INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
- The paper proposes methods of constructing automatic and logical-probabilistic models of cluster computing systems and creating software tools based on them.
- The concept of the logical-probabilistic model “temporal probabilistic system of canonical equations” is introduced.
- The work concludes that the choice of the system and functional architecture of a computing cluster should be determined mostly by the actual indicators achieved at the level of user applications and cluster usage modes.
Objectives. An urgent task is to improve the functional architecture of cluster computing systems by introducing methodologies for creating software at the applied and intermediate levels based on formalized specifications. One such methodology is based on the use of automatic specifications for computer systems software. The complexity of resolving the problem is caused by the branching of the algorithms built, as well as the presence of cyclic sections. The execution time of the branched sections of the program and the number of cycles run depends on the type of conditions entered. In practice it can be determined using a detailed simulation model and analysis of the control program created on its basis. The aim of the work is to find approaches to the definition of functional architecture which can be applied practically at the main levels of the subject orientation of cluster computing systems.
Methods. The methods proposed and used are based on the concept of organization and research of cluster-type computing systems with a functional architecture as defined by executable automatic models.
Results. The paper proposes methods of constructing automatic and logical-probabilistic models of cluster computing systems and creating software tools based on them. The concept of the logical-probabilistic model “temporal probabilistic system of canonical equations (CES)” is introduced. This enables a visual formalization to be obtained, as well as implementation of automatic models and work programs typical for cluster and other applications. It also significantly reduced the number of “incremental” additions when enumerating discrete time moments. The main feature of the new logical-probabilistic model is the preservation of the original CES in its basis.
Conclusions. The work concludes that the choice of the system and functional architecture of a computing cluster should be determined not so much by the peak characteristics of the communication equipment specified by the manufacturer, as by the actual indicators achieved at the level of user applications and cluster usage modes. It is also shown that executable automatic models can be applied at almost all levels of cluster computing systems subject orientation.
- The developed software package provides users with a graphical interface for conducting an analysis of a cloud quantum computing devices to identify the optimal and most error-resistant set of qubits.
- The findings from experiments conducted on three cloud quantum computing devices are reported.
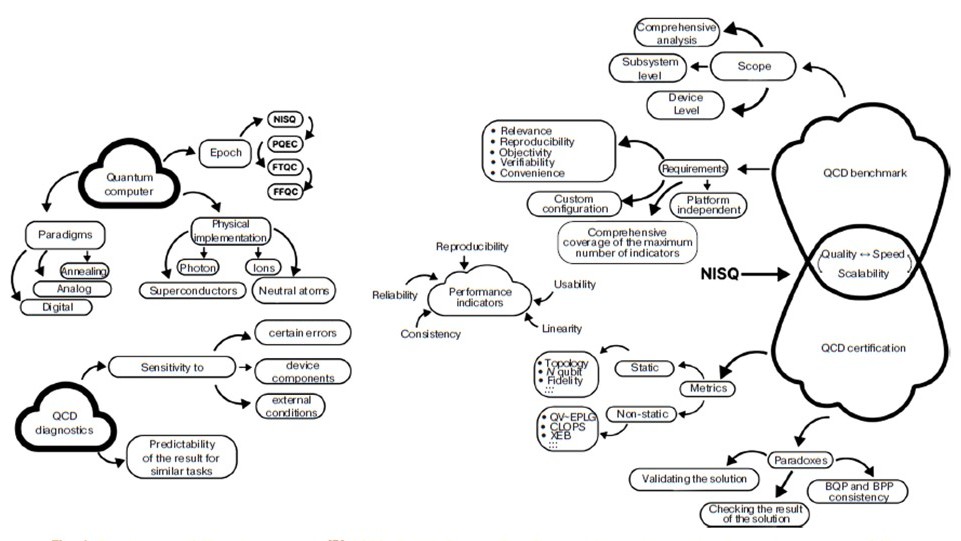
Objectives. The absence of error-resistant quantum computers, coupled with the challenges associated with providing unrestricted and fully operational physical access to cloud quantum computing systems, prompts a critical examination of the necessity to develop universal and independent methods for evaluating and verifying cloud quantum computers. A promising approach involves evaluating the capabilities of a quantum computer in relation to its effectiveness in addressing specific challenges encountered in the assessment of information security systems. A potential test for ascertaining the performance and computational quality of a quantum computing device (QCD) is based on a model designed to generate a random binary sequence. By analyzing this sequence, insights can be obtained into the accuracy and reliability of the quantum register under study. The paper presents a software program developed for simulating the operation of a quantum random number generator.
