INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
An analysis of links between the academic discipline program and key entities of the educational process is presented. The functionality of the self-developed academic discipline program module for implementing at RTU MIREA is aimed at providing interconnection, transparency, and availability of links between academic discipline parameters and its sections.
Objectives. The need to apply methods and models to support the educational process at universities including the formation and management of academic discipline programs (ADPs) is determined by the growing need for the active implementation of various automation tools including integrated information systems, which arise in response to a number of regulatory and legal factors. Such social factors result in the significant increase in the volume and categories of information circulating within business processes of an educational organization, as well as the expansion of the requirements for ensuring the protection, storage, and transmission of information. In recent years, the Government of the Russian Federation has approved the national “Digital Economy” and “Education” projects (including the Federal Project “Digital Educational Environment”) emphasizing the growing role of informatization and digitalization processes in education. In this connection, an obvious discrepancy arises between the theoretical characteristics of information flows existing in educational organizations and the methods of its collection, processing, storage, analysis, and application used in practice. One of the most important conceptual components of the educational process in higher education institutions is the ADP, which organizes the relationship between various components of the educational process: curriculum, competencies, training areas, learning technologies, and methods for conducting the control check of students’ knowledge. The labor-intensive and variable nature of ADP development and implementation requires the introduction of information technologies. Thus, the aim of the present work is to analyze the volume and structure of institutional educational programs in order to identify the necessary software requirements.
Methods. The classification of learning management systems according to various criteria, key requirements for academic disciplines, and ADP structure is considered.
Results. An analysis of links between the ADP and key entities of the educational process is presented. The functionality of the self-developed ADP module for implementing at RTU MIREA is aimed at providing interconnection, transparency, and availability of links between academic discipline parameters and its sections.
Conclusions. Introducing the ADP module allows reducing the time spent on developing the program by providing universal templates of academic disciplines, along with the possibility of autofilling the academic discipline parameters and tracking the current status of ADPs, as well as increasing the level of awareness of participants in the educational process.
MULTIPLE ROBOTS (ROBOTIC CENTERS) AND SYSTEMS. REMOTE SENSING AND NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
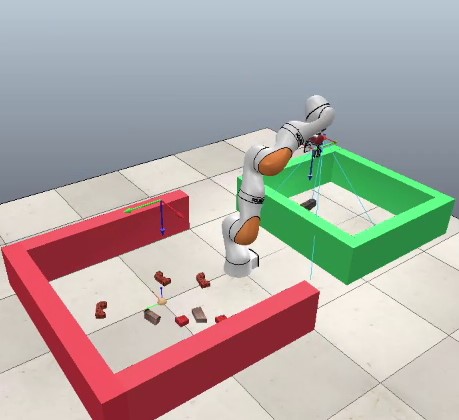
- The possibility of using a continuous genetic algorithm is analyzed in the problem of grasping an object of an a priori unknown shape avoiding collisions with other objects of a static scene.
- A complex scene analysis algorithm and implementation of a continuous genetic algorithm are presented for finding the target position of the gripper of a Kuka LBR iiwa 7 R800 robotic control system with redundant kinematics.
Objectives. The problem of providing the interaction of a robotic manipulator with a priori unknown objects in a given workspace is of great interest both to the research community and many industries. By developing a solution to this problem, it will be possible to reduce the time taken for robots to adapt to new environments and objects therein. One of the primary stages of providing the interaction of the robotic manipulator with objects is the search for the target position of the robot gripper based on the onboard sensor subsystem, which can be carried out by a number of methods. Methods associated with machine learning and self-learning technologies may not be suitable for some applications (for example, during rescue operations) when it is necessary to quickly search for the target position of the gripper for an a priori unknown object, about which there is no relevant information in the robot database. Therefore, for this problem, heuristic approaches – for example, genetic algorithms – seem to be applicable. The objectives of this work are to implement a search based on a continuous genetic algorithm for the target position of the robot gripper including collision avoidance and study its performance under virtual simulation.
