MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- This article describes a manufacturing technology and the possibility of forming fused multiplexers with low bending losses and optical isolation up to 20–22 dB.
- Possible mechanisms of the influence of twisting of the multiplexer fiber leads on the optical channel isolation are considered.
- The results obtained show that when mechanical stresses occur in the fused structure of the multiplexer, the change in the optical isolation factor at two operating wavelengths does not exceed 1 dB.
Objectives. One of the topical tasks in the development of radio electronic systems for various purposes is a sharp increase in the volume and data transfer rate between the elements of the system. This problem is most successfully solved using fiber optic technology, which has no alternative to meet a number of indicators. The use of optical fibers (OF) as a physical medium made it possible to transfer large information flows over considerable distances. Increasing the capacity of communication systems is pushing manufacturers to develop new OF brands with improved optical and operational characteristics, which makes it possible to improve various optical components that use an OF as an active information transmission medium. The dual-channel single-mode wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) multiplexers/demultiplexers, which are one of spectral selective splitters types, are most widely used in fiber-optic communication systems. Among the advantages of WDM, it is worth to note the transmission of a large amount of information over one OF by the arrangement of channels at different wavelengths and the ability to transmit signals of several wavelengths simultaneously in both directions via one OF that do not interact with each other (duplex communication). During operation, WDM multiplexers can be subjected to various external influences that affect the operation and stability of the device parameters. Currently, there are no data on the effect of OF bending on the optical characteristics of WDM multiplexers. In this regard, it is important to study this dependence, which includes measuring the parameters of optical isolation and insertion loss. The purpose of the study is to work out the manufacturing technology and investigate the manufactured WDM multiplexers based on certain types of bend-resistant OF.
Methods. For the formation of two-channel WDM multiplexers, the technology of fused biconical tapering was used, which makes it possible to achieve low insertion loss along with a high degree of channel isolation in the wide temperature range.
Results. In the paper, the possibilities of manufacturing fiber multiplexers based on bend-resistant fiber Corning SMF-28 Ultra were discussed. The results of manufacturing and studying the experimental samples of WDM multiplexers optical characteristics were presented. It was established that the use of SMF-28 Ultra quartz fiber made it possible to significantly reduce the deviation of the channel optical isolation in the event of mechanical stresses in the multiplexers OF structure.
Conclusions. The possibility of creating two-channel multiplexers with low bending losses and optical isolation up to 20–22 dB was experimentally shown. Possible mechanisms of the influence of the multiplexer fiber twisting on the optical isolation of channels were considered. The results obtained showed that when mechanical stresses in the fused structure of the multiplexer occur, the change in the optical isolation coefficient at two operating wavelengths does not exceed 1 dB.
- In connection with the pandemic and the massive transfer of employees to remote work, workplaces (WP) with PCs that do not meet environmental safety standards are used in residential premises. On the PC WM, electromagnetic fields (EMF) induced by electric single-phase networks of the TN type significantly exceed the maximum permissible levels laid down in the Russian sanitary norms and rules.
- In residential buildings, we recommend using IT (TT) type electrical networks, two-phase, symmetrical with a low level of EMF impact on people, which are effectively used in industrial enterprises.
Objectives. The aim of this paper is to analyze the electromagnetic safety of 50Hz industrial frequency electrical networks in residential buildings when using workplaces equipped with personal computers (PCs), as well as to develop recommendations on reducing the impact of levels of industrial frequency electromagnetic fields on human health in residential premises.
Methods. Electromagnetic fields in residential premises with the single-phase TN mode industrial frequency power supply system regulated by the Rules of Electrical Installations Design were measured and calculated in accordance with Russian and international legislative documents.
Results. It was established that electromagnetic fields induced by TN networks in workplaces equipped with PCs might increase significantly and even exceed the maximum permissible level of 25 V/m and 0.25 μT recommended by Sanitary and Epidemiological Standards. Residential buildings are not subject to the requirements of the Energy Supervision services; therefore, any unprofessional modification of electrical networks in residential premises, including the use of unapproved extension cords, may result in sparking, high-frequency harmonics, and, in turn, conditions which impact human health, as well as electric injures, fires, and gas explosions.
