INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
- The approach proposed in the article represents an efficient way to automate the retrieval of legal information without requiring a large amount of labeled data or consuming significant computational resources.
- The feasibility of a document retrieval approach in the context of Arabic legal texts using natural language processing and unsupervised clustering techniques was analyzed.
- Challenges of working with Arabic legal text, such as morphological complexity, ambiguity, and a lack of standardized terminology, are addressed by means of a proposed preprocessing pipeline that includes tokenization, normalization, stemming, and stop-word removal.
- The proposed approach provides 87% accuracy and 80% completeness.
Objectives. The retrieval of legal information, including information related to issues such as punishment for crimes and felonies, represents a challenging task. The approach proposed in the article represents an efficient way to automate the retrieval of legal information without requiring a large amount of labeled data or consuming significant computational resources. The work set out to analyze the feasibility of a document retrieval approach in the context of Arabic legal texts using natural language processing and unsupervised clustering techniques.
Methods. The Topic-to-Vector (Top2Vec) topic modeling algorithm for generating document embeddings based on semantic context is used to cluster Arabic legal texts into relevant topics. We also used the HDBSCAN densitybased clustering algorithm to identify subtopics within each cluster. Challenges of working with Arabic legal text, such as morphological complexity, ambiguity, and a lack of standardized terminology, are addressed by means of a proposed preprocessing pipeline that includes tokenization, normalization, stemming, and stop-word removal.
Results. The results of the evaluation of the approach using a dataset of legal texts in Arabic based on keywords demonstrated its superior effectiveness in terms of accuracy and memorability. The proposed approach provides 87% accuracy and 80% completeness. This circumstance can significantly improve the search for legal documents, making the process faster and more accurate.
Conclusions. Our findings suggest that this approach can be a valuable tool for legal professionals and researchers to navigate the complex landscape of Arabic legal information to improve efficiency and accuracy in legal information retrieval.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
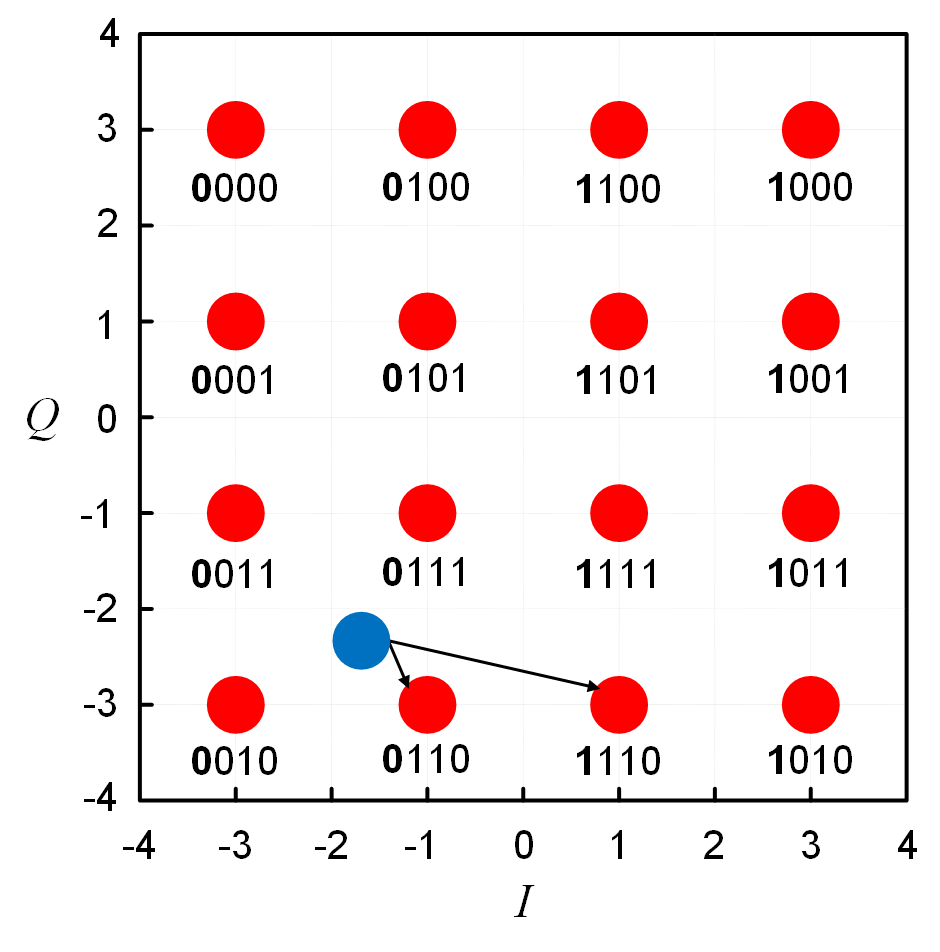
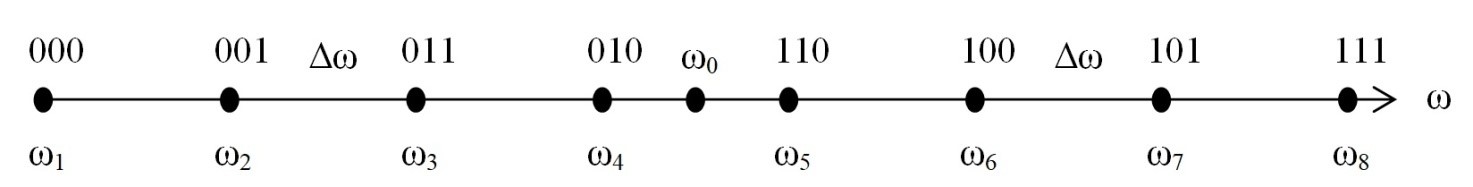
- The paper presents a simple method for calculating soft bit estimates in the M-point demodulator of quadrature amplitude modulation signal, where M is an even power of two.