Methods. The software implementation for interacting with cloud quantum computers was performed using the Qiskit open-source software kit. The graphical user interface of the software package was developed using a Qt5 crossplatform set of tools and widgets for creating applications. The analysis of the generated binary sequence was performed using a set of statistical tests NIST STS2.
Results. The developed software package provides users with a graphical interface for conducting an analysis of a cloud QCD to identify the optimal and most error-resistant set of qubits. The findings from experiments conducted on three cloud quantum computing devices are reported.
Conclusions. The proposed approach, which is constrained by limitations of computing power and duration of access to cloud-based QCD, imposes minimal demands on the productive capabilities of the quantum system. It offers clear and unequivocally interpretable insights into the technical characteristics of a cloud quantum computer, while also being reproducible, easily scalable, and universally applicable.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- Numerical study of the characteristics of maximum likelihood estimates of the direction of arrival for deterministic and random signals was performed over a wide range of signal-to-noise ratio(SNR) in multielement linear and circular antenna arrays.
- The study proposes a method for high-precision determination of threshold SNR values, below which anomalously large measurement errors occur.
- Numerical simulations demonstrate that coherent and incoherent signal processing yield the same ultimately achievable accuracy at the same SNR values above the threshold.
- The general relationships between these threshold values, antenna array configurations, the type of signal processed, and the estimation algorithm used were identified.
Objectives. The purpose of this work is to study in detail the properties of maximum likelihood (ML) estimates of the angles-of-arrival of deterministic and random signals in multielement antenna arrays, to develop effective algorithms for finding ML estimates and to determine the exact values of threshold signal-to-noise ratios (SNR), below which abnormally large errors occur significantly in excess of the theoretically minimum values determined by the Cramér– Rao bounds.
Methods. The methods used include: the theory of optimal signal detection; intensive numerical simulation of the signal processing system in multielement antenna arrays based on the developed algorithms for finding ML estimates; and comparison of the standard errors of the estimates obtained by means of the theoretically minimal analytically established Cramér–Rao bounds.
Results. Numerical study of the characteristics of ML estimates of the direction of arrival for deterministic and random signals was performed over a wide range of SNRs in multielement linear and circular antenna arrays. The study proposes a method for high-precision determination of threshold SNR values, below which anomalously large measurement errors occur. Numerical simulations demonstrate that coherent and incoherent signal processing yield the same ultimately achievable accuracy at the same SNR values above the threshold. At the same time, the threshold value is significantly influenced by the type of signal and the processing method. The general relationships between these threshold values, antenna array configurations, the type of signal processed, and the estimation algorithm used were identified.
Conclusions. The numerical and analytical results obtained allow recommendations to be developed relating to the choice of multielement antenna arrays configurations and the main parameters of systems for high-precision bearing of radiation sources of various signals. These enable abnormally large measurement errors to be avoided. The results can be directly utilized in the calculation of characteristics of systems under design.
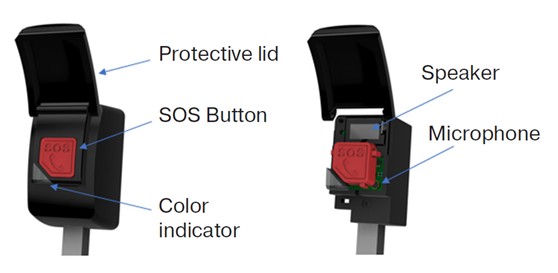
- An implementation of the interface of interaction between the driver of a two-wheeled vehicle and the operator of the ERA-GLONASS system is proposed, taking into account the specifics of its use.