Conclusions. It has been shown that IT (TT) mode symmetrical two-phase electrical networks may function efficiently for decades without accidents and effects of industrial frequency electromagnetic field on humans, as they are used in medical institutions, defense enterprises, and state institutions. Thus, legislative transition to installing IT (TT) systems in residential buildings, replacement of existing TN power supply systems with IT (TT) system, and legislative strengthening of requirements for household protection and commutation devices, may also be required to reduce man-made disaster risks in residential buildings.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
- Piezoelectric force microscopy is used to analyze the features of the distribution of local piezoelectric parameters near a submicron air channel in perforated ferroelectric Ba8Sr0.2TiO3 films when an electric field is applied in the film plane.
- The effect of a defective layer formed under the action of a focused ion beam on the parameters of the piezoresponse was discussed.
- It was shown that the piezoelectric tensor components in the gap between the channels increase significantly compared to the non-perforated film.
Objectives. Focused ion beam etching remains one of the most common methods for fabricating 2D photonic crystals and structures based on functional materials. This technique is quite well developed for semiconductors. But at the same time, the change in the properties of ferroelectric materials under the action of a focused ion beam, including parameters of distribution and switching of the polarization state under the action of an electric field, remains poorly studied. The purpose of this work is to determine the local piezoelectric parameters in perforated ferroelectric films of barium strontium titanate (Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3) with ordered vertical air channels fabricated by focused ion beam etching.
Methods. Experimental studies were conducted using piezoresponse force microscopy under applied electric field in planar geometry.
Results. It is shown that the perforation of a ferroelectric film leads not only to the formation of significant inhomogeneities in the piezoelectric response distribution in the structure, but also to the noticeable increase in the magnitude of both the vertical and lateral components of the piezoresponse near the perforation holes. The calculation results showed that the greatest enhancement is observed for the lateral component of the piezoresponse: from 5 pm/V for a nonperforated film to 65 pm/V in the perforated area.
Conclusions. The most probable mechanism for such a change in properties is the influence of a disturbed layer that occurs at the boundary and the inner surface of vertical air channels. The properties of this layer are due to two factors: amorphization of the structure as a result of the focused ion beam etching and the appearance of pinned domain states near the hole, leading to the formation of the complex piezoresponse distribution both at the hole boundary and in the gap between the perforations. The information obtained is important for understanding the peculiarities of the formation of local piezoelectric and ferroelectric responses in photonic crystals fabricated by focused ion beam etching, as well as for finding ways to control their state when an external electric field is applied.
ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
- The article is devoted to a complex technological method aimed at increasing the structural strength of parts of defense engineering products.
- The proposed technological solutions based on a synergistic approach provided a balanced improvement in material parameters by eliminating the shortcomings of the original semi-finished product.
- This approach consists in the vision of a metallic material as a system subjected to a chain of technological influences in the chemical, thermodynamic, and mechanical interaction of its components.
- In practice, thanks to the results obtained, the existing technological process for manufacturing the petal part was changed, which made it possible to improve the technological and technical characteristics of the part.
Objectives. The development of technological methods with the purpose of increasing the structural strength of defense engineering products can be carried out by creating new methods for obtaining and processing parts or improving traditional methods based on an integrated (synergistic) approach. The article presents a complex method for surface treatment of parts and assessment of the hardness and surface roughness of the initial workpiece from alloys of the Al–Mg system to improve the quality of manufacturing the module cases of the MSP-418K product related to electronic warfare devices.
Methods. This approach consists in the vision of a metallic material as a system subjected to a chain of technological impacts in the process of chemical, thermodynamic, and mechanical interaction of its components. The workpieces were obtained by metal pressure treatment according to various schemes and temperature conditions Then they were processed with a blade tool using a dynamometer. The resulting cut was examined using a metallographic method along the entire end face from the outer surface to the center of the sample of workpieces.
Results. Experiments were carried out for the case of Al–Mg alloys. It made it possible to reveal the relationship between the parameters of the change in the structure of the material being processed and the stability of the cutting process, as well as the quality of the surface during finishing turning.
Conclusions. The proposed technological solutions based on a synergistic approach provided a balanced improvement in material parameters by eliminating the shortcomings of the original semi-finished product. The obtained experimental data allowed concluding the deformation of workpieces according to complex schemes at low temperature has a beneficial effect on the machinability of the metal material, ordering the structure and improving the quality of the surface of the parts. Using a synergistic approach, it became possible to correct the poor technological heredity of material properties obtained in previous operations: the surface quality of the workpieces due to the continuity of the processed material and the strength properties of parts for critical and especially critical purposes were improved. The existing technological process for manufacturing the “petal” part was changed in practice using an integrated method, which made it possible to improve its technological and technical characteristics.
