INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
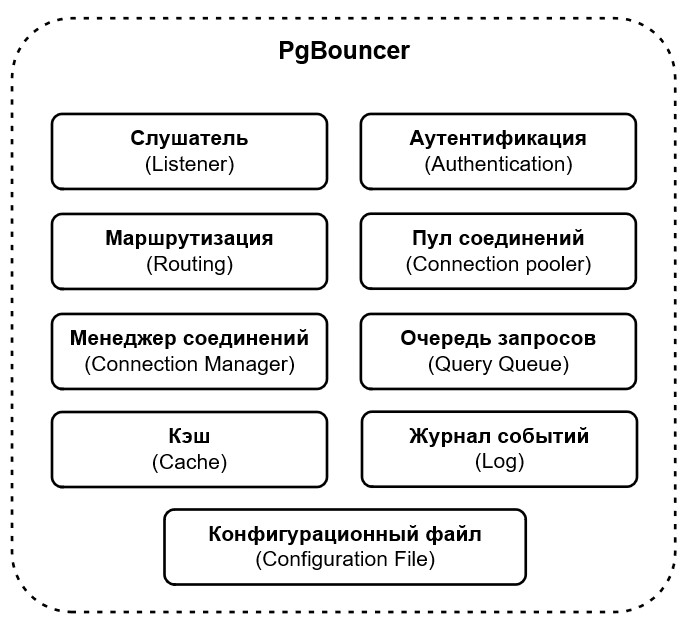
- The main features, architecture and modes of operation of the PgBouncer service are considered. Load testing was carried out on a virtual machine deployed on the basis of an open cloud platform with different configurations of computing resources (CPU, RAM) and according to several scenarios with different configurations and different numbers of balancer connections to the database, during which the following main indicators were investigated: distribution of processor usage, utilization of RAM, disk space, and CPU.
- A conclusion is presented on the usefulness of using the PgBouncer query balancer along with proposed configuration options for subsequent use in real installations.
Objectives. The aim of the research is to investigate the possibilities of using the PgBouncer connection pool with various configurations in modern database installations by conducting load testing with diverse real-world like scenarios, identifying critical metrics, obtaining testing results, and interpreting them in the form of graphs.
Methods. The research utilized methods of experimentation, induction, testing, and statistical analysis.
Results. The main features, architecture and modes of operation of the PgBouncer service are considered. Load testing was carried out on a virtual machine deployed on the basis of an open cloud platform with different configurations of computing resources (CPU, RAM) and according to several scenarios with different configurations and different numbers of balancer connections to the database, during which the following main indicators were investigated: distribution of processor usage, utilization of RAM, disk space, and CPU. The interpretation of the data obtained and the analysis of the results obtained by highlighting critical parameters are performed. On the basis of results analysis, conclusions and recommendations are formulated on the use of a connection balancer in real high-load installations for optimizing the resources utilized by the server on which the database management system (DBMS) is located. A conclusion is presented on the usefulness of using the PgBouncer query balancer along with proposed configuration options for subsequent use in real installations.
Conclusions. The degree of influence of the use of the PgBouncer connection balancer on the performance of the system as a whole deployed in a virtualized environment is investigated. The results of the work showed that the use of PgBouncer allows significantly optimization of the computing resources of a computing node for a DBMS server, namely, load on the CPU decreased by 15%, RAM—by 25–50%, disk subsystem—by 20%, depending on the test scenarios, the number of connections to the database, and the configuration of the connection balancer.
- An analysis of works in the field of investigation of computer incidents is presented. The terminology and main guiding documents on specifics of conducting information security incident investigations are described along with examples of digital artifacts defined in the form of classification.
- The expediency of forming criteria and indicators for assessing the quality of an information security incident investigation is substantiated.
- The suitability criterion and subsequent indicators for assessing the quality of the investigation are selected: the effectiveness (completeness) indicator for detecting digital artifacts by a computer criminologist is based on the conducted activities, resource intensity indicator, and promptness indicator for investigating an information security incident.
Objectives. The currently increasing number of targeted cyberattacks raises the importance of investigating information security incidents. Depending on the available means of protection, computer forensic experts use software and hardware tools for analyzing digital artifacts of various operating systems and network traffic to create an event chronology (timeline) of the incident. However, to date, there is no formal approach for assessing the effectiveness of expert activities when investigating an information security incident within the framework of a targeted cyberattack. The present study aims to develop partial indicators of promptness, effectiveness, and resource intensity as part of the suitability criterion for investigating an information security incident.
Methods. Methods informed by purposeful process efficiency and set theory are used along with expert evaluation approaches.