- The use of encoding with soft demodulator decisions significantly improves the noise immunity of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing signal reception, and enables narrowband interference to be managed efficiently.
Objectives. The aim of this paper is to study the noise immunity of digital information transmission in systems with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of subcarriers in the presence of narrowband interference. As a way of managing this interference, the paper studies the use of a demodulator with soft outputs and subsequent decoding of the convolutional code and low-density paritycheck (LDPC) code used in the system.
Methods. The results presented in the article were obtained using statistical radio engineering, mathematical statistics, encoding theory, and computer modeling.
Results. The paper presents a simple method for calculating soft bit estimates in the M-point signal QAM demodulator, where M is an even power of two. A considerable amount of numerical results were obtained which show the dependence of the transmitted information bit error rate on M, as well as on the signal-to-noise ratio, signal-to-narrowband interference, and code rates.
Conclusions. It can be concluded from the above results that the use of encoding with soft demodulator decisions significantly improves the noise immunity of OFDM signal reception, and enables narrowband interference to be managed efficiently. LDPC encoding is superior to convolutional encoding in increasing the noise immunity of OFDM signal reception both in the absence and in the presence of narrowband interference. Along with the use in QAM-OFDM systems, the proposed simple method for demodulating QAM signals with soft decisions can be used in any wireless communication system using M-position QAM signals, where M is 2 to an even power.
- The paper analyzes the noise immunity of coherent reception of multiple frequency-shift keyed (M-FSK) signals against the background of retransmitted interference.
- The impact of retransmitted interference is shown to result in a decrease in the noise immunity of M-FSK signal reception, which is greater the higher its intensity.
- The presence of interference with a relative intensity of 0.5 causes energy losses from 4 to 6 dB depending on the positionality. When M > 4, M-FSK signals gain significantly in terms of noise immunity over signals with M-PSK, quadrature amplitude modulation, and amplitude and phase-shift keying.
Objectives. Radio engineering information transmission systems are widely used in robotic systems employed in various military and civilian services. If such systems are used in a harsh environment, where a large amount of retransmitted interference occurs, for example, if a complex is buried under rubble or is located in reinforced concrete pipes or other utility facilities, communication with the command post may be lost. Thus, the task of maintaining reliable communications under difficult conditions of radio wave propagation is very urgent. In the field of telecommunications, multiposition types of modulation are widely used, which, despite their good spectral characteristics, provide low noise immunity under conditions of nonfluctuating interference, especially in cases of retransmitted interference. Therefore, it is relevant to explore the possibility of using multiple frequency-shift keying (M-FSK) signals in radio systems with complex interference environments. The paper sets out to analyze the noise immunity of coherent reception of M-FSK signals against the background of retransmitted interference.
Methods. Statistical radio engineering and mathematical modeling methods are used according to the theory of optimal signal reception.
Results. A model of the M-FSK signal and retransmitted interference is provided. The statistical parameters of the distributions of random processes occurring in a multichannel coherent receiver of M-FSK signals against retransmitted interference are obtained; based on this, the bit error rate is calculated when receiving M-FSK signals of different positionality M against retransmitted interference with different intensities.
Conclusions. The impact of retransmitted interference is shown to result in a decrease in the noise immunity of M-FSK signal reception, which is greater the higher its intensity. With increasing positionality of M-FSK signals at low intensity of retransmitted interference, the noise immunity of reception is significantly improved; however, high-intensity interference significantly increases the bit error rate. The presence of interference with a relative intensity of 0.5 causes energy losses from 4 to 6 dB depending on the positionality. When M > 4, M-FSK signals gain significantly in terms of noise immunity over signals with multiple phase-shift keying, quadrature amplitude modulation, and amplitude and phase-shift keying.
