INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
- In order to detect and quantify the differences between harmonic and anomalous signals, a comparative analysis of various anomaly detection methods was conducted, including fractal analysis, multifractal analysis, Shannon entropy calculation, and power spectral density (PSD) analysis.
- Use of the Shannon entropy method does not fully capture the complexity and uncertainty of harmonic and anomalous signals.
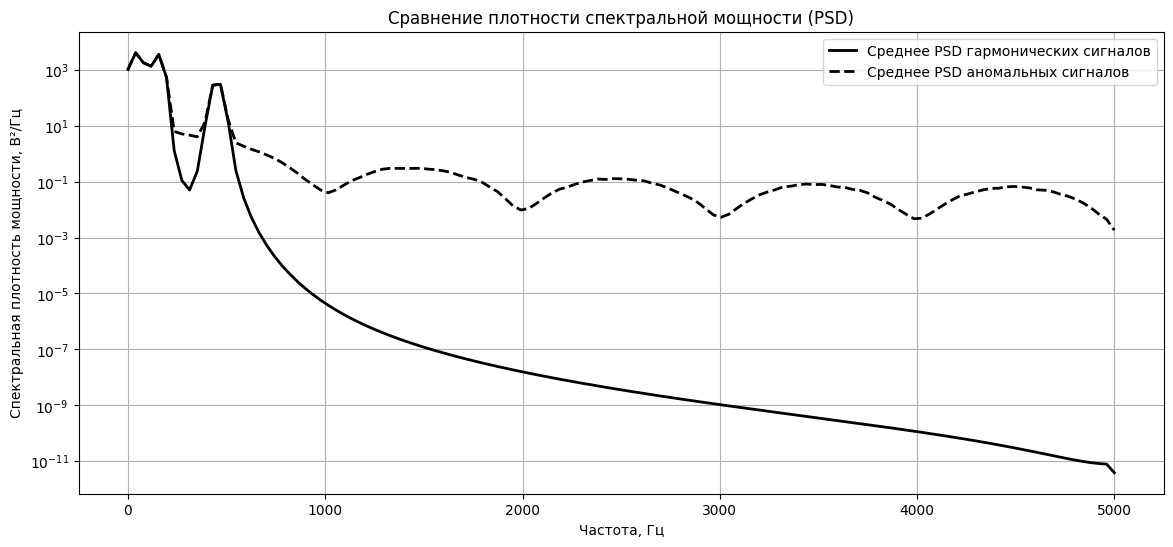
- Use of the PSD method revealed significant differences in energy distribution between these signals, permitting a more accurate identification of cyberattacks.
- For the effective detection of cyberattacks associated with harmonic signal distortions in power systems, a comprehensive approach is required, including time series analysis, frequency analysis, and machine learning methods.
Objectives. Cyberattacks are major potential sources of disturbances in modern electrical networks (Smart Grid). However, distinguishing between the various kinds of harmonic distortions and malicious interventions can be challenging. The objective of this work is to develop an effective tool for detecting and quantifying the differences between harmonic and anomalous signals. This will permit the identification of cyberattacks associated with harmonic signal distortions to provide a more accurate classification of patterns characteristic of malicious impacts.
Methods. A comparative analysis of various anomaly detection methods was conducted, including fractal analysis, multifractal analysis, Shannon entropy calculation, and power spectral density (PSD) analysis.
Results. Harmonic distortions and anomalous signals caused by cyberattacks may share similar fractal and multifractal characteristics, making it harder to distinguish between them. The use of the Shannon entropy method does not fully capture the complexity and uncertainty of harmonic and anomalous signals. To gain a deeper understanding of the nature of these signals, a comprehensive approach was applied, including analysis of their frequency characteristics and the use of other uncertainty assessment methods, such as multifractal analysis and PSD. Use of the PSD method revealed significant differences in energy distribution between these signals, permitting a more accurate identification of cyberattacks.
Conclusions. For the effective detection of cyberattacks associated with harmonic signal distortions in power systems, a comprehensive approach is required, including time series analysis, frequency analysis, and machine learning methods. This approach not only detects anomalies in signals but also provides their quantitative assessment to improve the accuracy of classifying malicious impacts. The integration of these methods enhances the reliability and security of power systems, making them less vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- The paper proposes a method for detecting percolation transitions in the dynamics of cluster formation of articles with similar content.
- Percolation transitions, which are indicators of sudden conceptual shifts in citation networks, allow us to identify and link articles into research schemes which form clusters of new ideas and theories.
- Improving the accuracy of information cycles in knowledge networks can help resolve applied problems related to the quality of scientometrics and its indicators.
Objectives. The object of the research is to study citation information networks structured on the basis of a sample from the arXiv database related to theoretical high energy physics (high energy physics, HEP). Since 1974, this database has indexed more than 500000 articles, including their complete citation trees. The paper proposes a method for detecting percolation transitions in the dynamics of cluster formation of articles with similar content. Improving the accuracy of information cycles in knowledge networks can help resolve applied problems related to the quality of scientometrics and its indicators.