Results. An analysis of works in the field of investigation of computer incidents is presented. The terminology and main guiding documents on specifics of conducting information security incident investigations are described along with examples of digital artifacts defined in the form of classification. The expediency of forming criteria and indicators for assessing the quality of an information security incident investigation is substantiated. The suitability criterion and subsequent indicators for assessing the quality of the investigation are selected: the effectiveness (completeness) indicator for detecting digital artifacts by a computer criminologist is based on the conducted activities, resource intensity indicator, and promptness indicator for investigating an information security incident.
Conclusions. The obtained results can be used not only by heads of departments but also by rank-and-file information security professionals for objective analysis of the available software and human resources, the time spent on these activities, and the identified digital artifacts as part of a cyber incident investigation.
- Approaches to the analysis of computational problems involving the construction of a computational graph abstracted from the computing platform, but limited by a set of architectural solutions, are considered.
- The proposed design methodology based on a register transfer level (RTL) representation synthesizer of a computing device is limited to individual computing architectures for which the relevant circuit is synthesized and optimized based on a high-level input description of the algorithm.
- Among computing node architectures, a synchronous pipeline and a processor core with a tree-like arithmetic-logical unit are considered.
- The efficiency of a computing system can be increased by balancing the pipeline based on estimates of the technological basis, and for the processor—based on optimizing the set of operations, which is performed based on the analysis of the abstract syntax tree graph with its optimal coverage by subgraphs corresponding to the structure of the arithmetic logic unit.
Objectives. Following the completion of development stages due to transistor scaling (Dennard’s law) and an increased number of general-purpose processor cores (limited by Amdahl’s law), further improvements in the performance of computing systems naturally proceeds to the stage of developing specialized computing subsystems for performing specific tasks within a limited computational subclass. The development of such systems requires both the selection of the relevant high-demand tasks and the application of design techniques for achieving desired indicators within the developed specializations at very large scales of integration. The purpose of the present work is to develop a methodology for designing specialized computing systems based on the joint optimization of hardware and software in relation to a selected subclass of problems.
Methods. The research is based on various methods for designing digital systems.
Results. Approaches to the analysis of computational problems involving the construction of a computational graph abstracted from the computing platform, but limited by a set of architectural solutions, are considered. The proposed design methodology based on a register transfer level (RTL) representation synthesizer of a computing device is limited to individual computing architectures for which the relevant circuit is synthesized and optimized based on a high-level input description of the algorithm. Among computing node architectures, a synchronous pipeline and a processor core with a tree-like arithmetic-logical unit are considered. The efficiency of a computing system can be increased by balancing the pipeline based on estimates of the technological basis, and for the processor—based on optimizing the set of operations, which is performed based on the analysis of the abstract syntax tree graph with its optimal coverage by subgraphs corresponding to the structure of the arithmetic logic unit.
Conclusions. The considered development approaches are suitable for accelerating the process of designing specialized computing systems with a massively parallel architecture based on pipeline or processor computing nodes.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- An analysis of BER for the signal modulation method in 5G networks, which uses a bank of filters with multiple carriers with offset quadrature amplitude modulation under noise conditions, is presented. The resistance of the method to intra-cell, inter-cell, and inter-beam types of interference in the 5G channel, as well as additive white Gaussian noise, is investigated.
- The graphical and numerical data obtained through computer modeling demonstrates improved BER in 5G networks using FBMC-OQAM.
- The presented comparative analysis of error probability in the FBMC-OQAM system under various types of noise and interference emphasizes the impact of these factors on the quality of information transmission.
Objectives. The work sets out to evaluate the noise immunity of the signal modulation method in 5G networks using a filter bank multicarrier with offset quadrature amplitude modulation (FBMC-OQAM) and to analyze the bit error rate (BER).
Methods. In the work, probability theory and mathematical statistics methods are applied according to computer modeling approaches.
Results. An analysis of BER for the signal modulation method in 5G networks, which uses a bank of filters with multiple carriers with offset quadrature amplitude modulation under noise conditions, is presented. The resistance of the method to intra-cell, inter-cell, and inter-beam types of interference in the 5G channel, as well as additive white Gaussian noise, is investigated. The graphical and numerical data obtained through computer modeling demonstrates improved BER in 5G networks using FBMC-OQAM. The presented comparative analysis of error probability in the FBMC-OQAM system under various types of noise and interference emphasizes the impact of these factors on the quality of information transmission.