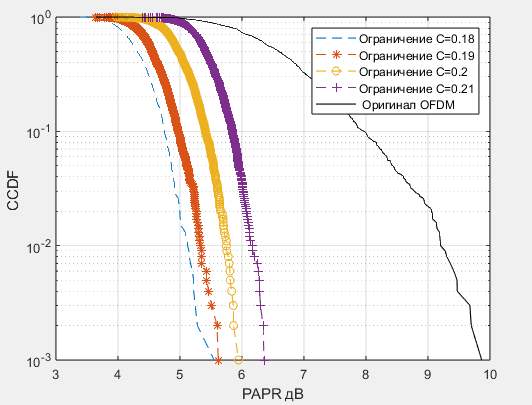
- The proposed limitation method with an additional signal when transmitting an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing signal in a channel with white Gaussian noise provides compensation for information losses due to signal level limitations in the transmission channel.
- Increasing the limitation level is shown to increase the peak-power-to-average-power ratio, while varying the number of additional signals changes peak-power-to-average-power ratio insignificantly.
Objectives. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) has become the standard for various high-speed wireless communication systems due to its several advantages, one of which is the efficient use of bandwidth. The main disadvantage of OFDM is the high peak-power-to-average-power ratio (PAPR), which is indicated by an increase in the bit error rate due to the nonlinearity of the power amplifier. The paper sets out to evaluate the possibility of reducing the PAPR value using a limitation method developed by the authors involving an additional compensation signal in a channel with white Gaussian noise, as well as to analyze its main parameters.
Methods. Statistical radio engineering and computer modeling methods are used according to optimal signal reception theory.
Results. The effect of the OFDM signal limitation level and the number of additional signals when using the limitation method with an additional compensation signal on the quality (reduction of transmission losses) of the OFDM signal is analyzed. The results show a decrease in the OFDM signal PAPR value, along with the dependencies of the bit error rate on the signal-to-noise ratio at fixed limitation values and a determined number of additional signals in the channel with white Gaussian noise.
Conclusions. The proposed limitation method with an additional signal when transmitting an OFDM signal in a channel with white Gaussian noise provides compensation for information losses due to signal level limitations in the transmission channel. Increasing the limitation level is shown to increase the PAPR value, while varying the number of additional signals changes PAPR insignificantly. In order to ensure the effective implementation of the limitation method with an additional compensation signal, the parameters of the threshold limitation level and number of additional signals should be selected depending on the predicted signal-to-noise ratio in the system.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
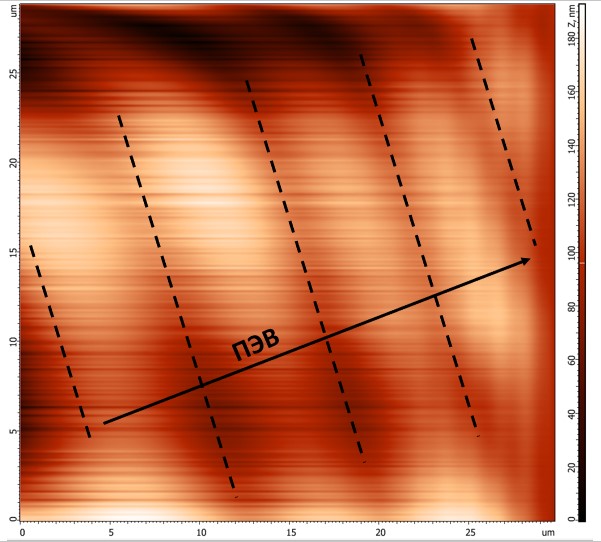
- The article investigates the effect of surface electromagnetic wave (SEW) treatment on the refractive properties of thin conducting films based on indium tin oxide (ITO) with laser-deposited single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The effective thickness of the layer of laser-deposited CNTs before and after SEW treatment is evaluated.
- For ITO-based thin films with laser-deposited CNTs, the described SEW treatment method provides a precise reduction in the thickness of the composite structure while preserving the antireflective properties of the CNTs.
- These capabilities make it possible to use the studied ITO modifications in solving problems in optical electronics, microfluidics, and biomedicine.
Objectives. The article investigates the effect of surface electromagnetic wave (SEW) treatment on the refractive properties of thin conducting films based on indium tin oxide (ITO) with laser-deposited single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The effective thickness of the layer of laser-deposited CNTs before and after SEW treatment is evaluated.
Methods. A laser-oriented deposition method employing a CO2 laser (λ = 10.6 µm) was used to form the structures. Diagnostics of modifications of ITO thin films were carried out using an ellipsometer operating in the spectral range of 300–1000 nm. The Cauchy model was used to describe the optical properties of K8 crown substrates and ITO thin films. To interpret the ellipsometry results of ITO modifications with CNTs, an effective-thickness virtual layer model was introduced. During post-processing of the surface, a CO2 marker (λ = 10.6 µm) was used to generate SEW. The influence of SEW treatment on the thickness of the virtual layer was assessed using ellipsometry and atomic force microscopy in contact mode.
