INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
- The overview of the literature on the topic of EMG signal processing is carried out.
- The signal filtering model using a convolutional neural network structure based on Python 3, TensorFlow and Keras technologies was developed.
- The possibility of using artificial neural networks to identify and suppress individual human characteristics in biological signals was demonstrated.
Objectives. In recent years, there has been growing scientific interest in the creation of intelligent interfaces for computer control based on biometric data, such as electromyography signals (EMGs), which can be used to classify human hand gestures to form the basis for organizing an intuitive human-computer interface. However, problems arising when using EMG signals for this purpose include the presence of nonlinear noise in the signal and the significant influence of individual human characteristics. The aim of the present study is to investigate the possibility of using neural networks to filter individual components of the EMG signal.
Methods. Mathematical signal processing techniques are used along with machine learning methods.
Results. The overview of the literature on the topic of EMG signal processing is carried out. The concept of intelligent processing of biological signals is proposed. The signal filtering model using a convolutional neural network structure based on Python 3, TensorFlow and Keras technologies was developed. Results of an experiment carried out on an EMG data set to filter individual signal components are presented and discussed.
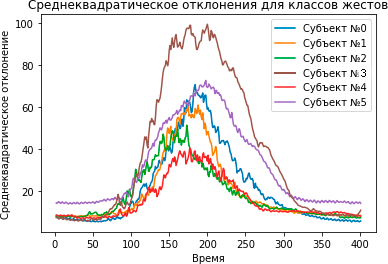
Conclusions. The possibility of using artificial neural networks to identify and suppress individual human characteristics in biological signals is demonstrated. When training the network, the main emphasis was placed on individual features by testing the network on data received from subjects not involved in the learning process. The achieved average 5% reduction in individual noise will help to avoid retraining of the network when classifying EMG signals, as well as improving the accuracy of gesture classification for new users.
- The present paper evaluates the current international research trends in Holographic Data Storage and produces a graphical mapping of co-authorship and countries.
- During the study period from 2000–2020 (21 years), 4636 authors contributed to 1052 publications.
- The highest number of publications was in 2009, with a linear adjustment of R2 = 0.0136. The most prolific author, Lee J., published 3.14% of the articles on this subject.
- In terms of country distribution, Japan took first-place ranking, claiming 16.54% of the total number of articles. The “holographic” keyword was used in 62.55% of the articles.
Objectives. Snapshots of data can be stored in a holographic medium at varying depths. Data can be written via a spiral data channel in spinning holographic media in the form of circular disks like CDs or DVDs. This data is then read by shining a reference beam through the refraction following writing. However, holographic storage is distinct from CD/DVD media in the sense that information is encoded in all three dimensions. Two-dimensional data is written using a single laser beam that spirals around the material. Prototype holographic storage solutions use minuscule cones formed by individual snapshots or pages to store one million pixels. As compared with magnetic disks and tapes, which have a finite lifespan of 50 years at most, the longevity and dependability of optical media storage is advantageous for long-term archiving. Holographic technology allows for the portability of data-intensive media such as broadcast or high-definition video. However, the shelf life of holographic media remains low due to its sensitivity to light. The primary goals of most storage devices are more storage space and faster data transport. Holographic storage devices have the potential to outperform traditional optical storage devices both in terms of capacity and performance. The present paper aims to evaluate the current international research trends in Holographic Data Storage (HDS) and produce a graphical mapping of co-authorship and countries.
Methods. The major outputs of the dataset were authors, document type, publication, institution, nation, and citations. After exporting 1052 data sources, HistCite software was used to analyze the citations; visualization mapping was carried out using VOSviewer software and R programming language for the analysis of the authorcountry-title association on Holographic Storage Devices.
Results. The most prominent authors, papers, journals, organizations, and nations in the field of HDS were identified in HistCite. Then, four clusters were investigated using VOSviewer based on author keywords, citation collaboration networks among different organizations, countries, and the HDS co-authorship network.
Conclusions. During the study period from 2000–2020 (21 years), 4636 authors contributed to 1052 publications. The highest number of publications was in 2009, with a linear adjustment of R2 = 0.0136. The most prolific author, Lee J., published 3.14% of the articles on this subject. In terms of country distribution, Japan took first-place ranking, claiming 16.54% of the total number of articles. The “holographic” keyword was used in 62.55% of the articles.