- Structural schemes of an echo compensator and a dual speech signal detector using an adaptive filter are presented.
- The algorithms implementing these processes and the possibility of their adaptation to the tasks of the emergency call device are considered.
- The procedure for automatically adjusting the amplification of the acoustic signal of the speech range is described, an analytical description of the technical problem and the applied methods of digital processing are given.
Objectives. The aim of the study is to improve road safety by developing an emergency call device for drivers of twowheeled vehicles, as the most vulnerable road users, and improving their technical equipment.
Methods. In the course of the study, the characteristics of the acoustic signal transmission channel and the processes accompanying its propagation were analyzed. When studying the parameters of voice communication, noise reduction, echo cancellation and echo compensation methods were used, as well as algorithms for converting acoustic information implemented in the hardware and software of the device.
Results. The results of practical implementation are presented: the design of a prototype device, its integration into the dashboard of a two-wheeled vehicle. During the design of the device, the control features of a two-wheeled vehicle, the influence of external factors and climatic conditions were taken into account. An implementation of the interface of interaction between the driver of a two-wheeled vehicle and the operator of the ERA-GLONASS system is proposed, taking into account the specifics of its use. Structural schemes of an echo compensator and a dual speech signal detector using an adaptive filter are presented. The algorithms implementing these processes and the possibility of their adaptation to the tasks of the emergency call device are considered. The procedure for automatically adjusting the amplification of the acoustic signal of the speech range is described, an analytical description of the technical problem and the applied methods of digital processing are given. A structural diagram of the test stand, software for qualitative analysis of the acoustic signal, visualization of the test results of the prototype are presented, and the effectiveness of the proposed solution is evaluated.
Conclusions. The results of a study on the design of an emergency call device have shown that the use of analog and digital speech signal processing algorithms implemented in the device’s codec and modem will ensure a highquality level of voice communication between the driver and the emergency services operator.
- An algorithm for parameter selection in the peak-to-average power ratio reduction method with an additional compensation signal for orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing systems using polynomial regression was developed.
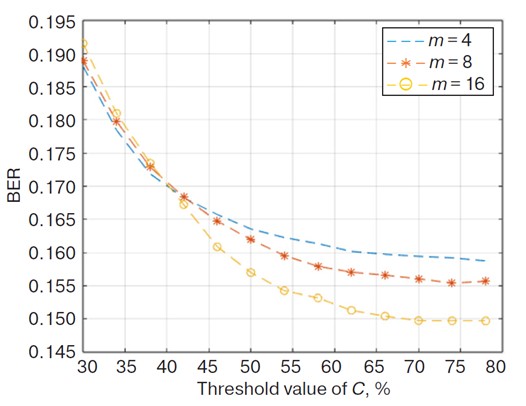
- It was confirmed that increasing the clipping threshold reduces bit error rate, while increasing the number of additional signals improves clipping accuracy at the cost of higher computational complexity.
- It was established that for a fixed clipping threshold, there exists an optimal number of additional signals providing the best trade-off between error probability and peak value reduction.
Objectives. The article aims to investigate the authors’ developed peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) reduction method using an additional compensation signal in orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) systems, employing polynomial regression for method parameter selection.
Methods. The study utilizes statistical radio technique methods and mathematical modeling to approximate the relationship between bit error rate (BER) versus clipping threshold level and number of additional signals using polynomial regression analysis.
Results. We developed an algorithm for parameter selection in the PAPR reduction method with an additional compensation signal for OFDM systems using polynomial regression. This approach enables rapid system performance evaluation without additional computational overhead for mathematical modeling. The method significantly simplifies the optimization of clipping threshold and number of additional signals, eliminating the need for complete simulation cycles for each configuration. Both simulation and analytical calculations confirm that increasing the clipping threshold reduces BER, while increasing the number of additional signals improves clipping accuracy at the cost of higher computational complexity. Optimal parameter selection achieves a compromise between PAPR reduction and signal quality preservation. Furthermore, we established that for a fixed clipping threshold, there exists an optimal number of additional signals providing the best trade-off between error probability and peak value reduction.