Methods. A heuristic search algorithm (continuous genetic algorithm) is used. The complex scene analysis algorithm uses classical image processing methods. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the algorithm, virtual simulation is used.
Results. The possibility of using a continuous genetic algorithm is analyzed in the problem of grasping an object of an a priori unknown shape avoiding collisions with other objects of a static scene. A complex scene analysis algorithm and implementation of a continuous genetic algorithm are presented for finding the target position of the gripper of a Kuka LBR iiwa 7 R800 robotic control system with redundant kinematics. The results of an experimental virtual simulation of the obtained algorithm are presented.
Conclusions. The conducted research demonstrates the effectiveness of the continuous genetic algorithm in obtaining the target position of the gripper of the robotic manipulator under conditions when the static scene represents randomly located objects of various shapes.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- An expression for gain in a hydroacoustic communication channel has been obtained.
- A novel expression derived for the spectral level of sea noise caused by sea surface waves is based on piecewise linear approximation of the curves of the spectral levels of noise obtained from four sources: turbulence, shipping, sea waves, and the thermal noise of the sea.
- Dependencies of the hydroacoustic channel capacity on communication distance, intensity of the transmitted signal, and sea state, are characterized.
- The definition of the optimal spectrum itself is determined along with the lower and upper boundary frequencies of the optimal spectrum of the transmitted signal.
- The dependence of the bandwidth usage on the intensity of the input signal at various communication distances has been investigated.
Objectives. Capacity, describing the maximum rate of information transmission, is an important characteristic of any communication channel. The main purpose of this work isto determine the capacity of a hydroacoustic communication channel with constrained average intensity of the transmitted signal. An additional aim consists in finding the optimal spectrum of a transmitted signal and calculate its boundary frequencies. A model of a single-path channel was considered, which is characteristic of the deep sea with the receiver or transmitter placed at a sufficient depth.
Methods. Concepts of applied hydroacoustics, the theory of random processes, and information theory were used.
Results. An expression for gain in a hydroacoustic communication channel has been obtained. A novel expression derived for the spectral level of sea noise caused by sea surface waves is based on piecewise linear approximation of the curves of the spectral levels of noise obtained from four sources: turbulence, shipping, sea waves, and the thermal noise of the sea. Dependencies of the hydroacoustic channel capacity on communication distance, intensity of the transmitted signal, and sea state, are characterized. The definition of the optimal spectrum itself is determined along with the lower and upper boundary frequencies of the optimal spectrum of the transmitted signal. The dependence of the bandwidth usage on the intensity of the input signal at various communication distances has been investigated.
Conclusions. On the basis of the Francois–Garrison attenuation coefficient, channel capacity was correlated with the parameters of the marine environment: temperature, salinity, and pH in the study area. At a given intensity of the input signal, channel capacity was shown to decrease significantly with increasing distance and sea wave intensity. It is also shown that the width of the optimal spectrum decreases with increasing distance. Sea wave noise was noted to affect significantly the shape of the optimal spectrum and its boundary frequencies. The possibility of cases where bandwidth usage increases with increasing distance at a given input signal intensity cannot be ruled out.
- Synthesis and analysis of the optimal algorithm for receiving multiple phase shift keying and quadrature amplitude modulation signals with incoherent processing of harmonic interference were carried out.
- In addition to calculating the correlation integrals in the receiver, it is necessary to form weight coefficients, whose value depends on the correlation of the interference oscillation (extracted from the received mixture) with a sample of the interference stored in the receiver.
- The dependences of the bit error probability on the signal-to-noise ratio, interference detuning, and inaccuracy in setting the frequency and level of the interference sample in the receiver were obtained.
- It is shown that the higher the gain in the noise immunity of reception, the greater the intensity of the harmonic interference.