Methods. An optimized algorithm for dynamic network separation in the Pajek software environment was applied, in order to detect the emergence of a largest component equivalent to a percolation transition. This approach enables a detailed study of dynamic and general parameters to be carried out in each reduced network with a given time step. The clustering algorithm combines citation structure and temporal information about data.
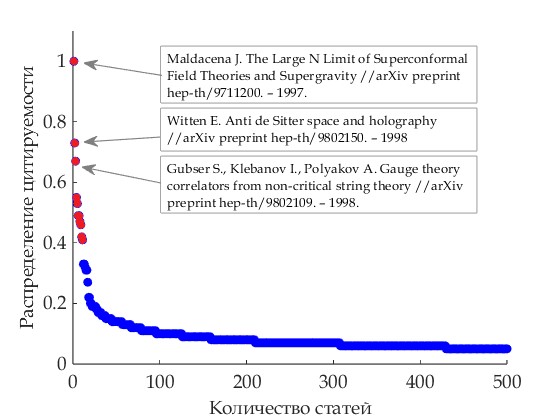
Results. It was found that a percolation transition occurs in the HEP network. The indicator of this transition is the formation of a largest component near the critical point which occurs at the 10th month of the time sample interval. At the same time, a generalized conclusion about the behavior of network parameters shows a positive trend in the growth of connectivity for the entire time period (from 1991 to 2003). Furthermore, a generalized analysis of citation distribution reveals eleven laureates of highly cited articles who set the basic vector for development in the field of HEP. It is worth noting that the prominent scientists from the top three in terms of citations are linked by a shared field of research: string theory. Verification of this fact confirms that our citation evaluation method is effective. Determining the characteristics of the HEP (high-energy physics) network enables an important indicator of the researcher’s activity and behavior to be identified.
Conclusions. In the column of authors linked by co-authorship, of the 9200 authors in the HEP physics community, 7304 belong to a single connected component. The temporal nature of citations indicates a rapid uptake and understanding of relevant new work. Percolation transitions, which are indicators of sudden conceptual shifts in citation networks, allow us to identify and link articles into research schemes which form clusters of new ideas and theories.
- The derived integral ratios were further used to estimate the probability characteristics of information processing security when performing functional tasks in various scenarios of attacks on digital substations, as well as multiple technologies used for protection against such threats.
- A protection technology with system diagnostic deterministic frequency can support customer requirements in the event of accidental and relatively rare virus attacks.
- Security technologies consider different maintenance personnel operation modes to ensure customer fulfillment requirements for safe information processing probability and the case of deliberate attacks on digital substations in each period.
Objectives. This study aims to create analytical methods for evaluating the probabilistic safety characteristics of information and software elements in digital substations in order to ensure security in different virus scenarios.
Methods. The methods of reliability theory, random process theory, and recovery theory were used.
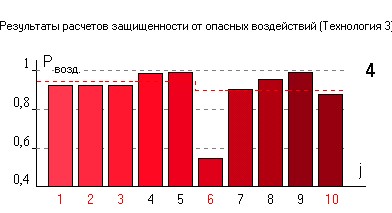
Results. The derived integral ratios were further used to estimate the probability characteristics of information processing security when performing functional tasks in various scenarios of attacks on digital substations, as well as multiple technologies used for protection against such threats. Numerical studies of safe information processing probability of different intensities of attacks and times of their activation were conducted, in order to consider the frequency of diagnostics of the system by the service personnel and customer requirements for the safe operation of the system in a certain period. We performed calculations for various protection technologies against similar attacks on digital substations. A protection technology with system diagnostic deterministic frequency can support customer requirements in the event of accidental and relatively rare virus attacks. Security technologies consider different maintenance personnel operation modes to ensure customer fulfillment requirements for safe information processing probability and the case of deliberate attacks on digital substations in each period.
Conclusions. The technologies considered herein for information protection from attacks on digital substations can provide the necessary level of information security system operation for all types of threats. These technologies can be applied when the system diagnostics frequency increases from twice an hour to at least once every 25 minutes. Our findings underline the importance of timely monitoring of ever-changing attack environments for digital substations.
- The work aims to develop and experimentally test a set of algorithms for a thematic model for automatically determining the main topics of information exchange and typical messages illustrating these topics.
- A thematic model in which clusters found with the presentation of their typical representatives and current weight can help decision-making in accordance with the subject of these most important messages was developed.
- The proposed algorithm of topic modeling allows the most important topics in current communication to be automatically identified. It shows posts that serve as indicators of these topics, and thereby significantly simplifies the solution of the problem.
Objectives. This work is devoted to the topic modeling of short messages received through social networks or in another way in the form of a series of short messages. This need arises in public relations systems in state and municipal structures, in public opinion polling centers, as well as in customer service systems and marketing departments. The aim of the work is to develop and experimentally test a set of algorithms for a thematic model for automatically determining the main topics of information exchange and typical messages illustrating these topics.
Methods. The work uses methods of variable statistical distributions applied to collocation statistics and approaches typical for resolving problems of topic modeling of short texts, but applied to successive messages. In this way, online machine learning and topic modeling are considered jointly.
