INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
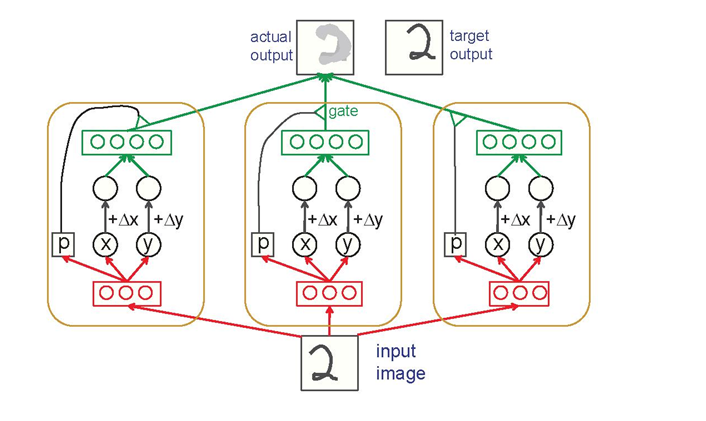
To recognize objects in images, a local detector for a reprint model of an object in an image was developed and described. A transforming autocoder, a model of a neural network, was developed for the local detector. The local detector is able, in addition to determining the modified object, to determine the original shape of the object as well. The transforming autocoder is a heterogeneous network (HS) consisting of a set of networks of smaller dimension. These networks are called capsules. The capsule can learn to display the pose of its visual object in a vector. The transforming autoencoder solves the problem of identifying facial images in conditions of interference (noise), changes in illumination and angle.
Currently, methods for recognizing objects in images work poorly and use intellectually unsatisfactory methods. The existing identification systems and methods do not completely solve the problem of identification, namely, identification in difficult conditions: interference, lighting, various changes on the face, etc. To solve these problems, a local detector for a reprint model of an object in an image was developed and described. A transforming autocoder (TA), a model of a neural network, was developed for the local detector. This neural network model is a subspecies of the general class of neural networks of reduced dimension. The local detector is able, in addition to determining the modified object, to determine the original shape of the object as well. A special feature of TA is the representation of image sections in a compact form and the evaluation of the parameters of the affine transformation. The transforming autocoder is a heterogeneous network (HS) consisting of a set of networks of smaller dimension. These networks are called capsules. Artificial neural networks should use local capsules that perform some rather complex internal calculations on their inputs, and then encapsulate the results of these calculations in a small vector of highly informative outputs. Each capsule learns to recognize an implicitly defined visual object in a limited area of viewing conditions and deformations. It outputs both the probability that the object is present in its limited area and a set of “instance parameters” that can include the exact pose, lighting, and deformation of the visual object relative to an implicitly defined canonical version of this object. The main advantage of capsules that output instance parameters is a simple way to recognize entire objects by recognizing their parts. The capsule can learn to display the pose of its visual object in a vector that is linearly related to the “natural” representations of the pose that are used in computer graphics. There is a simple and highly selective test for whether visual objects represented by two active capsules A and B have the correct spatial relationships for activating a higher-level capsule C. The transforming autoencoder solves the problem of identifying facial images in conditions of interference (noise), changes in illumination and angle.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