Objectives. Analysis of the reception noise immunity of multiple phase shift keying (M-PSK) and quadrature amplitude modulation (M-QAM) signals has demonstrated a significant reduction in the quality of reception of discrete information due to the presence of various types of non-fluctuating interference in a radio communication channel including targeted harmonic interference. Therefore, the development of algorithms for compensating the influence of such forms of interference is an urgent task. While various methods for combatting this kind of interference, these vary in terms of their effectiveness. The aim of the present work is to synthesize and analyze the optimal algorithm for the reception of M-PSK and M-QAM signals with incoherent processing of harmonic interference.
Methods. Various statistical radio engineering and computer simulation methods were used in accordance with optimal signal reception theory.
Results. Synthesis and analysis of the optimal algorithm for receiving M-PSK and M-QAM signals with incoherent processing of harmonic interference were carried out. In addition to calculating the correlation integrals in the receiver, it is necessary to form weight coefficients, whose value depends on the correlation of the interference oscillation (extracted from the received mixture) with a sample of the interference stored in the receiver. The dependences of the bit error probability on the signal-to-noise ratio, interference detuning, and inaccuracy in setting the frequency and level of the interference sample in the receiver were obtained. It is shown that the higher the gain in the noise immunity of reception, the greater the intensity of the harmonic interference.
Conclusions. The synthesized receiver circuit effectively compensates for harmonic interference. However, the efficiency of its operation depends on the detuning of the harmonic interference relative to the center frequency of the spectrum of the useful signal. The scheme for incoherent processing of harmonic interference remains operational even with small (within ±10%) inaccuracies in setting the frequency and the level of the interference copy in the receiver.
- The influence of various methods for ensuring the redundancy of transponder devices and the use of more reliable components on the reliability and durability indicators is considered.
- A gamma-percentage resource-based technique for determining the durability indicator based on the constructed mathematical models of the probability of failure-free operation is presented along with a comparative analysis of measures to increase the gamma-percentage resource of the transponder.
Objectives. Since the launch of satellite communication systems in practical use, approaches towards enhancing their operational quality and durability have been developing in the direction of increased reliability of airborne transponders. This is mainly achieved by increasing redundancy and using components with a lower failure rate. In this regard, the creation of new technologies and new materials is a particularly promising direction. However, since durability testing of complex systems can take several years, the problem of ensuring an effective combination of redundancy methods and elements having a reduced failure rate remains challenging. The purpose of the work is to analyze the effectiveness of methods for ensuring the reliability of a communication satellite transponder based on a proposed methodology for determining the durability index using a mathematical model of the probability of failure-free operation.
Methods. In order to describe the complex structure of a satellite communication system transponder, a logical- probabilistic method is used, in which the dependence of the system reliability indicators on the reliability indicators of the transponder elements is formulated as a logical function of operability. Mathematical models of system reliability are created on this basis including for redundant systems. Graphs and analytical methods are used to compare different systems.
Results. The influence of various methods for ensuring the redundancy of transponder devices and the use of more reliable components on the reliability and durability indicators is considered. A gamma-percentage resource-based technique for determining the durability indicator based on the constructed mathematical models of the probability of failure-free operation is presented along with a comparative analysis of measures to increase the gamma-percentage resource of the transponder.
Conclusions. The presented method for determining the durability index using a mathematical model of the probability of no-failure operation can be used to determine the time interval within which redundancy increases the probability of no-failure operation as compared with a decrease in the failure rate of elements. On this basis, the most effective combination of redundancy methods and approaches for reducing the failure rate of elements can be identified.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- An algorithm for finding k-shortest paths in contourless directed graphs having a strict order relation was developed.
- Abstract elements were defined according to group theory in graphs as p-contours, between which a multilevel structure of relations for implementing the necessary search of paths was then established.
- For substantiating the efficiency of the constructed algorithm, the validity of the main provisions was demonstrated as follows: firstly, the multilevel system of relations is exhaustive; secondly, there is no loss in the final solution during the operation of the algorithm; thirdly, the paths obtained as a result of the work of the algorithm satisfy the main required relation between them.