- The study investigates contemporary models, methods, and tools used for analyzing complex social network structures, both on the basis of ready-made solutions in the form of services and software, as well as proprietary applications developed using the Python programming language.
- Network analysis can be used to structure models of interaction between social units: people, collectives, organizations. Compared with other methods, the network approach has the undeniable advantage of operating with data at different levels of research to ensure its continuity.
- Almost all relevant studies use textual analysis methods in conjunction with machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies. Of these, convolutional neural networks demonstrated the best results. However, the use of support vector and decision tree methods should also be mentioned, since these contributed considerably to accuracy.
Objectives. The study aimed to investigate contemporary models, methods, and tools used for analyzing complex social network structures, both on the basis of ready-made solutions in the form of services and software, as well as proprietary applications developed using the Python programming language. Such studies make it possible not only to predict the dynamics of social processes (changes in social attitudes), but also to identify trends in socioeconomic development by monitoring users’ opinions on important economic and social issues, both at the level of individual territorial entities (for example, districts, settlements of small towns, etc.) and wider regions.
Methods. Dynamic models and stochastic dynamics analysis methods, which take into account the possibility of self-organization and the presence of memory, are used along with user deanonymization methods and recommendation systems, as well as statistical methods for analyzing profiles in social networks. Numerical modeling methods for analyzing complex networks and processes occurring in them are considered and described in detail. Special attention is paid to data processing in complex network structures using the Python language and its various available libraries.
Results. The specifics of the tasks to be solved in the study of complex network structures and their interdisciplinarity associated with the use of methods of system analysis are described in terms of the theory of complex networks, text analytics, and computational linguistics. In particular, the dynamic models of processes observed in complex social network systems, as well as the structural characteristics of such networks and their relationship with the observed dynamic processes including using the theory of constructing dynamic graphs are studied. The use of neural networks to predict the evolution of dynamic processes and structure of complex social systems is investigated. When creating models describing the observed processes, attention is focused on the use of computational linguistics methods to extract knowledge from text messages of users of social networks.
Conclusions. Network analysis can be used to structure models of interaction between social units: people, collectives, organizations, etc. Compared with other methods, the network approach has the undeniable advantage of operating with data at different levels of research to ensure its continuity. Since communication in social networks almost entirely consists of text messages and various publications, almost all relevant studies use textual analysis methods in conjunction with machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies. Of these, convolutional neural networks demonstrated the best results. However, the use of support vector and decision tree methods should also be mentioned, since these contributed considerably to accuracy. In addition, statistical methods are used to compile data samples and analyze obtained results.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
- The study aims to improve the efficiency of a large-area photoconductive terahertz (THz) emitter based on an optical-to-terahertz converter (OTC) having a radiating area of 0.3 × 0.3 mm2 for generating high-power THz radiation by using an array of close-packed profiled sapphire fibers having a diameter in the range of 100–300 μm as focusing optics.
- The use of a profiled sapphire fiber whose diameter has been optimized with respect to the gap parameters to significantly increase the concentration of charge carriers in the immediate vicinity of the electrodes of an OTC is demonstrated.
Objectives. The study aims to improve the efficiency of a large-area photoconductive terahertz (THz) emitter based on an optical-to-terahertz converter (OTC) having a radiating area of 0.3 × 0.3 mm2 for generating high-power THz radiation by using an array of close-packed profiled sapphire fibers having a diameter in the range of 100–300 μm as focusing optics.
Methods. As a photoconductive substrate, we used a semi-infinite LT-GaAs layer (low-temperature grown GaAs; GaAs layer grown by molecular beam epitaxy at a low growth temperature). Additional Si3N4 and Al2O3 layers are intended for reducing leakage currents in the OTC and reducing the reflection of the laser pump pulse from the air/semiconductor interface (Fresnel losses), respectively, at a gap width of 10 μm. For forming the antenna electrodes and feed strips, the Ti/Au metal system was used. The simulation was carried out by the finite element method in the COMSOL Multiphysics environment.