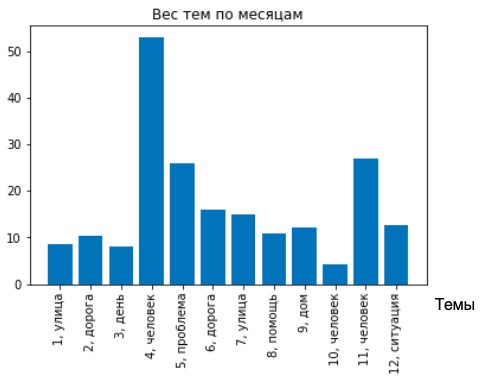
Results. The work considered the construction of a thematic model in which clusters found with the presentation of their typical representatives and current weight can help decision-making in accordance with the subject of these most important messages. The proposed method was experimentally tested on a corpus of real messages. The results of topic modeling (the constructed thematic models) are consistent with the results obtained manually. The messages selected illustrate that the topics with the highest weight are seen as such from the point of view of human experts.
Conclusions. The proposed algorithm of topic modeling allows the most important topics in current communication to be automatically identified. It shows posts that serve as indicators of these topics, and thereby significantly simplifies the solution of the problem.
- The article provides a technical and economic analysis of computing modules or servers created on the basis of Xeon (Intel) class microprocessors and the like.
- An overview of the microprocessor subclasses is given along with an indication of server organization options, as well as their main components and primary areas of use.
- Servers integrated into the warehouse scale computer class have to operate continuously in 24/7 mode for long periods.
- This requires the development of methods for assessing the reliability of such highly reliable systems, including backup elements, in relation to hardware and software failures, as well as methods for predicting failures and measures to combat their consequences.
Objectives. The work set out to technically and economically analyze servers as computing modules of computing systems of the warehouse scale computer (WSC) class.
Methods. The research was carried out using the methods of mathematical analysis and modeling.
Results. The article provides a technical and economic analysis of computing modules or servers. Servers are created on the basis of Xeon (Intel) class microprocessors and the like. An overview of the microprocessor subclasses is given along with an indication of server organization options, as well as their main components and primary areas of use. Server reliability is a complex property that may include durability, maintainability and persistence, or certain combinations of these properties depending on the purpose of the object and the conditions of its use. To ensure maximum reliability, backup elements, including arrays of disks and power supplies, as well as backup servers, are used alongside special solutions, including the use of hot swapping and connection, checking and correction of random access memory errors, and temperature control of server compartments.
Conclusions. The review of options for organizing servers and their main components allows permits the conclusion that their operation is sufficiently reliable. However, servers integrated into the WSC class have special requirements, namely, continuity of operation in 24/7 mode for long periods of time. This requires the development of methods for assessing the reliability of such highly reliable systems, including backup elements, in relation to hardware and software failures, as well as methods for predicting failures and measures to combat their consequences.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- Simulation of the Zeta converter with coupled inductors was carried out using the Multisim CAD system, during which the load and transfer characteristics of the converter were obtained. These characteristics show the dependencies of currents flowing through the coupled inductors and voltages on the capacitors on the input voltage, as well as the dependence of the output voltage on the load current.
- The proposed design method allows for the calculation of element ratings for the Zeta topology both with and without considering the inductive coupling of inductors.
- Additionally, using this method, it is possible to calculate the steady-state values and ripple currents of the inductors and voltages on the capacitors.
Objectives. The work set out to develop a new design method for DC/DC converters based on the Zeta topology to calculate the ratings of inductors and capacitors of the Zeta converter with magnetically coupled inductors and verify the accuracy of the ultimate continuous mathematical model and design method based on it using SPICE simulation in the Multisim computer-aided design (CAD) system.
Methods. The proposed method analyzes an ultimate continuous mathematical model to calculate the ratings of coupled inductors and capacitors of the converter.
