INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
The paper presents an analytical review of the application of biometric recognition systems. In 2020, there was a trend of transition of the use of biometric recognition technologies to the commercial sphere. The demand has increased for contactless biometric solutions. These technologies are implemented to conduct additional biometric verification of users. This allows to minimize possible fraud or violation of the internal rules of the service.
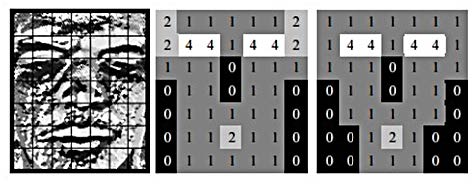
The paper presents an analytical review of the application of biometric recognition systems in relation to facial image identification technologies. The classification of biometric systems is presented. The trends of technological progress in the field of biometrics and facial recognition capabilities are considered. It is determined that in 2020 there is a trend of transition from the use of biometric recognition technologies in traditional state security systems to the sphere of commercial and user applications. The process of «linking» encryption keys and passwords with the biometric parameters of the data subject is described. It is proposed that a biometric feature and a biometrics parameter mean a certain value that has a physical meaning that characterizes the subject itself. The possibility of using circular neighborhood and bilinear interpolation of pixel intensity values in biometrics is also presented. This will make it possible to build a local binary template. In order to solve the problem of identification of persons, it is advisable to investigate the essence of biometric systems in the technologies of identification of persons, their types, identifying the shortcomings of each of them, on the basis of which to present the directions of elimination and search for the most reliable technologies. The essence of the use of biometric systems in the technologies of identification of persons is, for example, that the user can provide the bank or other counterparty with evidence that it is he who wants to use the services on his accounts. At the same time, the demand has increased for contactless biometric solutions. These technologies are implemented in order to conduct additional biometric verification of users. This allows to minimize possible fraud or violation of the internal rules of the service, for example, the transfer of accounts of some registered users to others.
MULTIPLE ROBOTS (ROBOTIC CENTERS) AND SYSTEMS. REMOTE SENSING AND NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
This article presents the algorithmic support of the external monitoring and routing system of autonomous mobile robots. The video image was obtained from an external video camera located above the working area of mobile robots. The locations of both robots and nearby obstacles were recognized. This technology extracts key points in the video frame and compares them with key points of reference images of robots.
This article presents the algorithmic support of the external monitoring and routing system of autonomous mobile robots. In some cases, the practical usage of mobile robots is related to the solution of navigation problems. In particular, the position of ground robots can be secured using unmanned aerial vehicles. In the proposed approach based on the video image obtained from an external video camera located above the working area of mobile robots, the location of both robots and nearby obstacles is recognized. The optimal route to the target point of the selected robot is built, and changes in its working area are monitored. Information about the allowed routes of the robot is transmitted to third-party applications via network communication channels. Primary image processing from the camera includes distortion correction, contouring and binarization, which allows to separate image fragments containing robots and obstacles from background surfaces and objects. Recognition of robots in a video frame is based on the use of a SURF detector. This technology extracts key points in the video frame and compares them with key points of reference images of robots. Trajectory planning is implemented using Dijkstra’s algorithm. The discreteness of the trajectories obtained using the algorithm for finding a path on the graph can be compensated for on board autonomous mobile robots by using spline approximation. Experimental studies have confirmed the efficiency of the proposed approach both in the problem of recognition and localization of mobile robots and in the problem of planning safe trajectories.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
The article discusses the features of the radiation of ultrafast point clusters of charged particles moving uniformly near a gyrotropic medium interface. Ultrafast (relativistic) particles can be used as «generators» of quasiparticles that determine the «dynamic» properties of the materials under study, as well as the features of their interaction with radiation of various nature and response to external influences. The mechanisms of interaction of electromagnetic radiation with chiral materials (structures and media) are one of the possible physical approaches to solve the problem of the chiral purity of the biosphere and to elucidate the factor of deracemization of the organic primeval environment.