PRODUCT QUALITY MANAGEMENT. STANDARDIZATION
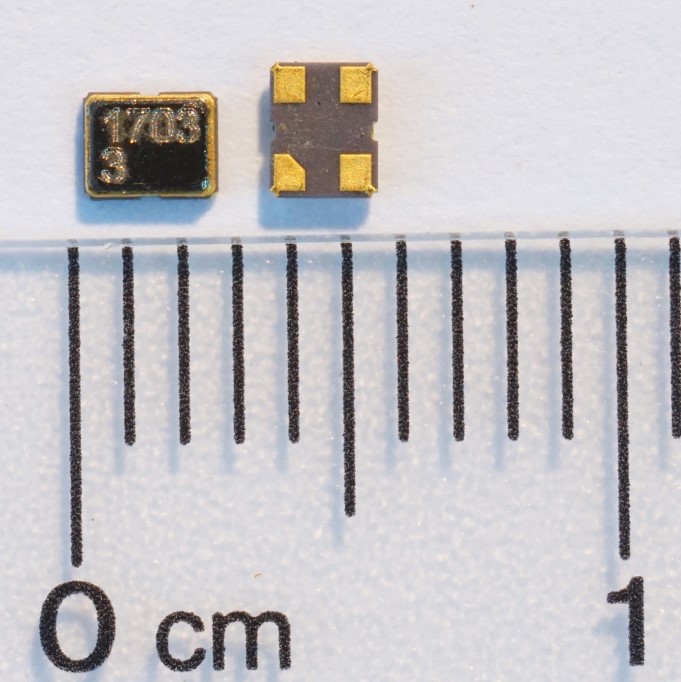
- This article studies the possibility of developing optimal requirements for the thermal training regime when applied to miniature quartz resonators RK588 used at high ambient temperatures.
- The requirements for the reliability characteristics of RK588 quartz resonators were established.
- The method of statistical modeling in radio engineering and the method of testing quartz resonators for reliability were used.
- The requirements for frequency drift under the influence of high ambient temperature on the type of crystalline plate were established at a size of 1.5 × 1.0 mm.
Objectives. In the development of radio electronics and communications, it is important that the requirements for the reliability, stability of the generated frequencies, and selectivity of the receiving equipment are fulfilled. The use of quartz resonators, widely used in radio circuits today, has partially allowed for the reliability of communication devices and guaranteed high frequency stability to be enhanced without complicating the circuit. Modern global trends in the development of electrical equipment are associated with miniaturization. The dimensions of quartz resonators are decreasing every year, while the requirements for reliability remain high. The study aimed to evaluate the possibility of using quartz resonators packaged in a miniature ceramic case 2.5 × 2.0 × 0.6 mm, under conditions of elevated ambient temperature. It has also allowed for the development of optimal requirements for the thermal training regime as the basic technological operation for stabilizing the oscillation frequency.
Methods. Reliability testing of quartz resonators and methods of statistical modeling in radio engineering.
Results. The results established the requirements for the reliability of RK588 quartz resonators in miniature ceramic cases 2.5 × 2.0 × 0.6 mm in size under the influence of elevated ambient temperatures of +85 °C and +125 °C. The requirements for frequency drift when exposed to elevated ambient temperature on the crystalline plate type based on RF patent No. 27122426 “Method of manufacturing thin crystalline plates and thin crystalline elements” were also specified. The method of thermal training was optimized and the ageing coefficients were established.
Conclusions. The coefficients of ageing calculated for the resonators during the reliability tests was as follows: Batch No. 1 at a temperature of +85 °C was 0.75; and for Batch No. 2 at a temperature of +125 °C was 0.18. For this type of piezoelectric element with a size of 1.5 × 1.0 mm at an operating temperature of +125 °C the ageing coefficient is 4 times lower than at a temperature of +85 °C. This indicates the possibility of using the RK588 resonator at elevated ambient temperatures.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
- The brightness alignment for satellite images is very important due to their high contrast, which fills the weak parts of the image and makes them invisible. Parts of a high-density image are blurred and out of shape.