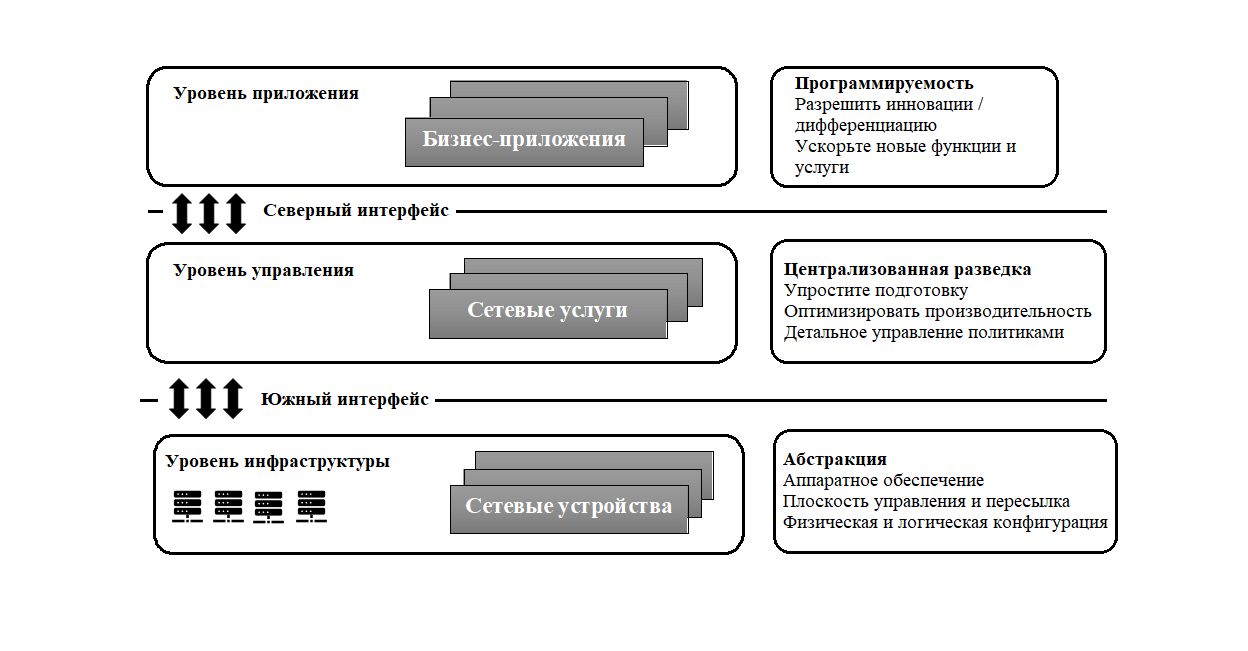
A traditional network carries several challenges: the vendor dependency, complexity of managing a large network, dynamically changing forwarding policies. Software-defined networking is a new networking strategy designed to address these challenges. We discuss various architectural issues of open-source SDN controllers network and examine their impact on the QoS.
The quality of service (QoS) in networking is the process of managing network resources to reduce packet loss and to lower network jitter and latency. QoS has been widely used in traditional network and can also be implemented in the 5G standard based on a software-defined network (SDN). A traditional network carries several challenges, such as vendor dependency, the complexity of managing a large network, dynamically changing forwarding policies, and more. Software-defined networking is a new networking strategy designed to address the challenges of a traditional IP network, such as high levels of complexity and inability to adapt to the new quality of service requirements in a timely manner. The fundamental idea behind SDNs compared to the conventional networking paradigm is the creation of horizontally integrated systems through the separation of the control and the data plane while providing an increasingly sophisticated set of abstractions. Recently, various SDN-enabled QoS frameworks have emerged that offer many possibilities for network reconfiguration and high-level definition of policies. QoS requirements for 5G networks have been defined on the basis of three main categories of use cases: extreme mobile broadband (xMBB), massive machine type communications (mMTC) IoT/M2M devices, and highly reliable М2М-communication (ultra-reliable machine-type communications – uMTC). This paper analyzes and surveys the QoS based on the openflow protocol method and QoS based on open-source SDN controllers method in 5G network. In addition, we discuss various architectural issues of open-source SDN controllers network and examine their impact on the QoS. Furthermore, we outline the characteristics of the QoS parameters such as latency, availability, reliability, jitter, and bandwidth in the 5G network. Finally, the article discusses and compares parameters of the QoS in 5G determined by world’s leaders in 5G technology.
- Local content modification provided to subscribers of the terrestrial digital television signal is necessary to provide the technical possibility of organizing inserts of local content signals, such as TV programs of regional broadcasters, as well as information on emergency situations.
- The reliability parameters of the restorable system for organizing terrestrial television broadcasting at a remote station with the content modification were calculated.