Results. Based on the ellipsometry data, the effective thickness of the CNT layer was in the range of 24–26 nm. Following SEW treatment, the thickness of the effective CNT layer decreased to 4–8 nm, indicating the possibility of precision processing of the ITO surface with CNTs using SEW. When CNTs are deposited on an ITO surface with subsequent SEW treatment of the surface, reflection losses for p-polarized radiation are reduced. In a spectral range of 400–750 nm at an angle of incidence relative to the normal to the plane of structures α = 65°, a decrease in reflection is observed from 18.5% to 13.5% relative to ITO without CNTs and SEV treatment; at α = 71°, a decrease from 6.4% to 4.7% is observed; at α = 77°, a decrease from 1.8% to 1.2%.
Conclusions. For ITO-based thin films with laser-deposited CNTs, the described SEW treatment method provides a precise reduction in the thickness of the composite structure while preserving the antireflective properties of the CNTs. These capabilities make it possible to use the studied ITO modifications in solving problems in optical electronics, microfluidics, and biomedicine.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- The influence of excitation constancy on estimates of the two-channel system parameters is demonstrated on the basis of the proposed approach for estimating the identifiability of two-channel systems with cross-connections.
- The synthesis of adaptive algorithms of parameter estimation for two-channel systems with cross-connections based on input-output data is generalized to the case of interconnected systems.
- The results are applied to building models of tracking system and two-channel corrector for automatic control systems.
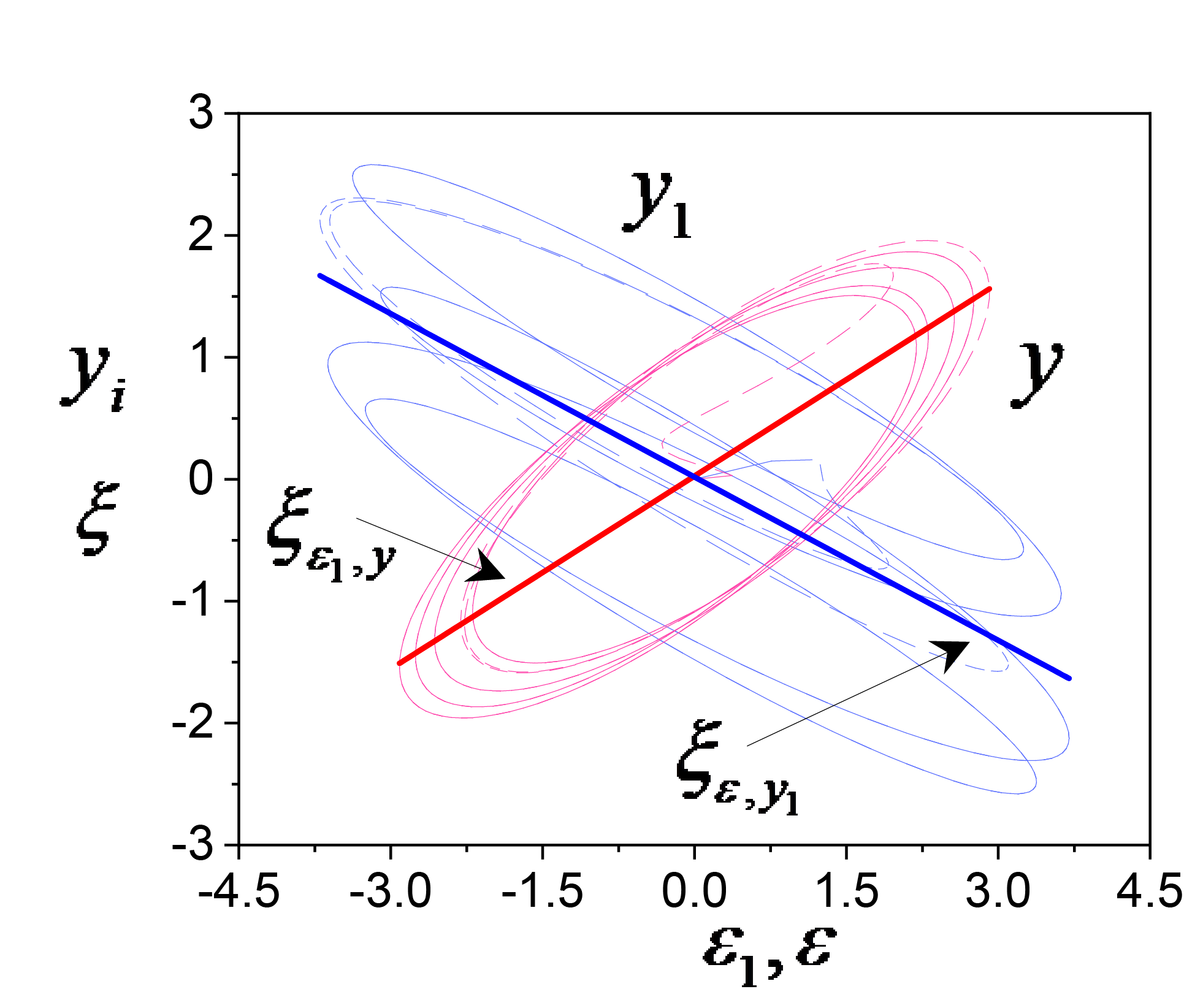
Objectives. Interconnected control systems are widely used in various technical contexts, generally involving multichannel systems. However, due to the complexity of their description, the problem of identifying interconnected systems has received insufficient attention. As a result, simplified models are commonly used, which do not always reflect the specifics of the object. Thus, the synthesis of mathematical models for the description of interconnected control systems becomes a relevant endeavor. The paper sets out to develop an approach to obtaining models under conditions of incomplete a priori information. A mathematical model is developed on the example of two-channel systems (TCSs) having cross-connections and identical channels. The case of asymmetric cross-connections is considered, along with estimates of their influence on the quality of the adaptive identification system. The problem of estimating the identifiability of the parameters of a TCS is formulated on the basis of available experimental information and subsequent synthesis of the adaptive system. The proposed approach is then generalized to the case of an interconnected system.
