and the voltages across the capacitors on a number of parameters. The limiting continuous mathematical model of the DC/DC converter based on SEPIC topology is the basis for its circuit design and physical-and-mathematical analysis.
ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
- The paper presents the theoretical basis for controlling the required motors. It proposes a block diagram of the implementation of the controller, and a technique for switching windings when controlling with a trapezoidal signal is proposed. Examples are given in the form of an oscillogram.
- Based on theoretical research, an invariant algorithmic apparatus was developed for building software for various types of microcontrollers.
- Block diagrams of all the main modules of the software are also presented. The main ones include: the event switching algorithm; and the main endless loop of the microcontroller.
- The requirements for microcontrollers to create the various types of speed controllers are formalized herein and presented in the form of a set of mathematical expressions.
Objectives. The high demand for unmanned aircraft and their efficiency makes the production of their components a matter of relevance. One of these components is the speed controller of the brushless electric motor of the propeller motor group. At the current time, Russian industry, however, does not mass-produce them. In order to start production, control methods and algorithms for the hardware and software parts of devices of this type are needed. Criteria for selecting the main components also need to be formalized. The aim of this work is to develop a method for the software control of electric motors. This includes block diagrams and invariant algorithms and methods for the calculated selection of parameters of the main microcontroller of the electronic speed controller.
Methods. Methods of algorithmization, expert assessments, linear computational processes and experimental studies were used.
Results. The paper presents the theoretical basis for controlling the required motors. It proposes a block diagram of the implementation of the controller, and a technique for switching windings when controlling with a trapezoidal signal is proposed. Examples are given in the form of an oscillogram. Based on theoretical research, an invariant algorithmic apparatus was developed for building software for various types of microcontrollers. Block diagrams of all the main modules of the software are also presented. The main ones include: the event switching algorithm; and the main endless loop of the microcontroller. The requirements for microcontrollers to create the various types of speed controllers are formalized herein and presented in the form of a set of mathematical expressions. They enable the number of required peripheral devices and microcontroller ports to be calculated according to the requirements for the microcontroller, as well as the computing power of the core used.
Conclusions. Experimental studies show the reliability of the theoretical research presented herein. The results obtained can be used to select the optimal element base and develop software for speed controllers of electric motors of the propellers of unmanned aircraft.
- One pressing problem when recording brain activity signals by electroencephalography is the need to reduce the effect of interference.
- The proposed Laplacian montage scheme ensures a good suppression of interference signals, the sources of which are located far beyond the projection of the electrode complex.
- A complex consisting of 16 + 1 electrodes was shown to be preferable.
Objectives. One pressing problem when recording brain activity signals by electroencephalography (EEG) is the need to reduce the effect of interference (artifacts). This study presents a method for resolving this problem using the Laplace differential operator. The aim is to determine the number of electrodes included in the Laplacian montage, as well as to clarify the requirements for the geometric shape of their placement, in order to ensure the best quality of EEG signal processing.
Methods. The Laplacian montage method is based on the use of individual electrodes to determine the second derivative of the signal, proportional to the electric current at the corresponding point on the surface of the head. This approach allows the potential of neural activity of the source located in a small area limited by the electrode complex to be evaluated. By using a small number of equidistant electrodes placed around the target electrode, the Laplacian montage can produce a significantly higher quality signal from the area under the electrode complex.
Results. Among all the methods for constructing the Laplacian montage discussed in the article, a complex consisting of 16 + 1 electrodes was shown to be preferable. The choice of the 16 + 1 scheme was determined by the best compromise between the quality of EEG signal processing and the complexity of manufacturing the electrode complex with given geometric parameters. The quality assessment was carried out by simulating the interference signal which allowed the correctness of the choice of installation design to be evaluated.
Conclusions. The use of the Laplacian montage method can significantly reduce the effect of artifacts. The proposed montage scheme ensures a good suppression of interference signals, the sources of which are located far beyond the projection of the electrode complex. However, not all interference arising from sources deep inside the brain, can be effectively suppressed using the Laplacian montage scheme alone.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- When using bagging, the best results are obtained when modeling seasonal time series.
- The quality of forecasts of seigniorage models is somewhat inferior to the quality of forecasts of neural network models, but is at the same level as that of standard ARIMA and ETS models.
- Bagging-based models should be used for time series modeling.
Objectives. The purpose of the article is to build different models of bagging, to compare the accuracy of their forecasts for the test period against standard models, and to draw conclusions about the possibility of further use of the bagging technique in time series modeling.
Methods. This study examines the application of bagging to the random component of a time series formed after removing the trend and seasonal part. A bootstrapped series combining into a new random component is constructed. Based on the component thus obtained, a new model of the series is built. According to many authors, this approach allows the accuracy of the time series model to be improved by better estimating the distribution.