The article discusses the features of the radiation of ultrafast point clusters of charged particles moving uniformly near a gyrotropic medium interface. It is shown that some types of electromagnetic radiation – transient and/or Cherenkov radiation – have the characteristics of superchiral fields. Therefore, they can be effectively used to study chiral structures (for example, to detect circular dichroism, the frequency characteristics of refractive indices), various materials, including biomaterials. Ultrafast (relativistic) particles can serve as a «tool» not only for studying the structure of various materials. They can also be used as «generators» of quasiparticles that determine the «dynamic» properties of the materials under study, as well as the features of their interaction with radiation of various nature and response to external influences. In this paper, some types of circularly polarized EM waves propagating in optically active (magnetoactive, naturally active, gyrotropic, and chiral) media are considered. Using the generalized reciprocity theorem for media characterized by the Hermitian permittivity tensor, we consider the transient and Cherenkov radiation excited by a uniformly moving bunch of charged particles when it crosses (or moves along) the interface of media, one of which is an optically active gyrotropic medium. It is shown that the superchiral electromagnetic fields of the transition and Cherenkov radiation of dipoles can serve as a source of chiral collective excitations in magnetoactive and naturally active media. The investigated mechanisms of interaction of electromagnetic radiation with chiral materials (structures and media) are one of the possible physical approaches to solving the problem of the chiral purity of the biosphere and to elucidate the factor of deracemization of the organic primeval environment. A new hypothesis is presented, suggesting that ultra-high-speed clumps of charged particles of cosmic origin can cause deracemization of the prebiosphere.
This review introduces the study of state-of-art methods for assessing the mechanical properties of insulating materials with low dielectric constant. The main features of measuring Young’s modulus of thin films insulating materials with low dielectric constant are determined by usage of Brillouin light scattering, surface acoustic wave spectroscopy, picosecond laser-acoustic method, ellipsometric porosimetry, nanoindentation and atomic force microscopy in various modes. The method of atomic force microscopy is superior to other methods described above, both in lateral (8 nm) and optimum depth (10 nm) resolution.
This review introduces the study of state-of-art methods for assessing the mechanical properties of insulating materials with low dielectric constant. The main features of measuring Young’s modulus of thin films insulating materials with low dielectric constant are determined by usage of Brillouin light scattering, surface acoustic wave spectroscopy, picosecond laser-acoustic method, ellipsometric porosimetry, nanoindentation and atomic force microscopy in various modes. The author estimated the optimum lateral and optimum depth resolution for each above method. The review analyzes the degree of sample preparation complexity for the measurements by these methods and describes what methods of measurement are destructive for the samples. Besides, the review makes a comparison for the results of evaluating Young’s modulus of insulating materials with low dielectric constant achieved by different methods. Comparative analysis of the methods for assessing mechanical properties lead us to the conclusion that the method of atomic force microscopy is superior to other methods described above, both in lateral (8 nm) and optimum depth (10 nm) resolution. It is shown that due to the small impact force of the atomic force microscope probe on the surface, the method does not have a destructive effect on the sample. In addition, there is no need to create special conditions for the experiment (e.g., the cleanliness level of the premises, the possibility of an experiment under environmental conditions, etc.). This makes the experiment relatively simple in terms of preparing the object of research. It has been also established that the method of atomic force microscopy in the mode of quantitative nanomechanical mapping allows forming a map of the distribution of the Young’s modulus of the insulating material as part of the metallization system of integrated circuits.
The spectral dependences of the transverse Kerr effect are studied experimentally and theoretically. The expediency of using the effective medium approach for calculating magneto-optical effects in granular systems, taking into account the size distribution of granules within the lognormal distribution of granules, is shown. Taking into account the size effects and the particle size dispersion makes it possible to find new promising functional materials and control their properties in a wide spectral range.
In this paper, the spectral dependences of the transverse Kerr effect (ТКЕ) are studied experimentally and theoretically. The results are obtained for deposited and annealed samples with a corresponding variation in the size of the granules. It was found that thermomagnetic annealing leads to an increase in the ТКЕ value in magnetic nanostructures, while the most noticeable changes in the effect value were observed in the range of medium and high concentrations of the magnetic component in the visible region of the spectrum. The expediency of using the effective medium approach for calculating magneto-optical effects in granular systems, taking into account the size distribution of granules within the lognormal distribution of granules, is shown. Based on this approach, the main features of the optical and magneto-optical properties of nanocomposites are explained by the example of (Co45Fe45Zr10)X(Al2O3)1–X. All calculations are performed in the Bruggemann approximation, which effectively describes the properties of nanostructures in the region of average concentrations. Size effects are clearly manifested in nanocomposites and have a significant impact on the optical and magneto-optical properties of nanocomposites, especially in the IR region of the spectrum, which is associated with intraband transitions. Taking into account the particle size distribution makes it possible to significantly improve the description of such promising inhomogeneous nanostructures. The solved problem is very important and relevant both from the fundamental point of view – the study of magneto-optical, optical and transport phenomena in nanocomposites – and from the point of view of the great possibilities of their application in modern electronics and nanoelectronics. Taking into account the size effects and the particle size dispersion makes it possible to find new promising functional materials and control their properties in a wide spectral range.
ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
It is proposed to use an algorithm for visualizing electric fields in three-dimensional space and time. The algorithm is easily embedded into applications as a component of a mathematical modeling system. Three ways of visualizing the electric field strength: starting from a simple setting of points in space and ending the use of algorithms that make it possible to arrange points equidistantly based on a given number of points in space for the formation of an electric field were analyzed. The proposed methodology will be useful to developers as an embedded solution for point visualization of the electric field in any project in any algorithmic language with the ability to animate in time.
Testing of electronic devices is an integral part of the technological process of any manufacturer of such equipment. In this case, an electronic device is understood as an energy-intensive unit such as a mobile phone, data center or spacecraft. One of the key stages of testing is to identify the effect of electric fields on various electronic components of the device. This stage often requires making a mock-up of some part of an unfinished device in order to fix interference with special equipment. This requires time, financial and human resource costs. In order to reduce these costs in the modern world, the use of mathematical modeling tools for testing noise immunity and electromagnetic compatibility is becoming popular. In this paper, it is proposed to use an algorithm for visualizing electric fields in three-dimensional space and time. The algorithm is easily embedded into applications as a component of a mathematical modeling system. The work considered three ways of visualizing the electric field strength: starting from a simple setting of points in space, on the basis of which the electric field will be built, around the source of electric field radiation, to the use of algorithms that make it possible to arrange points equidistantly based on a given number of points in space for the formation of an electric field. The performance and visual implications of these methods were analyzed. The proposed methodology will be useful to the developer community as an embedded solution for point visualization of the electric field in any project in any algorithmic language with the ability to animate in time.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR14 statistical dataset about many astronomical objects was investigated. The handled data contains measures of three types of astronomical objects of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR14 dataset (star, quasar, galaxy). The CART decision tree, logistic regression, naïve Bayes classifiers and ensembles of classifiers (random forest, gradient boosting) were implemented. Conclusions about special features of each machine learning classifier trained to solve this task are made. The accuracy of the classifiers built in this research is more than 90%.
In the paper Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR14 dataset was investigated. It contains statistical information about many astronomical objects. The information was obtained within the framework of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey project. There are telescopes at the Earth surface, at the Earth orbit and in the Lagrange points of some systems (Earth–Moon, Sun–Earth). The telescopes gain information in different frequency ranges. The large quantity of statistical information leads to the demand for analytical algorithms and systems capable of making classification. Such information is marked up well enough to build machine learning classification systems. The paper presents the results of a number of classifiers. The handled data contains measures of three types of astronomical objects of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR14 dataset (star, quasar, galaxy). The CART decision tree, logistic regression, naïve Bayes classifiers and ensembles of classifiers (random forest, gradient boosting) were implemented. Conclusions about special features of each machine learning classifier trained to solve this task are made at the end of the paper. In some cases, classifiers’ structure can be explained physically. The accuracy of the classifiers built in this research is more than 90% (metrics F1, precision and recall are implemented, because the classes are unbalanced). Taking these values into account classification task is supposed to be successfully solved. At the same time, the structure of classifiers and importance of features can be used as a physical explanation of the solution.
The study aimed to find such a law of motion of the remote sensing spacecraft which will allow, when applied in the control loop, to compensate for the image motion velocities that are unsuitable for a photodetector. The result was the derived equation of space photogrammetry in kinematic form, as well as the functional dependences of angular rate on time, and a mathematical model for scanning images of the Earth’s landscapes with the help of remote sensing spacecraft was compiled.