Conclusions. An algorithm for selecting the parameters of the clipping method with an additional compensation signal based on polynomial regression has been developed. This algorithm enables real-time evaluation of system characteristics without additional computational costs associated with repeated mathematical modeling. The proposed approach reduces calculation time by more than a factor of five, offering flexibility and adaptability in the design of OFDM systems with PAPR reduction.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
- The study developed a method for calculating interface traps concentration and radiation-induced charge density from subthreshold drain-gate characteristics.
- The results obtained can be used to assess the failure-free operation time of devices operating under conditions of ionizing radiation and electrostatic discharges.
Objectives. The aim of the study is to confirm that the robustness of high-power metal–oxide–semiconductor fieldeffect transistor (MOSFET) to electrostatic discharge (ESD) after gamma irradiation is determined by the concentration of built-up interface traps (IT). The reason for such dependence is the degradation of the gain of the parasitic bipolar transistor in the structure of high-power MOSFETs during accumulation of IT. As a result, higher ESD pulse voltage is required to activate the parasitic bipolar transistor and cause the subsequent catastrophic failure of MOSFET.
Methods. The study describes the physical mechanism of the influence of IT accumulation on the robustness of highpower MOSFETs to ESD. Experimental studies included determination of ESD robustness for two types of highpower MOSFETs before irradiation, 60Co gamma irradiation to several levels of total ionizing dose, and subsequent determination of the ESD robustness of irradiated samples.
Results. The study developed a method for calculating IT concentration and radiation-induced charge density from subthreshold drain-gate characteristics. It was also shown that for the first type of MOSFET, when irradiated to total ionizing dose level of 3 krad, the build-up IT did not occur, nor was any change or insignificant decrease in the breakdown voltage observed when exposed to ESD. For the second type of MOSFET, build-up IT was observed when irradiated to total ionizing dose level of 2 and 4 krad and an increase in the breakdown voltage was also observed when exposed to ESD.
Conclusions. The study shows the relationship between the IT concentration and the change in the breakdown voltage when exposed to ESD. The results obtained can be used to assess the failure-free operation time of devices operating under conditions of ionizing radiation and electrostatic discharges.
ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
- Data on working zones between opposing flat poles are obtained for different values of the distance b between the poles and their diameter D.
- It is found that as D increases and b/D decreases, the working area increases.
Objectives. The work set out to develop an approach for assessing the working (local) zone in magnetometerelectromagnet measuring devices designed for controlling the magnetic properties of samples in which the homogeneity of the magnetic field should be observed in terms of constancy of the field strength or induction.
Methods. The coordinate characteristics of the field strength (induction) between pole components were experimentally obtained to identify the desired working zone (in the vicinity of the minimum of each of these characteristics), taking into account the distance b between the poles and their diameter D.
Results. Data on working zones between opposing flat poles are obtained for different values b and D. With increased ratios b/D = 0.7–1.3, the size of the working zone concentrated in the middle axial part of the interpolar area is estimated at a value not exceeding 25–30% of the distance b such that the characteristic longitudinal size of the sample does not exceed 5–10 mm. As D increases and b/D decreases, the working area increases. In particular, at b/D ≅ 0.5, the size of the working area is estimated to be up to 90% and even 100% of the distance b.
Conclusions. A principled approach to the assessment of the working (axial) zone between opposing flat poles is demonstrated by obtaining and analyzing the necessary coordinate (significantly dependent on b and D) characteristics of the field strength (induction) between them.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- A special mathematical apparatus constituting a generalized integral Fourier–Hankel transform for three coordinate systems simultaneously was developed.
- Based on the developed special mathematical apparatus, an exact analytical solution to the generalized third boundary value problem of heat conductivity with time-varying heat transfer coefficient and ambient temperature, simultaneously in three coordinate systems, was obtained.