Methods. The adaptive system identification and Lyapunov vector function methods are used along with implicit identification representation for the model.
Results. The influence of excitation constancy on estimates of the TCS parameters is demonstrated on the basis of the proposed approach for estimating the identifiability of TCS with cross-connections. The synthesis of adaptive algorithms of parameter estimation for TCSs with cross-connections based on input-output data is generalized to the case of interconnected systems. The results are applied to building models of tracking system and two-channel corrector for automatic control systems.
Conclusions. The features of adaptive identification of TCSs with identical channels, cross-connections and feedbacks are considered. The conditions for the TCS identifiability are obtained. Adaptive algorithms for estimating TCS parameters are synthesized. The proposed approach is generalized to the case of nonidentical channels and multi-connected systems. The exponential dissipativity of the adaptive identification system is verified. The proposed methods can be used in the development of systems for identification and control of complex dynamic systems.
- The theory developed in this paper supports the unambiguous description of the transverse distributions of the stationary electric field in planar symmetrical three-layer waveguides in an explicit analytical form.
- The results extend the understanding of the physical properties of non-linear waves and the localization patterns of light beams in distributed media, and may be useful in the design of various optical waveguide devices.
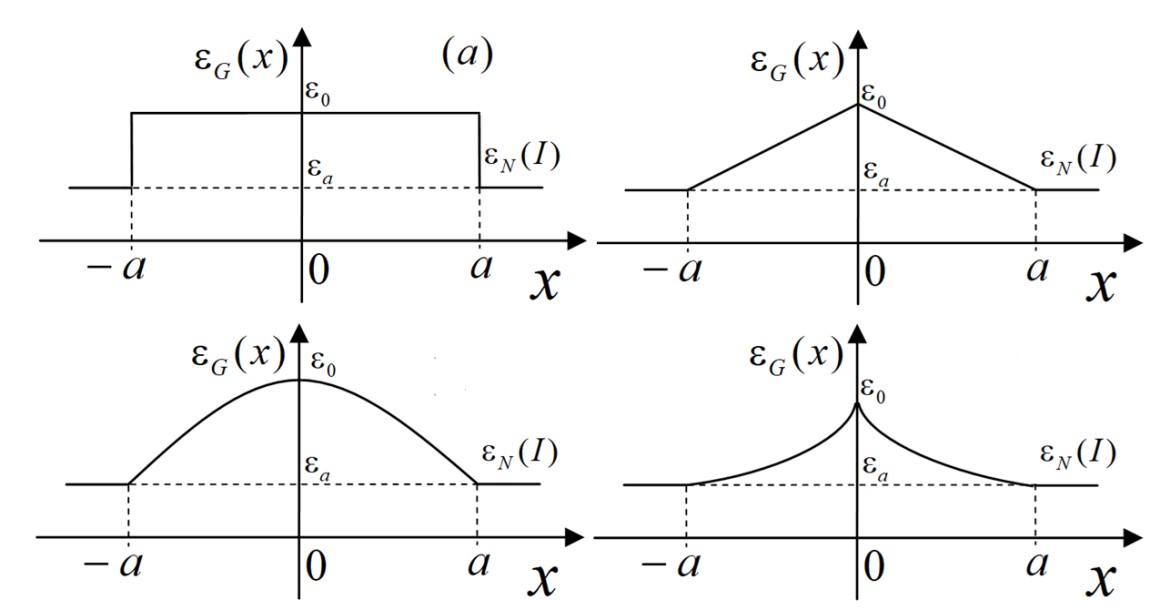
Objectives. Determining the patterns of dispersion properties of waveguide modes of the optical range in layered media with distributed optical properties is a both a pressing and significant matter for study. It has fundamental and applied importance in nonlinear optics and optoelectronics. The combination of a nonlinear response and gradedindex distributions of the optical properties of adjacent layers of a layered structure enables the desired values of the output characteristics using a wide range of control parameters to be selected easily. This renders such waveguides the most promising from the point of view of possible technical applications. The aim of this paper is to develop the theory of three-layer planar waveguide structures with a graded-index core and nonlinear optical liners with arbitrary profiles. By doing so it may be possible to find exact analytical solutions to nonlinear stationary wave equations describing explicitly the transverse electric field distribution of waveguide modes.