- We propose a new method called gradient which flattens an image and creates synthesized outline images from images with different densities.
- The method involves to form a conditional coordinate system on images, which allows transferring image fragments with low and high densities as gradients to the synthesized image.
- The synthesized image contains low-medium and high-density images aligned with a gradient. It shows images that are not visible at the same time in the original image.
Objectives. The aim of the study is to develop a methodology for assessing the semantics of weakly structured or morphologically complex visual information models. In order to achieve the goal, a criterion for classifying visual models as complex and an algorithm for obtaining a gradient image with several levels of density were introduced. The gradient image is not binary, thus increasing the reliability of finding boundaries or contours. An auxiliary structural visual model was introduced, and a series of images of different densities was used in processing. Next, the concept of a conditional image coordinate system was introduced. This allows for information to be transferred from different visual models to a synthetic resulting visual model.
Methods. Using gradient image processing and constructing a new intermediate structural model allows models with different densities to be linked. A system of conditional image coordinates was introduced and a series of models with different densities to obtain a synthetic image was processed.
Results. The visual models obtained from satellite images with poor visibility of objects were processed in the Sun– Earth–Moon system. The Sun–Earth system was chosen as the basis. A characteristic of space images is the fact that the bright light of the Sun “clogs” the images of other objects with large phase angles. The use of the contouring technique allows for the visibility of images of low brightness and high brightness to be equalised. The shift of the frequency response after detection of all objects enabled the formation of a clear visual model.
Conclusions. In primary visual models, low brightness images were not visible. They appeared when exposure was increased, while high-density objects merged into one. Because of this, it is fundamentally impossible to obtain a high-quality image of all objects, or the complete semantics of a visual model from a single high, medium, or lowdensity image. In order to obtain the complete semantics of the visual model, a series of images need to be processed with the transfer of images to a common synthetic image. The proposed technique allowed for such problems to be resolved. A comparison of the results obtained using the methods of processing a single image proved the reliability and high information content of the method.
- We analyzed the intelligent input weights selection problem of an extreme learning machine (ELM) using biology-inspired algorithms in regression problems.
- The results showed that the use of bioinspired algorithms can improve prediction accuracy of an ELM.
- The ELM with input weights adjusted by bioinspired optimization algorithms requires fewer hidden neurons in order to achieve the best prediction accuracy on test data.
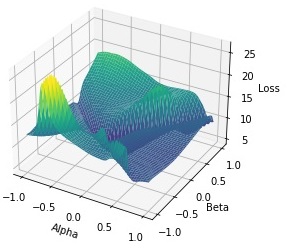
- Additionally, we provided visualizations of high-dimensional loss functions optimized by the considered bioinspired algorithms in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system near the discovered optimum.
Objectives. Recent research in machine learning and artificial intelligence aimed at improving prediction accuracy and reducing computational complexity resulted in a novel neural network architecture referred to as an extreme learning machine (ELM). An ELM comprises a single-hidden-layer feedforward neural network in which the weights of connections among input-layer neurons and hidden-layer neurons are initialized randomly, while the weights of connections among hidden-layer neurons and output-layer neurons are computed using a generalized Moore– Penrose pseudoinverse operation. The replacement of the iterative learning process currently used in many neural network architectures with the random initialization of input weights and the explicit computation of output weights significantly increases the performance of this novel machine learning algorithm while preserving good generalization performance. However, since the random initialization of input weights does not necessarily guarantee optimal prediction accuracy, the purpose of the present work was to develop and study approaches to intelligent adjustment of input weights in ELMs using bioinspired algorithms in order to improve the prediction accuracy of this data analysis tool in regression problems.
Methods. Methods of optimization theory, theory of evolutionary computation and swarm intelligence, probability theory, mathematical statistics and systems analysis were used.
Results. Approaches to the intelligent adjustment of input weights in ELMs were developed and studied. These approaches are based on the genetic algorithm, the particle swarm algorithm, the fish school search algorithm, as well as the chaotic fish school search algorithm with exponential step decay proposed by the authors. By adjusting input weights with bioinspired optimization algorithms, it was shown that the prediction accuracy of ELMs in regression problems can be improved to reduce the number of hidden-layer neurons to reach a high prediction accuracy on learning and test datasets. In the considered problems, the best ELM configurations can be obtained using the chaotic fish school search algorithm with exponential step decay.