Objectives. This paper presents the development of a rather rare method for splitting the integral Fourier–Hankel transform when finding an exact analytical solution to the generalized third boundary value problem of complex heat transfer, where both the heat transfer coefficient and ambient temperature vary in time. The generalization lies in the simultaneous consideration of the problem in three different coordinate systems: Cartesian (a half-space bounded by a flat surface), cylindrical (a space bounded by a cylindrical cavity from the inside), and spherical (a space bounded by a spherical cavity from the inside). The aim was to develop a method for splitting the integral transformation as applied to finding an exact analytical solution to a generalized model problem of non-stationary thermal conductivity of complex heat exchange with an arbitrary dependence of the heat exchange coefficient and ambient temperature on time.
Methods. The generalized integral transformation developed for these purposes is used simultaneously in three coordinate systems, and the method for its splitting is applied to the problem of complex heat transfer.
Results. Initially, a special mathematical apparatus constituting a generalized integral Fourier–Hankel transform for three coordinate systems simultaneously was developed. For comparison, in the literature, such a transformation is formulated, as a rule, separately for each coordinate system. The availability of this mathematical apparatus made it possible to develop a method for its splitting and to obtain an exact analytical solution to the third boundary value problem for nonstationary thermal conductivity in complex heat transfer, simultaneously for all three coordinate systems. To illustrate this, a specific case in Cartesian coordinates was considered and a rapid growth of the Picard process was established.
Conclusions. Based on the developed special mathematical apparatus, an exact analytical solution to the generalized third boundary value problem of heat conductivity with time-varying heat transfer coefficient and ambient temperature, simultaneously in three coordinate systems, was obtained. These results constitute the scientific novelty of the work and represent a significant contribution to analytical thermal physics.
- A modification of the known mathematical apparatus of almost periodic analysis is proposed for processing large and multidimensional datasets.
- It was shown that it is possible to apply almost periodic analysis to the identification of characteristic patterns of tropical cyclone structures and carry out qualitative forecast estimates of the dynamics of emergency situations caused by tropical cyclones.
Objectives. The article sets out to identify the characteristics of tropical cyclones using almost periodic analysis of images of cloud dynamics of hurricanes in order to forecast the cyclone structure. Almost periodic analysis is applied in the processing and analysis of tropical cyclone structure images based on the obtained almost period values using a modified mathematical computational apparatus.
Methods. The main tool for processing and analyzing images of the tropical cyclone structure is almost periodic analysis, i.e., analysis of data with an ordered argument to identify dependencies that are close to periodic. By this means critical boundaries of changes in the trends of the studied data can be identified regardless of a priori assumptions. In the course of analysis the almost period information parameter, corresponding to the values closest to the periods, is determined. A modification of the known mathematical apparatus of almost periodic analysis is proposed for processing large and multidimensional datasets.
Results. In the course of the study, the characteristic almost periodic values of the structural zones at the moment of the beginning of the formation of the dynamics of the cyclone development were revealed on the example of the analysis of the frames of the dynamics of tropical cyclone Milton, operating from October 5, 2024 to October 10, 2024. Based on the identified values, forecast estimates of the tropical cyclone structure development were made to an accuracy of 95%.
Conclusions. Together with the results of studies published earlier, the results of this study support the conclusion that it is possible to apply almost periodic analysis to the identification of characteristic patterns of tropical cyclone structures and carry out qualitative forecast estimates of the dynamics of emergency situations caused by tropical cyclones.
- A simulation of the temperature distribution in a material half-space upon the action of a moving heat source on its boundary, has been carried out by solving the equation of nonstationary thermal conductivity in Cartesian coordinates.
- The obtained solution representing the evolution of temperature in time at different points of the medium shows that at a certain point of time after the passage of the heating pulse, the temperature inside the medium reaches its maximum value rapidly followed by its relatively slow relaxation to the equilibrium temperature of the environment. Penetrating deeper into the bulk of the medium, the thermal pulse is spreading out while decreasing its amplitude and increasing its width, accompanied by a monotonic increase in the time to reach the maximum.