Results. The use of a profiled sapphire fiber whose diameter has been optimized with respect to the gap parameters to significantly increase the concentration of charge carriers in the immediate vicinity of the electrodes of an OTC is demonstrated. The integrated efficiency of a large-area photoconductive THz emitter was determined taking into account the microstrip topology of the array with a characteristic size of feed strips proportional to the gap width in the OTC and with the upper (masking) metal layer. The maximum localization of the electromagnetic field in close proximity to the edges of electrodes at the “fiber–semiconductor” interface is achieved with a profiled sapphire fiber diameter of 220 μm.
Conclusions. By optimizing the diameter of the sapphire fiber, the possibility of improving the localization of incident electromagnetic waves in close proximity to the edges of the OTC electrodes by ~40 times compared to the case without fiber, as well as increasing the overall efficiency of a large-area emitter by up to ~7–10 times, was demonstrated.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- The fractal dimension parameter calculated for a sequence of R–R intervals was determined and the boundaries of its change for healthy and sick patients were identified.
- In order to determine the fractal dimension parameter, the Hurst-, Barrow-, minimum coverage area-, and Higuchi methods were used.
- The difference between the fractal dimension indicators of the duration of R–R intervals of healthy and sick patients is shown to be statistically significant when using the Higuchi method.
Objectives. The aim of the present work is to determine the fractal dimension parameter calculated for a sequence of R–R intervals in order to identify the boundaries of its change for healthy and sick patients, as well as the possibility of its use as an additional factor in the detection of cardiac pathology.
Methods. In order to determine the fractal dimension parameter, the Hurst-, Barrow-, minimum coverage area-, and Higuchi methods are used. For assessing the stationarity of a number of electrocardiography (ECG) intervals, a standard method is used to compare arithmetic averages and variances from samples of the total data array of ECG intervals. To identify differences in fractal dimensions of healthy and sick patients, this parameter was ranked. Using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov two-sample criterion, the difference between the distribution laws in the samples for healthy and sick patients is shown.
Results. Among the considered methods for calculating the fractal dimension, the Higuchi method demonstrates the smallest data spread between healthy patients. By ranking the calculated fractional dimension values, it was possible to identify the difference between this parameter for healthy and sick patients. The difference in the distribution of fractal dimension of healthy and sick patients is shown to be statistically significant for the coverage and Higuchi methods. At the same time, when using the traditional Hurst method, there is no reason to reject the null hypothesis that two groups of patients belong to the same general population.
Conclusions. Based on the obtained data, the difference between the fractal dimension indicators of the duration of R–R intervals of healthy and sick patients is shown to be statistically significant when using the Higuchi method. The fractal dimensions of healthy and sick patients can be effectively distinguished by ranking samples. The results of the research substantiate prospects for further studies aimed at using fractal characteristics of the heart rhythm to identify abnormalities of the latter, which can serve as an additional factor in determining heart pathologies.
- A mathematical model and algorithm were developed to optimize the parameters of a spline as a multivalued function consisting of circular arcs conjugated by line segments. The initial approximation is the spline obtained at the first stage.
- The previously proposed two-stage spline approximation scheme for an unknown number of spline elements is also suitable for approximating multivalued functions given by a sequence of points in a plane, in particular, for designing a plan of routes for linear structures.
Objectives. Methods for spline approximation of a sequence of points in a plane are increasingly used in various disciplines. A spline is defined as a single-valued function consisting of a known number of repeating elements, of which the most widely used are polynomials. When designing the routes of linear structures, it is necessary to consider a problem with an unknown number of elements. An algorithm implemented for solving this problem when designing a longitudinal profile was published earlier. Here, since the spline elements comprise circular arcs conjugated by line segments, the spline is a single-valued function. However, when designing a route plan, the spline is generally a multivalued function. Therefore, the previously developed algorithm is unsuitable for solving this problem, even if the same spline elements are used. The aim of this work is to generalize the obtained results to the case of approximation of multivalued functions while considering various features involved in designing the routes of linear structures. The first stage of this work consisted in determining the number of elements of the approximating spline using dynamic programming. In the present paper, the next stage of solving this problem is carried out.