Methods. The analytical methods of mathematical physics and the theory of special functions applied to nonlinear and waveguide optics are used herein.
Results. The study provides a theoretical description of transverse stationary waves propagating along a symmetrical three-layer planar waveguide structure consisting of the inner graded-index layer sandwiched between nonlinear optical plates. It assumes an arbitrary spatial profile of the interlayer dielectric constant and the nature of the nonlinear response of the liner medium. The mathematical model of this waveguide structure formulated herein is based on nonlinear equations with distributed coefficients. The solutions obtained describe in general terms the transverse distribution of the amplitude of the electric field envelope. The transverse symmetry of the three-layer waveguide structure enables even and odd stationary modes corresponding to symmetric and antisymmetric transverse field profiles to be excited in it. A method was developed for constructing even (symmetric) and odd (antisymmetric) solutions which exist at certain discrete values of the effective refractive index/propagation constant. These discrete spectra were obtained in layers with graded-index linear, parabolic, and exponential profiles. The symmetrical threelayer waveguide structure with inner graded-index layer characterized by parabolic spatial profile and outer liners as Kerr nonlinear optical media is analyzed in detail, as an example of the application of the formulated theory. Analysis of the resulting exact analytical solution indicates that the electric field strength for the fundamental and first-order modes increases with increasing parabolic profile parameter, characterizing the relative change of the dielectric constant in the interlayer, while decreasing for higher order modes.
Conclusions. The theory developed in this paper supports the unambiguous description of the transverse distributions of the stationary electric field in planar symmetrical three-layer waveguides in an explicit analytical form. The results extend the understanding of the physical properties of nonlinear waves and the localization patterns of light beams in distributed media, and may be useful in the design of various optical waveguide devices.
ECONOMICS OF KNOWLEDGE-INTENSIVE AND HIGH-TECH ENTERPRISES AND INDUSTRIES. MANAGEMENT IN ORGANIZATIONAL SYSTEMS