Conclusions. The FBMC-OQAM method is characterized by the low impact on the error probability of the data transmission system in 5G networks of various types of interference including intra-cell and inter-cell interference, inter-beam interference, and nonlinear distortions. However, it will be necessary to further optimize the method and develop algorithms for enhancing error probability in the FBMC-OQAM system under real conditions in 5G networks. The research results can be used in the development of 5G networks.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
- Using the Bruggeman effective medium approximation (EMA) to describe the optical and magneto-optical properties of nanocomposites on the example of Co-Al2O3, the characteristics of MRE are obtained, namely, the change in MRE for reflection and transmission of light at normal incidence and at the angle of incidence near the Brewster angle (below the percolation threshold) or the main angle of incidence for metals (above the percolation threshold), which enhances MRE.
- The advantage of the EMA is the ability to study magneto-optical spectra in the range of average volume concentrations of the metal component.
Objectives. To investigate the magnetorefractive effect (MRE) in nanocomposites, which consists in changing the reflection, transmittance and light absorption coefficients of samples with large magnetoresistance (MR) upon their magnetization. Materials offering high magneto-optical activity and significant MR include magnetic nanocomposites. These materials are based on a polymer matrix, which includes inorganic magnetic particles, fibers or layered particles, whose nanometer sizes range from 1 to 100 nm in at least one dimension. The main purpose of creating such nanocomposites is to combine the special properties of several components in one material. The presence in such materials of gigantic, colossal and tunneling MR, as well as the giant anomalous Hall effect, is of practical interest. Uses range from magnetic recording, light modulation, and receivers for thermal radiation, while the MRE itself is a promising method for the non-destructive testing of any nanostructures, e.g., measuring MR.
Methods. The use of effective medium theory to describe the optics and magneto-optics of dispersed media provides a means to determine the complex permittivity of a medium through the permittivity of its constituent components or vice versa. The present work considers the example of a Co-Al2O3 nanocomposite with a concentration of ferromagnetic metal Co 0.4 near the percolation threshold. This particular case was considered for study, since all the properties of nanocomposites change dramatically near the percolation threshold.
Results. Using the Bruggeman effective medium approximation (EMA) to describe the optical and magneto-optical properties of nanocomposites on the example of Co-Al2O3, the characteristics of MRE are obtained, namely, the change in MRE for reflection and transmission of light at normal incidence and at the angle of incidence near the Brewster angle (below the percolation threshold) or the main angle of incidence for metals (above the percolation threshold), which enhances MRE. The advantage of the EMA is the ability to study magneto-optical spectra in the range of average volume concentrations of the metal component.
Conclusions. The obtained values correspond well to the known experimental data. Moreover, the described approach can be used to study any nanostructures.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- The 2D-DoA sequential algorithm of azimuth and elevation estimation is proposed. The comparative analysis results for the developed algorithm and classical 2D Capon method based on numerical simulation using Monte Carlo method are presented.
- The proposed scheme of DoA estimation for coherent signal processing of distributed radars is shown to lead to an improvement of the main considered metrics representing the probability of correctly estimating the number of targets, mean square error, and square error compared to a single radar system.
- The proposed low-computational algorithm shows the gain in complexity compared to full 2D Capon algorithm.
Objectives. One of the main tasks of radiolocation involves the problem of increasing spatial resolution of the targets in the case of limited aperture of the radar antenna array and short length of time samples (snapshots). Algorithms must be developed to provide high angular resolution and low computational complexity. In order to conform with the existing Advanced Driver Assistance Systems requirements, modern cars are equipped with more than one radar having a common signal processing scheme to improve performance during target detection, positioning, and recognition as compared to a single radar. The present study aims to develop a two-dimensional Direction-of-Arrival algorithm with low computation complexity as part of distributed coherent automotive radar system for cases involving short time samples (snapshots).
Methods. A virtual antenna array formation algorithm is formulated according to the two-dimensional Capon method. A proposed modification of two-dimensional Capon algorithm is based on sequentially estimating the directions of arrival for the distributed radar system. The Monte Carlo method is used to compare the effectiveness of the considered algorithms.
Results. The 2D-DoA sequential algorithm of azimuth and elevation estimation is proposed. The comparative analysis results for the developed algorithm and classical 2D Capon method based on numerical simulation using Monte Carlo method are presented. The proposed scheme of DoA estimation for coherent signal processing of distributed radars is shown to lead to an improvement of the main considered metrics representing the probability of correctly estimating the number of targets, mean square error, and square error compared to a single radar system. The proposed low-computational algorithm shows the gain in complexity compared to full 2D Capon algorithm.
Conclusions. The proposed two-stage algorithm for estimating the directions of arrival of signals in azimuth and elevation planes can be applied to the distributed system of coherent radars with several receiving and transmitting antennas representing multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radars. The algorithm is based on sequentially estimating the directions of arrival, implying estimation in the azimuthal plane at the first stage and estimation in the vertical plane at the second stage. The performance of a coherent radar system with limited antenna array configuration of separate radar is close in characteristics to a high-performance 4D-radar with a large antenna array system.