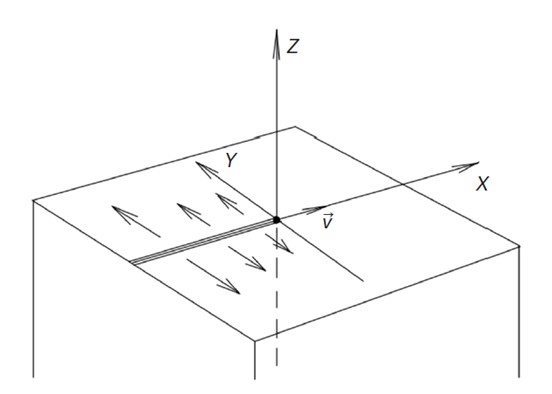
Objectives. Thermal spraying and powder laser cladding are promising technologies widely used in various industries, including aerospace, energy, and mechanical engineering. The efficiency of these technologies depends on the management of thermal processes occurring during coating application, which directly affect the quality and durability of the resulting materials and products. This article considers a nonstationary problem of heat transfer during single-pass spraying on a half-space. The research aim was to simulate the temperature distribution in a material half-space upon the action of a moving heat source on its boundary.
Methods. A theoretical study of the temperature distribution on the surface and in the bulk of the processed material during movement of the spray head was carried out by solving the equation of nonstationary thermal conductivity in Cartesian coordinates. This equation employs a special type of the heat source power density function in the form of a thermal strip, simulating the process of heat transfer from the spray path to the material half-space of the part base.
Results. The obtained solution representing the evolution of temperature in time at different points of the medium shows that at a certain point of time after the passage of the heating pulse, the temperature inside the medium reaches its maximum value rapidly followed by its relatively slow relaxation to the equilibrium temperature of the environment. Penetrating deeper into the bulk of the medium, the thermal pulse is spreading out while decreasing its amplitude and increasing its width, accompanied by a monotonic increase in the time to reach the maximum. The transverse temperature distribution has the form of symmetrical peaks, less pronounced in depth.
Conclusions. The obtained solution can be used when describing the general temperature field at some distance from the spray head area, where specific heating details are lacking. In particular, the work shows that significant temperature gradients arise in the vicinity of the primary spray area, which will cause noticeable nonstationary temperature stresses.
- A method for automatic quantitative estimation of the Gaussian blur parameter in digital images, which typically arises due to defocus of the optical system was developed.
- Tests on synthetic data demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves high accuracy: the relative error in estimating the Gaussian blur parameter within the range of 0.7 to 2.0 pixels is less than 5%, and in most cases does not exceed 2–3%. The method is robust to noise, compression, local artifacts, and texture inhomogeneities.
Objectives. The aim of this study is to develop a method for automatic quantitative estimation of the Gaussian blur parameter in digital images, which typically arises due to defocus of the optical system, various optical and camerainduced aberrations, as well as the influence of the propagation medium. This task is highly relevant for a wide range of applied fields, including remote sensing, forensic analysis, photogrammetry, medical imaging, automated inspection, and preprocessing of visual data prior to solving restoration, classification, or recognition problems.
Methods. The proposed method is based on comparing the two-dimensional histogram of gradients of the analyzed image with reference histograms precomputed for a high-sharpness image with similar texture and scale. The reference image is artificially blurred using convolution with a Gaussian kernel at various blur levels. For each level of blur, a two-dimensional gradient histogram is constructed, representing the distribution of directions and magnitudes of local intensity changes. The comparison with the corresponding histogram of the target image is performed after applying a logarithmic transformation and computing the Euclidean norm. This approach provides high sensitivity, interpretability, and numerical stability. The method does not require edge detection, neural network training, or labeled data, and can be implemented with minimal computational cost.
Results. Tests on synthetic data demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves high accuracy: the relative error in estimating the Gaussian blur parameter within the range of 0.7 to 2.0 pixels is less than 5%, and in most cases does not exceed 2–3%. The method is robust to noise, compression, local artifacts, and texture inhomogeneities.
Conclusions. The developed approach can be applied in automated image analysis systems as well as in blind deconvolution preprocessing tasks. It offers high accuracy, implementation simplicity, and reproducibility, providing reliable blur estimation under minimal data assumptions.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)