- The nonlinear aggregation methodology to quality indicators obtained by decomposing the system is described with the further calculation of a single indicator that takes all the essential initial parametric indicators into account.
- The decomposition of complex systems to the level of elementary relationship subsystems more adequately reflects interrelated phenomena in a complex system.
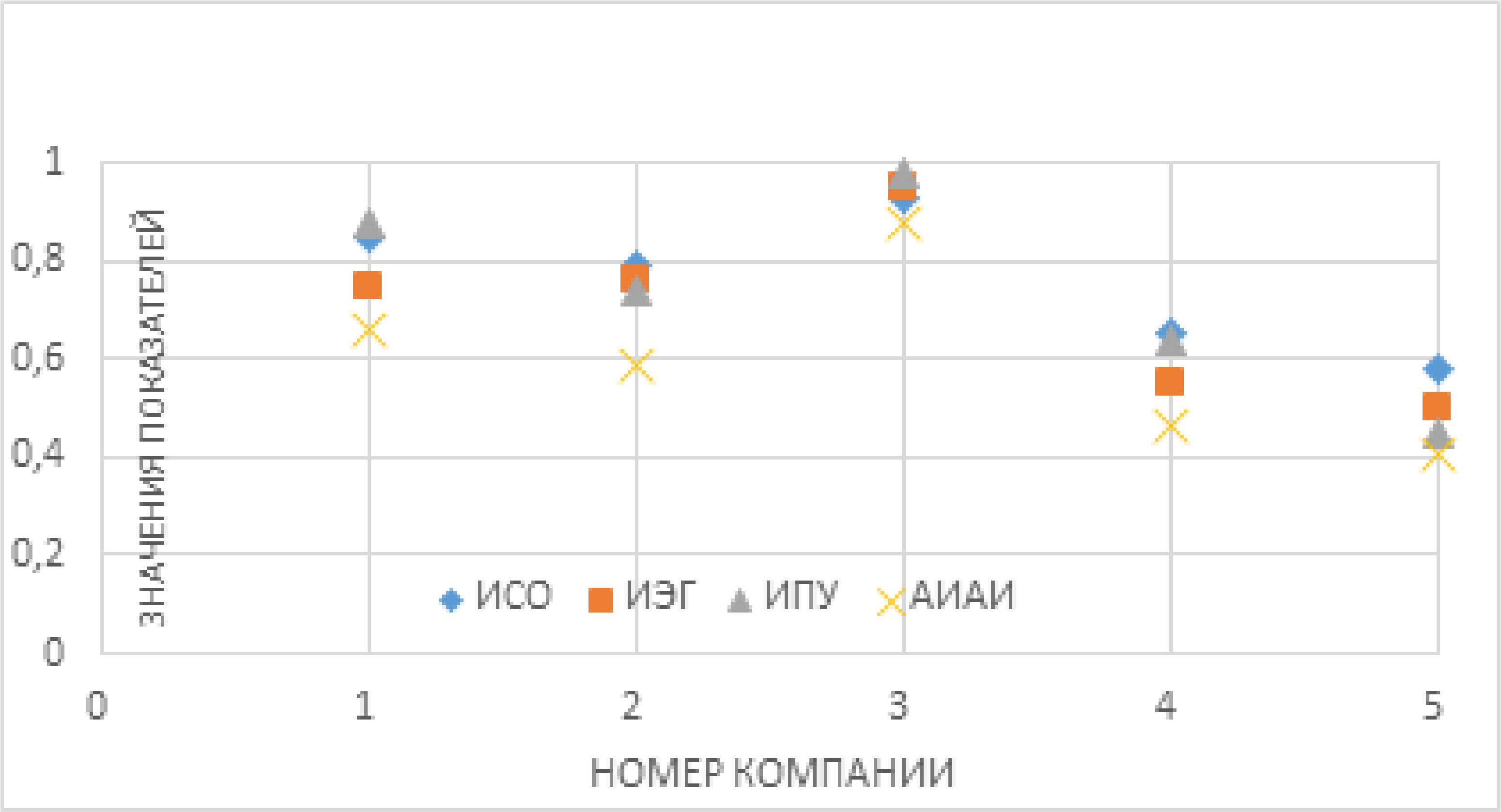
Objectives. Due to the need for prompt and rational assessment of service quality within the framework of complex IT projects, including infrastructure servicing and maintenance, which often involve a large number of identical or similar iterations, it becomes necessary to develop novel analysis methods based on nonlinear aggregation of indicators. As a result of changes in the structure of the process, territorial remoteness, automation, informatization, and the emergence of big data, the use of existing assessment methods often becomes impossible or labor-intensive. The purpose of the present work is to develop an approach to assessing the quality of work (services) in the framework of IT projects based on nonlinear aggregation of indicators.
Methods. The proposed approach to assessing service quality within IT projects is based on nonlinear aggregation of a number of indicators involving a preliminary decomposition of the system into private indicators. In order to meet the requirements of the decomposition process, service quality indicators must fully characterize the properties of the service as a whole at the different stages of its life cycle.
Results. The application of the proposed nonlinear aggregation methodology to quality indicators obtained by decomposing the system is described with the further calculation of a single indicator that takes all the essential initial parametric indicators into account. The decomposition of complex systems to the level of elementary relationship subsystems more adequately reflects interrelated phenomena in a complex system.
Conclusions. The practical application of the neural network parametric data aggregation model for assessing the quality of IT services is demonstrated. The use of an aggregated information and analytical indicator for assessing service quality increases the availability of analytical information for decision makers, reduces the dimension of analytical data, and improves the objectivity of the obtained generalized information.
PHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY
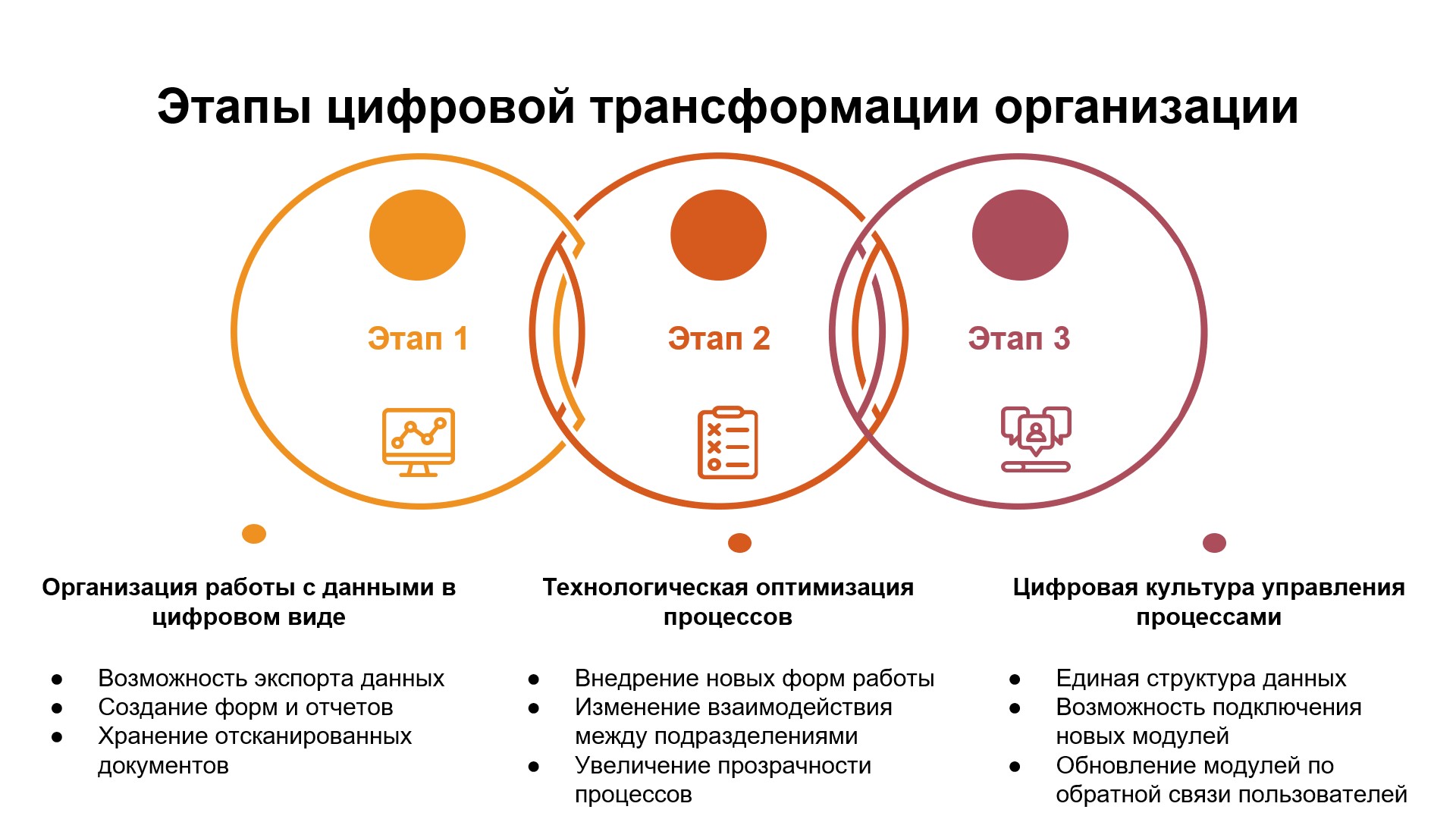
- The conceptual approach is proposed for setting goals and organizing the planning of digital transformation processes in education.
- As well as providing a detailed description of the major participants and components of the educational process, comprising students, teachers and educational programs, the article discusses data selection criteria.
- The development of a conceptual approach for creating a data-driven educational process management system at a university is becoming a priority task, whose successful execution will underpin further university advancement and competitiveness.
Objectives. The research aims to develop a conceptual approach to the digital transformation of university educational processes. The approach is based on a detailed analysis of the stages, participants, and components of the educational process at universities in order to develop a roadmap for digitalization and the development of a datadriven educational process management system. The main objectives of digital transformation are: (1) improve convenience for all groups of end users by providing access to data and operations with data related to the educational process; (2) increase the transparency of all components of the educational process; (3) release human and time resources by minimizing routine operations and improving the quality of decisions. The development of a data-driven educational process management system is based on digital culture principles of process management, which imply that the data collected in university systems are consistent, organized into a single structure. and stored in a form convenient for the development of new digital services. The development of tools for intelligent decision support and learning analytics is executed cooperatively by developers, analysts, and end users at all levels.
Methods. The research considers the work experience of the authors and their colleagues in Russian and international universities as users of information systems and services, developers of educational analytics services, and managers at various levels, as well as the stages of university digital transformation.
Results. The proposed conceptual approach increases comprehension by setting goals and organizing the planning of digital transformation processes in education. As well as providing a detailed description of the major participants and components of the educational process, comprising students, teachers and educational programs, the article discusses data selection criteria.
Conclusions. The development of a conceptual approach for creating a data-driven educational process management system at a university is becoming a priority task, whose successful execution will underpin further university advancement and competitiveness.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)