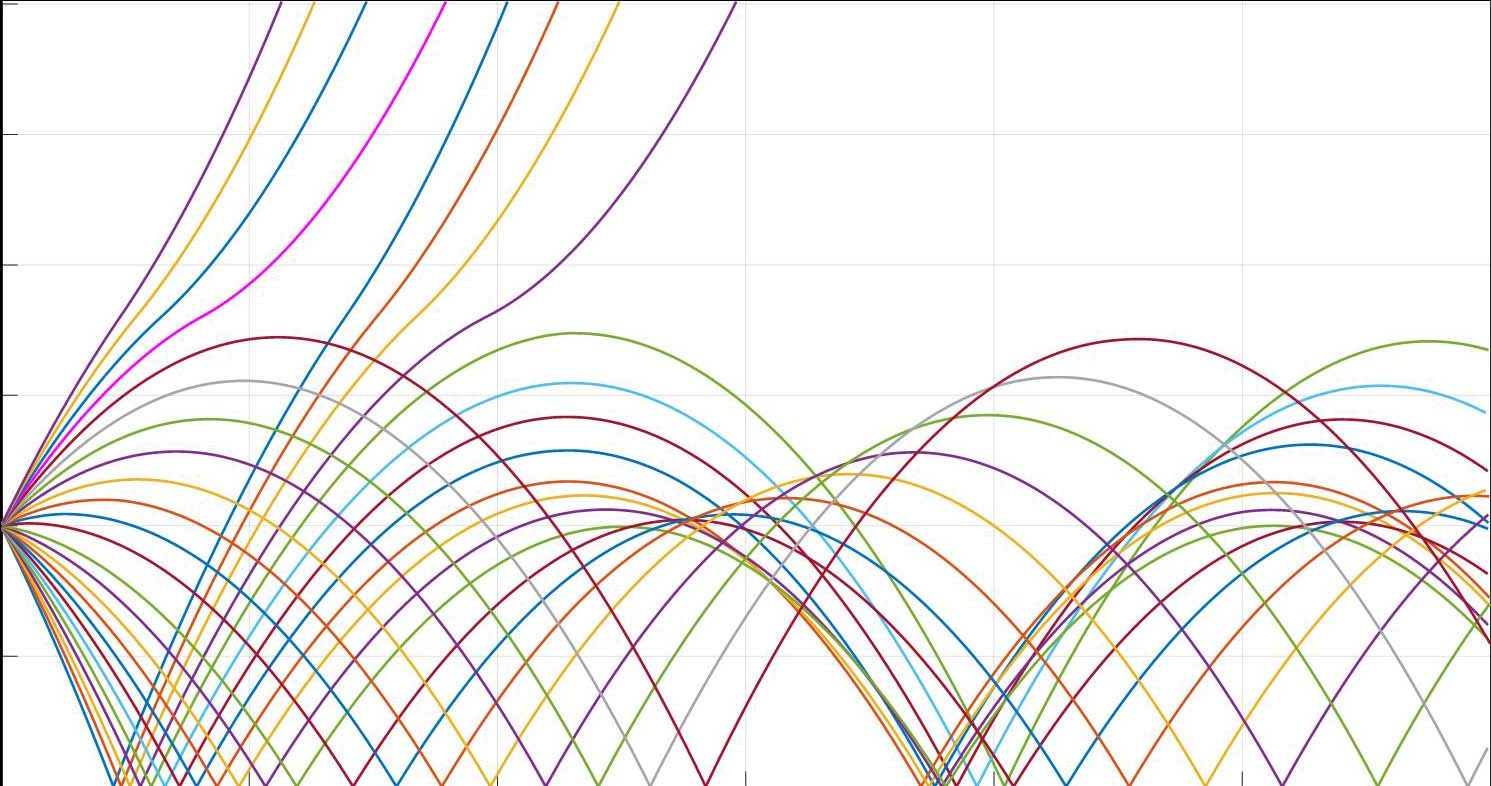
Results. The simulation of the Zeta converter with coupled inductors was carried out using the Multisim CAD system, during which the load and transfer characteristics of the converter were obtained. These characteristics show the dependencies of the currents flowing through the coupled inductors and voltages across the capacitors on the input voltage, as well as the dependence of the output voltage on the load current. The presented design method is shown to be accurate and in full agreement with the simulation results. A correlation between the transfer and load characteristics of currents and voltages obtained by simulation and calculation is established. The differences between the values calculated using the ultimate continuous mathematical model and the results of simulation in the Multisim CAD system are comparable to measurement errors.
Conclusions. The proposed design method is used calculate element ratings for the Zeta topology both with and without taking the inductive coupling into account. The method can also be used to calculate the steady-state values and ripple currents of the inductors and voltages across the capacitors. The design method for DC/DC converters presented in the paper can be used for both preliminary evaluation calculations and more detailed calculations, including analysis of the device operation under various input voltages and load resistances.
- A method of increasing the accuracy of indoor positioning by taking into account obstacles known at the design stage of the system was improved by automating the stage of preparing information about the grouping of stations.
- The criteria for automatic station grouping and a universal algorithm for dividing stations into groups were developed, enabling the automated preparation of the minimum necessary initial data for a program implementing an algorithm for positioning in a zone of heterogeneous radio transparency.
Objectives. A pressing problem for indoor positioning systems in the absence of access to global navigation satellite systems is low positioning accuracy. This is usually associated with uneven coverage of the work area due to its geometric features or the presence of massive obstacles and walls within its boundaries. This problem is frequently resolved by placing an excessive number of positioning system base stations in the work area. This approach generates a high cost for such systems, which in turn prevents their deployment. Therefore, research and development aimed at improving the accuracy of indoor positioning systems using a minimum number of stations is of great relevance. The author previously proposed a method of increasing the accuracy of indoor positioning by taking into account obstacles known at the design stage of the system. Consideration of such obstacles in calculating the location is achieved through the mechanism of preliminary splitting of radio beacons into groups, and the allocation of reference stations of these groups among the base stations. The aim of the work is to improve this algorithm by automating the stage of preparing information about the grouping of stations.