- The power law observed in practice for the dependence of the stationary probability density of news distribution by the number of comments can be obtained from solving the stationary Fokker–Planck equation, while the non-stationary equation can be used to describe processes in complex network structures.
- The vector representation can be used to describe the comment network states of news media users. Achieving or implementing desired or not desired states of the whole social network can be specified on the basis of base vectors. By solving the non-stationary Fokker–Planck equation, an equation is obtained for the probability density of transitions between system states per unit time, which agree well with the observed data.
- Analysis of the resulting model using the characteristics of the real time series to change the graph of comments of users of the RIA Novosti portal and the structural parameters of the graph demonstrates its adequacy.
Objectives. The study aims to theoretically derive the power law observed in practice for the distribution of characteristics of sociodynamic processes from the stationary Fokker–Planck equation and apply the non-stationary Fokker–Planck equation to describe the dynamics of processes in social systems.
Methods. During the research, stochastic modeling methods were used along with methods and models derived from graph theory, as well as tools and technologies of object-oriented programming for the development of systems for collecting data from mass media sources, and simulation modeling approaches.
Results. The current state of the comment network graph can be described using a vector whose elements are the average value of the mediation coefficient, the average value of the clustering coefficient, and the proportion of users in a corresponding state. The critical state of the network can be specified by the base vector. The time dependence of the distance between the base vector and the current state vector forms a time series whose values can be considered as the “wandering point” whose movement dynamics is described by the non-stationary Fokker–Planck equation. The current state of the comment graph can be determined using text analysis methods.
Conclusions. The power law observed in practice for the dependence of the stationary probability density of news distribution by the number of comments can be obtained from solving the stationary Fokker–Planck equation, while the non-stationary equation can be used to describe processes in complex network structures. The vector representation can be used to describe the comment network states of news media users. Achieving or implementing desired or not desired states of the whole social network can be specified on the basis of base vectors. By solving the non-stationary Fokker–Planck equation, an equation is obtained for the probability density of transitions between system states per unit time, which agree well with the observed data. Analysis of the resulting model using the characteristics of the real time series to change the graph of comments of users of the RIA Novosti portal and the structural parameters of the graph demonstrates its adequacy.
- The study set out to compare the forecasting quality of time series models that describe the trend in different ways and to form a conclusion about the applicability of each approach in describing the trend depending on the properties of the time series.
- Since the LOESS method for groups of seasonal and non-seasonal series gives the best results for all indicators, this method can be recommended for obtaining the most accurate results for series of different nature.
- Trend modeling using Fourier series decomposition leads to quite accurate results for time series of different natures. For seasonal series, one of the best results is given by the combination of modeling a trend on the basis of a polynomial and seasonality in the form of the ARIMA model.
Objectives. The study set out to compare the forecasting quality of time series models that describe the trend in different ways and to form a conclusion about the applicability of each approach in describing the trend depending on the properties of the time series.
Methods. A trend can be thought of as the tendency of a given quantity to increase or decrease over the long term. There is also an approach in which a trend is viewed as some function, reflecting patterns in the behavior of the time series. In this case, we discuss the patterns that characterize the behavior of the series for the entire period under consideration, rather than short-term features. The experimental part involves STL decomposition, construction of ARIMA models (one of the stages of preparation for which includes differentiation, i.e., removal of the trend and transition to a weakly stationary series), construction of ACD models (average conditional displacement) and other approaches. Time-series models based on various trend models are compared with respect to the value of the maximum likelihood function. Many of the combinations have not been constructed before (Fourier series as a trend model, combination of ACD model for trend with seasonal models). Example forecasts of macroeconomic statistics of the Russian Federation and stock prices of Sberbank on the Moscow Exchange in the time range of 2000–2021 are presented.
Results. In the experiments, The LOESS method obtained the best results. A combination of polynomial model for trend description and ARIMA for seasonally description and combination of ACD algorithm for trend and ETS for seasonal model obtained good forecasts in case of seasonal time series, while Fourier time series as a trend model also achieved close quality of prediction.
Conclusions. Since the LOESS method for groups of seasonal and non-seasonal series gives the best results for all indicators, this method can be recommended for obtaining the most accurate results for series of different nature. Trend modeling using Fourier series decomposition leads to quite accurate results for time series of different natures. For seasonal series, one of the best results is given by the combination of modeling a trend on the basis of a polynomial and seasonality in the form of the ARIMA model.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)