Methods. The spline parameters were optimized using a new mathematical model in the form of a modified Lagrange function and a special nonlinear programming algorithm. In this case, it is possible to analytically calculate the derivatives of the objective function with respect to the spline parameters in the absence of its analytical expression.
Results. A mathematical model and algorithm were developed to optimize the parameters of a spline as a multivalued function consisting of circular arcs conjugated by line segments. The initial approximation is the spline obtained at the first stage.
Conclusions. The previously proposed two-stage spline approximation scheme for an unknown number of spline elements is also suitable for approximating multivalued functions given by a sequence of points in a plane, in particular, for designing a plan of routes for linear structures.
- The article considers the problem of constructing a vector of objective ratings of alternatives based on the results of expert pair comparisons.
- It is proved that in the mathematical formulation this problem is reduced to the approximation of the matrix of paired comparisons by a consistent matrix of unit rank.
- A formula for calculating the components of a consistent matrix that minimize the deviation from the components of the original matrix in the log-Euclidean metric is derived and proved.
- A comparison with the results for other approaches and for other metrics is given.
Objectives. An analysis of the problem of evaluating alternatives based on the results of expert paired comparisons is presented. The importance and relevance of this task is due to its numerous applications in a variety of fields, whether in the technical and natural sciences or in the humanities, ranging from construction to politics. In such contexts, the problem frequently arises concerning how to calculate an objective ratings vector based on expert evaluations. In terms of a mathematical formulation, the problem of finding the vector of objective ratings can be reduced to approximating the matrices of paired comparisons by consistent matrices.
Methods. Analytical analysis and higher algebra methods are used. For some special cases, the results of numerical calculations are given.
Results. The theorem stating that there is always a unique and consistent matrix that optimally approximates a given inversely symmetric matrix in a log-Euclidean metric is proven. In addition, derived formulas for calculating such a consistent matrix are presented. For small dimensions, examples are considered that allow the results obtained according to the derived formula to be compared with results for other known methods of finding a consistent matrix, i.e., for calculating the eigenvector and minimizing the discrepancy in the log-Chebyshev metric. It is proven that all these methods lead to the same result in dimension 3, while in dimension 4 all results are already different.
Conclusions. The results obtained in the paper allow us to calculate the vector of objective ratings based on expert evaluation data. This method can be used in strategic planning in cases where conclusions and recommendations are possible only on the basis of expert evaluations.
- A direct and reverse handle on the oscillation of a rectangular rod with a longitudinal notch is considered.
- Measurements of the frequency of occurrence and the possibility of forming proportions of frequency were studied using the location and size of the notch.
- A method that uniquely determines the measurement of the length of the notch using the frequency of measuring the length of the rod was developed.
Objectives. To study the direct and inverse problem of vibrations of a rectangular rod having a longitudinal notch, to analyze regularities of the behavior of natural frequencies and natural forms of longitudinal vibrations when changing the location and size of the notch, and to develop a method for uniquely identifying the parameters of the longitudinal notch using the natural frequencies of longitudinal vibrations of the rod.
Methods. The rod with a longitudinal notch is modeled as two rods, where the first one does not have a notch, while the second one does. For connection, conjugation conditions are used, in which longitudinal vibrations and deformations are equated. The solution of the inverse problem is based on the construction of a frequency equation under the assumption that the desired parameters are included in the equation. Substituting natural frequencies into this equation, the nonlinear system with respect to unknown parameters is derived. The solution of the latter is the desired notch parameters.
Results. Tables of eigenfrequencies and graphs of eigenforms are given for different notch parameters. The results for different boundary conditions are obtained and analyzed. A method for identifying notch parameters by a finite number of eigenfrequencies is presented. The inverse problem is shown to have two solutions, which are symmetrical about the center of the rod. The unambiguous solution requires eigenfrequencies of the same problem with different boundary conditions at the right end. By adding additional conditions at the ends of the rod, the inverse problem can be solved with new boundary conditions to construct the exact solution and develop an algorithm for checking the uniqueness of the solution.
Conclusions. The developed method can be used to solve the problem of identification of geometric parameters of various parts and structures modeled by rods.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)