Methods. A computer simulation method was used, in order to confirm the operability of the algorithm to divide the stations of the positioning system into overlapping groups.
Results. The criteria for automatic station grouping and a universal algorithm for dividing stations into groups were developed, enabling the automated preparation of the minimum necessary initial data for a program implementing an algorithm for positioning in a zone of heterogeneous radio transparency.
Conclusions. Modeling of the proposed algorithm has confirmed its operability. The results obtained can be used as a significant addition to the previously proposed algorithm for taking into account obstacles when calculating distances to base stations.
- Multi-position amplitude-phase shift keying (APSK) with a ring-shaped signal constellation is one of the most effective ways for transmitting discrete information in satellite systems.
- The optimization of ring-shaped constellations of 16-APSK and 32-APSK signals is attained by changing the distribution of points along the radius and phase for a case in which the communication channel, along with noise, contains non-fluctuating interference: frequency-shift keyed, retransmitted, phase-shift keyed, and harmonic ones.
- The best constellations of 16-APSK and 32-APSK are determined, and a minimum bit error rate is provided.
Objectives. Multi-position amplitude-phase shift keying (APSK) with a ring-shaped signal constellation is one of the most effective ways for transmitting discrete information in satellite systems. The use of APSK is regulated by several standards. The main are DVB-S2 and VSAT which define both the modulation parameters, and the parameters of the signal constellations. The aim of the paper is to determine the best constellations of 16-APSK and 32-APSK, and provide a minimum BER for cases when the communication channel, along with noise, contains non-fluctuating interference.
Methods. Methods of statistical radio engineering, the theory of optimal signal reception, and computer modeling were used.
Results. The optimization of ring-shaped constellations of 16-APSK and 32-APSK signals is attained by changing the distribution of points along the radius and phase for a case in which the communication channel, along with noise, contains non-fluctuating interference: frequency-shift keyed, retransmitted, phase-shift keyed, and harmonic ones. The best constellations of 16-APSK and 32-APSK are determined, and a minimum bit error rate is provided.
Conclusions. In order to improve the quality of communication in information transmission systems in the presence of non-fluctuating interference, the existing constellations 16-APSK (4, 12) and 32-APSK (4, 12, 16) can be used by changing the ratios between the radii of circles 2.5 for 16-APSK and 2.5/3.9 for 32-APSK. Due to the more efficient use of signal power, the use of constellations with a zero-amplitude point for 16-APSK allows reception noise immunity to be increased. For example, when using constellation (1, 5, 10), the energy gain compared to the standard constellation (4, 12) can reach 1 dB.
- Typical cases of a tropospheric waveguide based on a modified refractive index were considered.
- The bit error rate curves are obtained as a function of the geometry of the antenna arrays after the signal has passed through the tropospheric waveguide. Circular and spherical antenna arrays composed of directional antenna elements are considered.
- Numerical studies suggest that the range of communication links using digital antenna arrays increases in the centimeter band.
- The best geometry for this purpose is circular, since providing the lowest bit error rate for binary phase-shift keyed signals.
Objectives. A radio beam traveling through the layers of the atmosphere depends on the refractive index and its vertical variation. In this regard, attenuation may occur when radio rays propagate in a waveguide manner at low altitudes. A multipath fading effect may also occur when several rays reflected from different layers of the troposphere and having different spatial coordinates in elevation arrive at the receiver. The aim of the study is to simulate the operational algorithms of digital antenna arrays (DAA) in order to increase the range and reliability of radio communication using a tropospheric waveguide. The main advantage of the DAA consists in the high gain and controllability of the pattern shape. In order to evaluate algorithms for direction-of-arrival estimation with superresolution and beamforming, it is necessary to select an appropriate method for modeling beam propagation in the layers of the troposphere. It is proposed to use DAA to increase the range and reliability of radio communications using a tropospheric waveguide. The performance of algorithms for direction-of-arrival estimation and beamforming in the troposphere can be evaluated using ray tracing simulation.
Methods. Parabolic equations are used to estimate the path losses of radio waves in the centimeter range. A ray tracing algorithm referring to a tropospheric waveguide is used to estimate the phases in the aperture of the receiving array. A spatial correlation matrix is reliably generated to form the basis for calculating coordinates using a superresolution multiple signal classification (MUSIC) method and the weighting factor vector (algorithm for maximizing the signal-to-noise + noise ratio).
Results. Typical cases of a tropospheric waveguide based on a modified refractive index were considered. The bit error rate curves are obtained as a function of the geometry of the antenna arrays after the signal has passed through the tropospheric waveguide. Circular and spherical antenna arrays composed of directional antenna elements are considered.
Conclusions. Numerical studies suggest that the range of communication links using digital antenna arrays increases in the centimeter band. The best geometry for this purpose is circular, since providing the lowest bit error rate for binary phase-shift keyed signals.