Conclusions. The obtained results showed that the prediction accuracy of ELMs can be improved by using bioinspired algorithms for the intelligent adjustment of input weights. Additional calculations are required to adjust the weights; therefore, the use of ELMs in combination with bioinspired algorithms may be advisable where it is necessary to obtain the most accurate and most compact ELM configuration.
ECONOMICS OF KNOWLEDGE-INTENSIVE AND HIGH-TECH ENTERPRISES AND INDUSTRIES. MANAGEMENT IN ORGANIZATIONAL SYSTEMS
- The study analyzes the general principles and approaches to methods of evaluating project effectiveness. A model of priorities of high-tech projects is given.
- Models are presented which take into account cash flows after the expiration of the payback period. This allows investors, despite the complexity of project financing in innovative developments, to make informed investment decisions. The study also provides an algorithm for economic evaluation of the investment attractiveness of high-tech projects.
Objectives. The creation of high-tech projects is one of the main stages of the transition to an innovative economy. This can further be explained by the intensive development of globalization processes in the economic system of Russia. High-tech projects have lower profitability when compared to venture projects, but a higher probability of commercial success. In Russia, there are currently six areas of support programs for high-tech projects. Moreover, there are a large number of operators supporting high-tech projects actively working in the Russian market. The acceleration of the technological development requires an intensification of innovation policy and a revision of the portfolio of its acting instruments. In turn, this makes the matter of analyzing their significance and relevance for participants in innovation processes more pertinent. The purpose of this work is to identify features of the investment process in the Russian Federation, and determine criteria for selecting priority high-tech projects and methods of evaluating high-tech projects, in the aim of making informed investment decisions.
Methods. Models for assessing the investment attractiveness of high-tech projects were constructed using economic and mathematical modeling methods, in particular, nonlinear and dynamic programming methods.
Results. The general principles and approaches to methods of evaluating the efficiency were analyzed. A model of the priorities of high-tech projects was presented. Models which take into account cash flows after the expiration of the payback period were also considered (by means of the nonlinear programming of calculation of the discounted payback period of investment costs and the modernized discounted payback period of investment costs). An algorithm for assessing the investment attractiveness of high-tech projects was demonstrated.
Conclusions. To date, there has been no single algorithm for assessing the investment attractiveness of high-tech projects. However, the integrated application of the methods and models proposed in this work will allow investors to make informed investment decisions despite the complexity of project financing in innovative developments.
PHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY
- The key sources of knowledge on micro- and nanoelectronics technologies include universities, institutions of the Russian Academy of Sciences, industry-specific institutions, customers, manufacturers, and consumers.
- The knowledge management system is aimed at solving problems of the social, commercial, and scientific and technical aspects of the company’s activities in micro- and nanoelectronics.
- Fundamental and applied research, requirements management, manufacturing, and operation correspond to main sections of the life cycle curve for the considered technologies.
Objectives. Over the past few decades, multiple knowledge management models have been developed by many research groups studying the innovation process in companies. However, these knowledge and information management models are rather general, and do not consider the dynamics and variability of technology development. This implies involving specific organizations in different types of knowledge generation activities. The paper aims to reveal the importance of a knowledge management system in micro- and nanoelectronics technologies as well as identify and systematize the sources of knowledge in the scientific and technical field.
Methods. In this paper, the method for analyzing the relationship between key business indicators of the companies is applied. The results are then represented in a causal loop diagram. The stakeholder analysis method is also used here.
Results. Three relevant trends in developing the knowledge management system for knowledge-intensive enterprises involved in micro- and nanoelectronics technologies are identified with respect to the social, commercial, and scientific and technical aspects in research organizations. The key sources of knowledge on micro- and nanoelectronics technologies include universities, institutions of the Russian Academy of Sciences, industry-specific institutions, customers, manufacturers, and consumers. Also, the authors consider digital twins to be a promising source of knowledge on micro- and nanoelectronics technologies.
Conclusions. The analysis of the technology life cycle curve using the example of micro- and nanoelectronics allows correlating single stages of this life cycle with specific activities during which new knowledge is generated. These activities include fundamental and applied research, requirements management, implementation in manufacturing, and operation analysis. For microelectronics, they correspond to the areas of emergence, peak of inflated expectations, trough of disillusionment, slope of enlightenment, and plateau of productivity on the technology life cycle curve.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)