The article considers a spacecraft for remote sensing of the Earth with high-resolution or ultra-high-resolution optical-electronic equipment. During the shooting process, the recorded image constantly moves through the photodetector matrix at a non-constant and/or excessive velocity, which is not suitable for this photodetector. The purpose of the article is to synthesize a method for the control of the orientation and stabilization of the remote sensing spacecraft, which will provide a strictly specified velocity of the image motion on the photodetector. It is proposed to find such a law of motion (functional dependences of the angular rate of the remote sensing spacecraft on time), which will allow, when applied in the control loop, to compensate for the image motion velocities that are unsuitable for this photodetector. The method used consists in time differentiation of the fundamental equation of space photogrammetry in the guiding cosines, as well as in differentiation of the matrix of guiding cosines. This provides a transition between the guiding cosines in the space of images and the space of objects. The result obtained in the article is the derived equation of space photogrammetry in kinematic form, as well as the functional dependences of angular rate on time. In the present article, a mathematical model of scanning images of the Earth’s landscapes with the help of remote sensing spacecraft is compiled. The obtained functional dependences can be applied in the development of on-board algorithms for controlling the orientation and stabilization of the remote sensing spacecraft. When implementing orientation and stabilization control in the on-board computer based on the obtained functional dependencies, a strictly specified speed of image movement in the focal plane of the on-board shooting equipment can be provided, and, consequently, the quality of the scanned image is improved by improving the function of transmitting the modulation of the kinematic “smudge” (blurring) of the image.
The study aimed to estimate the Pareto distribution parameters, first of all, an indicator of this distribution for a given sample. It is proved that the product of the sample elements, as well as any function of this product, in particular, the geometric mean, is a sufficient statistic for the Pareto distribution parameter. It is proved that the geometric mean of the sample is a more convenient sufficient statistic from a practical point of view than the product of the sample elements.
The task of estimating the parameters of the Pareto distribution, first of all, of an indicator of this distribution for a given sample, is relevant. This article establishes that for this estimate, it is sufficient to know the product of the sample elements. It is proved that this product is a sufficient statistic for the Pareto distribution parameter. On the basis of the maximum likelihood method the distribution degree indicator is estimated. It is proved that this estimate is biased, and a formula eliminating the bias is justified. For the product of the sample elements considered as a random variable the distribution function and probability density are found; mathematical expectation, higher moments, and differential entropy are calculated. The corresponding graphs are built. In addition, it is noted that any function of this product is a sufficient statistic, in particular, the geometric mean. For the geometric mean also considered as a random variable, the distribution function, probability density, and the mathematical expectation are found; the higher moments, and the differential entropy are also calculated, and the corresponding graphs are plotted. In addition, it is proved that the geometric mean of the sample is a more convenient sufficient statistic from a practical point of view than the product of the sample elements. Also, on the basis of the Rao–Blackwell–Kolmogorov theorem, effective estimates of the Pareto distribution parameter are constructed. In conclusion, as an example, the technique developed here is applied to the exponential distribution. In this case, both the sum and the arithmetic mean of the sample can be used as sufficient statistics.
PHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY
The study analyzed reproductive method in the system of teaching Russian as a foreign language and its innovative aspects: reproductive-cognitive and reproductive-creative methods. The reproductive method in the system of teaching Russian as a foreign language is aimed at reproducing the ways of activity by foreign students according to the algorithms presented by the teacher, at enriching them with knowledge, skills and abilities. Thanks to the developed system of tasks, where the algorithmization of the educational process is clearly traced, the teacher organizes the students’ activities by repeatedly reproducing the knowledge communicated to them and the ways of activity.
The reproductive method in the system of teaching Russian as a foreign language is aimed at reproducing the ways of activity by foreign students according to the algorithms presented by the teacher, at enriching them with knowledge, skills and abilities, as well as at forming the main mental operations: abstraction, analysis, synthesis, generalization, and others. When learning the «language of the profession», the main mental operations are formed: abstraction, analysis, synthesis, generalization, and others. The reproductive method, having the basis of algorithmization, integrated with the cognitive theory of learning, has reached a new level – the reproductivecognitive method. System analysis in combination with algorithmization becomes the basis of the reproductive and creative method. The methods outlined in the article enrich the knowledge, skills and abilities of students, which are most often carried out at the stages of correction, diagnosis and consolidation of knowledge, but do not guarantee the development of creative abilities, do not allow them to be systematically and purposefully formed. In particular, the concept of the reproductive-creative method is the principle of communicative orientation, which formed the basis of competence-based learning. In competence-based learning, the activity component, unlike other possible approaches, is considered from the viewpoint of competence, i.e., the ability of the student to effectively and independently, but with the help of the teacher, use the language being studied on the basis of the acquired experience in the form of knowledge, skills, and abilities. The knowledge obtained as a result of the use of the explanatory and illustrative method weakly forms skills and abilities. Therefore, thanks to the developed system of tasks, where the algorithmization of the educational process is clearly traced, the teacher organizes the students’ activities by repeatedly reproducing the knowledge communicated to them and the ways of activity shown.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)