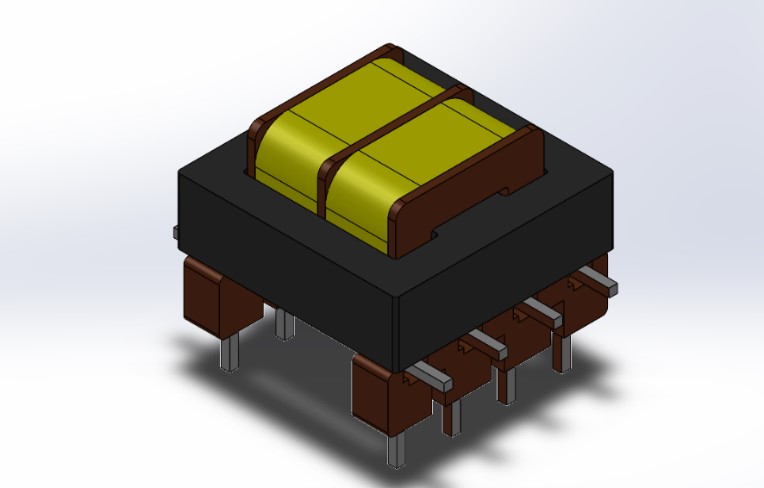
- Approaches for designing secondary supplies are described along with the method for developing the cathode heating and bias supplies for a floating-drift multipath klystron.
- The calculation method used for testing the design of the transformer windings is presented. The design avoids the use of chokes as separate elements by integrating them inside a magnetic system and providing isolation by high potential of the secondary winding.
- The results of testing the power supply using complex test bench waveforms are given along with the main obtained parameters.
- The operation of the power supply is demonstrated in switching mode at zero voltage for the minimum, nominal, and maximum input voltages in the range of the inductive resistance of the circuit when the voltage phase precedes the current phase.
Objectives. The ever-increasing demands on the technical parameters of microwave radio transmission devices necessitate a search for ways of improving their efficiency and reliability, as well as means for reducing their weight and size parameters. Since such requirements largely relate to secondary power supplies, the present work set out to develop secondary power supplies for the cathode heating and bias circuits of a floating-drift multibeam klystron capable of operating at a high potential of the klystron cathode and providing stable voltage in all operating modes.
Methods. In order to calculate the parameters of the resonant circuit, the first harmonic approximation method is used.
Results. Approaches for designing secondary supplies are described along with the method for developing the cathode heating and bias supplies for a floating-drift multipath klystron. The calculation method used for testing the design of the transformer windings is presented. The design avoids the use of chokes as separate elements by integrating them inside a magnetic system and providing isolation by high potential of the secondary winding. The results of testing the power supply using complex test bench waveforms are given along with the main obtained parameters. The operation of the power supply is demonstrated in switching mode at zero voltage for the minimum, nominal, and maximum input voltages in the range of the inductive resistance of the circuit when the voltage phase precedes the current phase.
Conclusions. The calculated efficiencies of the presented cathode heating and bias supplies are 85% and 92%, respectively. The developed supplies, which have smaller dimensions than their transformer analogues, allow a stable output voltage to be maintained when the input voltage varies, while the use of the soft start method allows the life of the klystron to be extended.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
- Experimental spectra of the magneto-optical transverse Kerr effect in Cox(CoO)1−x nanocomposites were studied and Kerr effect spectra in the range of 1.5–3.0 eV were obtained by computer modeling.
- The optimal parameters of the sample under study are established: form factor, average granule size, and the anomalous Hall effect coefficient.
- The described approach allows the magneto-optical properties of promising nanomaterials to be studied in a non-contact and non-destructive manner.
Objectives. The aim of this paper is to attain and investigate the spectra of the magneto-optical transverse Kerr effect (TKE) in Cox(CoO)1−x nanocomposites, to compare the obtained results with experimental data, and identify their specific features. Magneto-optical spectroscopy is a method for non-destructive testing and research of a wide class of nanostructures with promising and interesting properties, and such studies are essential in terms of both fundamental and practical aspects.
Methods. Computer modeling is used as part of the promising effective medium method. This is in the form of the Bruggeman approximation, according to which the structure under study is replaced by a medium with effective properties.
Results. TKE experimental spectra were studied and Kerr effect spectra in the range of 1.5–3.0 eV were obtained by computer modeling. In this case, the modeling is performed by means of two methods, ignoring and considering the quasiclassical size effect. The final result is the comparison of the model and experimental Kerr effect spectra, in which the influence of size effects on the appearance of the TKE spectra is shown. The reliability of methods is well confirmed by comparing the results obtained with empirical data. The value of the results obtained stems from the fact that all the calculated parameters of the nanocomposite under study and the shape of TKE spectral dependencies are in good agreement with the observation results.
Conclusions. The optimal parameters of the sample under study are established as part of computer modeling: form factor, average granule size, and the anomalous Hall effect coefficient. The described approach allows the magneto-optical properties of promising nanomaterials to be studied in a non-contact and non-destructive manner. These results are useful for creating new types of devices as well as electronics and nanoelectronics elements.
ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
- The electronic unit for joint operation with a liquid nitrogen cooled mercury–cadmium–tellurium photodetector was developed and its noise properties were investigated.