Results. The theoretical part summarizes the characteristics of the different bagging models. The difference between them comes down to the bias estimate obtained, since the measurements making up the bootstraps are not random. We present a computational experiment in which time series models are constructed using the index of monetary income of the population, the macroeconomic statistics of the Russian Federation, and the stock price of Sberbank. Forecasts for the test period obtained by standard, neural network and bagging-based models for some time series are compared in the computational experiment. In the simplest implementation, bagging showed results comparable to ARIMA and ETS standard models, while and slightly inferior to neural network models for seasonal series. In the case of non-seasonal series, the ARIMA and ETS standard models gave the best results, while bagging models gave close results. Both groups of models significantly surpassed the result of neural network models.
Conclusions. When using bagging, the best results are obtained when modeling seasonal time series. The quality of forecasts of seigniorage models is somewhat inferior to the quality of forecasts of neural network models, but is at the same level as that of standard ARIMA and ETS models. Bagging-based models should be used for time series modeling. Different functions over the values of the series when constructing bootstraps should be studied in future work.
- A new mathematical model and algorithm for optimization of compound spline parameters comprising arcs of circles conjugated by clothoids and lines were developed.
- This mathematical model in the form of a modified Lagrange function is used together with a special nonlinear programming algorithm to optimize spline parameters.
- In this case, it is possible to calculate the derivatives of the objective function by the spline parameters in the absence of its analytical expression through these parameters.
Objectives. The aim of the work is to develop the theory of spline-approximation of a sequence of points on a plane for using compound splines with a complex structure. In contrast to a simple spline (e.g., polynomial), a compound spline contains repeating bundles of several elements. Such problems typically arise in the design of traces for railroads and highways. The plan (projection on the horizontal plane) of such a trace is a curve consisting of a repeating bundle of elements “line + clothoid + circle + clothoid ...,” which ensures continuity not only of curve and tangent but also of curvature. The number of spline elements, which is unknown, should be determined in the process of solving the design problem. An algorithm for solving the problem with respect to the spline, which consists of arcs conjugated by straight lines, was implemented and published in an earlier work. The approximating spline in the general case is a multivalued function, whose ordinates may be limited. Another significant factor that complicates the problem is the presence of clothoids that are not expressed analytically (in a formula). The algorithm for determining the number of elements of a spline with clothoids and constructing an initial approximation was also published earlier. The present work considers the next stage of solving the spline approximation problem: optimization using a nonlinear programming spline obtained at the first stage by means of the dynamic programming method.
Methods. A new mathematical model in the form of a modified Lagrange function is used together with a special nonlinear programming algorithm to optimize spline parameters. In this case, it is possible to calculate the derivatives of the objective function by the spline parameters in the absence of its analytical expression through these parameters.
Results. A mathematical model and algorithm for optimization of compound spline parameters comprising arcs of circles conjugated by clothoids and lines have been developed.
Conclusions. The previously proposed two-step scheme for designing paths of linear structures is also suitable for the utilization of compound splines with clothoids.
PRODUCT QUALITY MANAGEMENT. STANDARDIZATION
- Deviations of the angular dependence of bactericidal radiation UV radiometer sensitivity from the cosine characteristic lead to a significant underestimation of the irradiance measurements results from extended emitters.
- An effective solution is the use of digital angular sensitivity correction coefficients to measure the irradiance of bactericidal radiation determined during tests.
Objectives. Quality control of instruments for measuring bactericidal irradiance of ultraviolet (UV) radiation is based on studying the main metrological characteristics. These characteristics include: angular and spectral sensitivity; linearity range; and absolute calibration in irradiance units. Deviations of the angular sensitivity of measuring instruments from the ideal cosine characteristic can significantly impact error estimation. They can also lead to the distortion of measurement results and a significant difference in instrument readings. The aim of this work is to enhance accuracy in resolving metrological problems of determining irradiance of bactericidal radiation.
Methods. An effective method of resolving this problem is to introduce correction coefficients for the angular sensitivity of radiometers, spectroradiometers and dosimeters. The values are calculated based on the results of measurements on the goniometer when testing measuring instruments. An important role is played by computer models and digital twins of measuring instruments based on the results of studies of the metrological characteristics of radiometers by means of software. This includes modeling the measuring task.
Results. The study of angular dependence of bactericidal UV radiometer sensitivity complemented by an analysis of measurement results obtained by other authors allows determining the value of the angular sensitivity correction coefficients by the deviation of the angular sensitivity of the irradiance measuring instruments of bactericidal radiation from the standard cosine dependence.
Conclusions. Deviations of the angular dependence of bactericidal radiation UV radiometer sensitivity from the cosine characteristic lead to a significant underestimation of the irradiance measurements results from extended emitters. An effective solution is the use of digital angular sensitivity correction coefficients to measure the irradiance of bactericidal radiation determined during tests. When assessing the quality of radiometers, spectroradiometers and dosimeters for bactericidal radiation, incomplete control of the main metrological characteristics of the measuring instruments creates risks of serious errors in the measurement results of bactericidal irradiance.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)