- Numerically, the algorithm was implemented by the dynamic programming method.
Objectives. Network diagrams are used as an information support element in planning and project management processes for structuring planned work and calculating project efficiency characteristics. In order to optimize and balance resources used in projects, it becomes necessary to locate in these models not only the critical path of the maximum weighted length, but also the subcritical paths closest to it having a shorter length in relation to it. The aim of the work is to synthesize and analyze an algorithm for finding k-shortest paths between the input and output network vertices, on which basis the above-mentioned subcritical paths can be identified.
Methods. The provisions of graph theory and group theory, as well as the method of dynamic programming, were used.
Results. An algorithm for finding k-shortest paths in contourless directed graphs having a strict order relation was developed. Abstract elements were defined according to group theory in graphs as p-contours, between which a multilevel structure of relations for implementing the necessary search of paths was then established. For substantiating the efficiency of the constructed algorithm, the validity of the main provisions was demonstrated as follows: firstly, the multilevel system of relations is exhaustive; secondly, there is no loss in the final solution during the operation of the algorithm; thirdly, the paths obtained as a result of the work of the algorithm satisfy the main required relation between them. Numerically, the algorithm was implemented by the dynamic programming method extended by means of an additional functional relationship, implying the presence of suboptimal policies.
Conclusions. The conducted runs of computational experiments confirmed the operability and efficiency of the software-implemented algorithm. The performed analysis demonstrated the good convergence characteristics of the proposed algorithm as compared with other algorithms of this class applied to network diagrams. On this basis, it can be recommended for practical use in project management information systems.
ECONOMICS OF KNOWLEDGE-INTENSIVE AND HIGH-TECH ENTERPRISES AND INDUSTRIES. MANAGEMENT IN ORGANIZATIONAL SYSTEMS
The approach to the formation of a metastructure of production process digital twin (PPDT) based on the models of production facilities and their relationships is substantiated. The procedure and rules for constructing a PPDT system model are developed along with an approach to the structural and parametric identification of DT models, taking logical and semantic restrictions into account.
Objectives. A methodology currently being developed for generalizing and presenting knowledge about studied subject-oriented areas is based on a “model hypothesis” for determining the distinguished objects and their relationships. Such system models can be used in any information system to define the knowledge about subject-oriented areas. Systems engineering methods already make it possible to create information models of real objects supplemented by virtual components, and vice versa, i.e., models of virtual objects supplemented by real components. So, for example, the availability of information models of technological and production facilities and their connections with real equipment allow the creation and management of real-virtual production processes (PP) in accordance with Industry 4.0 methodologies. From a theoretical aspect, the development of system models of objects and their connections in subject-oriented areas is based on the problem of a formal consistent description (grammatical calculus) of the functional regularities of a given set of objects and their relationships. The purpose of the study is to develop an approach and principles of methodology for system modeling of production facilities and their connections to provide closed-loop control (forecasting, planning, accounting, regulation, etc.) in the production environments of machinery enterprises taking the form of their digital twins (DTs).
Methods. The basic provisions of the theory of sets and graph theory—in particular, the provisions of the theory of categories of sets—are used according to the formal logic and control theories. System Engineering methods are also applied in the organization and management of machinery production.
Results. The approach to the formation of a metastructure of production process digital twin (PPDT) based on the models of production facilities and their relationships is substantiated. The procedure and rules for constructing a PPDT system model are developed along with an approach to the structural and parametric identification of DT models, taking logical and semantic restrictions into account.
Conclusions. A presented example for identifying the basic set of objects of the organization of the PPDT based on the logical-semantic analysis of production activities and the provisions of the unified standards of the unified system for technological preparation of production of machinery production as a researched subject area confirms the main provisions of the proposed methodology for constructing the PPDT.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)