- The noise properties of comparatively modern integrated circuits currently used for this task were considered. The noise density spectra of the first stage (ADA4898-2), the second stage (AD8034), and bias current sources (AD8397 and LT3009) were measured. It was found that the spectral density of the input noise of the operational amplifier ADA4898-2 is comparable to the Nyquist (thermodynamically expected) noise of a 20–100-Ohm resistor corresponding to the resistance of the photosensitive element. This means that the selected operational amplifier is ideal for resolving the technical problem discussed herein.
- It is shown that the spectral noise density of the electronic components, reduced to the input of the device, is several times lower than the noise density of the photodetector used.
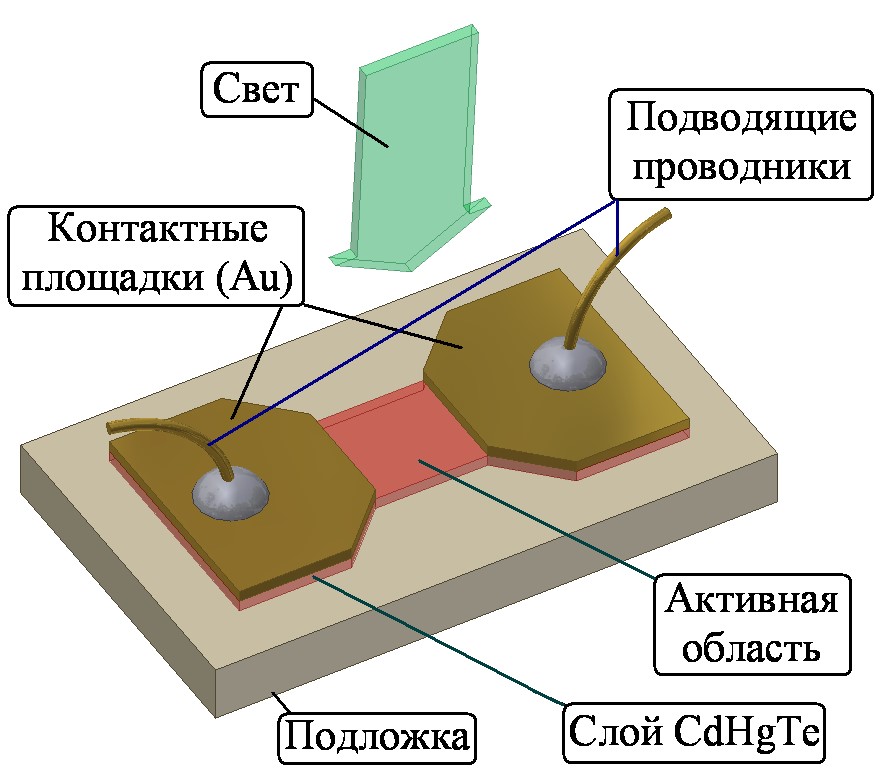
Objectives. Photoresistors based on a solid solution of mercury–cadmium–tellurium (MCT) have been used in infrared (IR) technology for over 60 years. They can have a sensitivity range in the wavelength region from 1 μm to 15 μm, depending on Hg1−xCdxTe composition. The resistance of photosensitive MCT elements is (depending on their area) tens of Ohms, and for such a resistor the thermodynamically expected Nyquist noise is less than 1 nV/√Hz. Modern semiconductor technologies ensure a high level of quality of both photodetectors and input stages of integrated circuits for amplifying the signal from them. The aim of this work is to study the noise properties of the electronic unit developed for joint operation with a liquid nitrogen cooled MCT-photodetector.
Methods. An analog input-output digital signal processor card P25M (Innovative, Inc., USA) was used to measure and accumulate the noise spectra of the signal in the frequency range 0–1 MHz. The card has four 16-bit ADCs of sampling rate up to 25MSpS, a Spartan-3 field-programmable gate array controlling them, a TMS320C6713 processor, and RAM, in order to transmit the collected digital data to the motherboard through a common PCI-X slot. The spectra of the received data were calculated using the fast Fourier transform algorithm with subsequent averaging of the square of the amplitude for all spectral components.
Results. The noise properties of comparatively modern integrated circuits currently used for this task were considered. The noise density spectra of the first stage (ADA4898-2), the second stage (AD8034), and bias current sources (AD8397 and LT3009) were measured. It was found that the spectral density of the input noise of the operational amplifier ADA4898-2 is comparable to the Nyquist (thermodynamically expected) noise of a 20–100-Ohm resistor corresponding to the resistance of the photosensitive element. This means that the selected operational amplifier is ideal for resolving the technical problem discussed herein. Meanwhile, it was also established that the noise spectrum of the LT3009, ADR510 voltage and current stabilizer integrated circuits contains a noticeable drift component with a spectral density of “pink noise” 1/f α (f – frequency, α ≈ 1).
Conclusions. It was shown that the spectral noise density of the electronic components, reduced to the input of the device, is several times lower than the noise density of the photodetector used.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- Heat transfer intensity was analyzed for tubes of circular and rectangular cross-sections. In cases where the cross sections of tubes in the heat exchanger are elongated in a given direction, the influence of the tube position in relation to the oncoming flow was studied. This was performed either with the long side along the flow or across it.
- The influence of finned tubes in the laminar flow regime of heated fluid through the bundle of heat transfer tubes is insignificant. The highest value of the heat flux was observed for tubes of rectangular cross section with the long side transverse to the flow, and the difference with the data obtained for standard round tubes was found to be more than 15%.
Objectives. In the confined space of heat exchangers, heat transfer rate plays a key role. The cross-sectional shape of the tubes can affect the heat transfer characteristics. Although circular tubes are easier and less expensive to manufacture, heat transfer in heat exchangers with tubes of other cross-sections can take place at higher rates, thus providing economic advantages. This makes the mathematical modeling of hydrodynamics and heat exchange in a tube apparatus relevant and interesting both from the theoretical and applied point of view. The aim of this study is to determine the influence of the shape of the tube cross-section on the heat transfer intensity.
Methods. Numerical investigations were carried out using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. The possibilities of the smoothed particle method for resolving industrial heat transfer problems were demonstrated.
Results. Heat transfer intensity was analyzed for tubes of circular and rectangular cross-sections. In cases where the cross sections of tubes in the heat exchanger are elongated in a given direction, the influence of the tube position in relation to the oncoming flow was studied. This was performed either with the long side along the flow or across it. The influence of tube surface protrusions on heat exchange was investigated. The flow around tubes with different cross-sectional shapes was also analyzed. The features of the flow around the tubes were established, and the velocity and temperature fields in the heat exchanger volume were defined. The values of the dimensionless heat flux (Nusselt number) for each case were also found.
Conclusions. The influence of finned tubes in the laminar flow regime of heated fluid through the bundle of heat transfer tubes is insignificant. The highest value of the heat flux was observed for tubes of rectangular cross section with the long side transverse to the flow, and the difference with the data obtained for standard round tubes was found to be more than 15%.
- The work aims to identify the parameters of variational pulsometry, which provide the best distinction between healthy patients and patients with arrhythmia, by means of discriminant analysis.
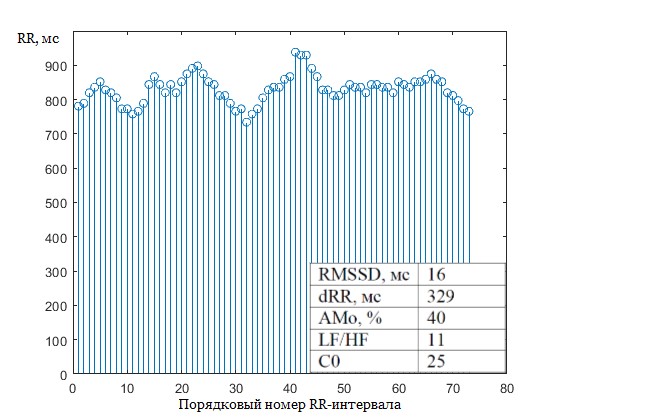
- Two discriminant functions were obtained: the first depended on three time-domain parameters, while the second included one spectral and one autocorrelation parameter in addition to time-domain parameters.
- The values of the first discriminant function are shown to differ insignificantly between healthy and sick patients, while the inclusion of autocorrelation and spectral parameters in the number of arguments of the discriminant function provides pronounced and statistically significant differences between patients of the two groups.
Objectives. The article presents a study of heart rate variability using multivariate discriminant analysis. Representing an effective statistical method of classification, discriminant analysis can be used to divide objects into groups based on differences in the parameters characterizing these objects. The effectiveness of multivariate discriminant analysis, which is actively used in medicine to diagnose cardiovascular pathologies, is due to the wide range of analyzed parameters: statistical, spectral, and autocorrelation. The aim of the work is to identify the parameters of variational pulsometry, which provide the best distinction between healthy patients and patients with arrhythmia, by means of discriminant analysis.
Methods. The durations of cardiac intervals of patients aged 63–72 years, which had been placed in the open database of biomedical signals PhysioNet.org, were used as initial data. When selecting the arguments of the discriminant function, priority was given to parameters that were weakly correlated with each other, had a normal distribution, and differed between healthy and ill patients. The statistical significance of differences between the parameters of the two groups was tested using Student’s t-test and Mann–Whitney U test.
Results. Two discriminant functions were obtained: the first depended on three time-domain parameters, while the second included one spectral and one autocorrelation parameter in addition to time-domain parameters. In both cases, the average values of the discriminant function for healthy and sick patients were calculated. The statistical significance of differences in the average values of the discriminant function in the two groups was investigated using Student’s t-test.
Conclusions. The values of the first discriminant function are shown to differ insignificantly between healthy and sick patients, while the inclusion of autocorrelation and spectral parameters in the number of arguments of the discriminant function provides pronounced and statistically significant differences between patients of the two groups. Thus, the high significance of spectral and autocorrelation parameters in arrhythmia diagnosis was demonstrated.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)