- It was found that additional redundancy organized by connecting the output stream from the RX1 receiver directly to the transmitting device allows for a 2.5-fold increase in the average operating time between failures.
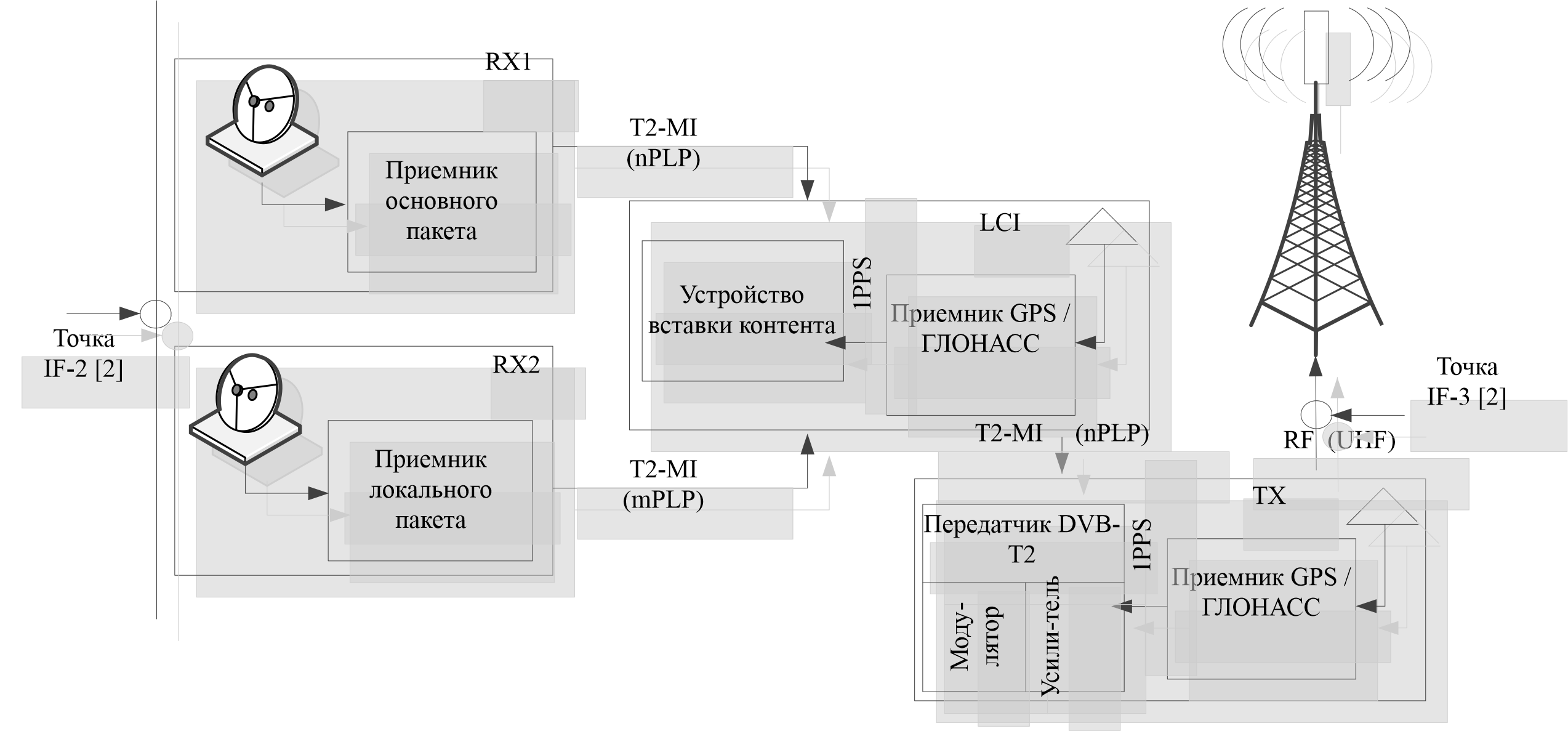
Local content modification provided to subscribers of the terrestrial digital television signal is necessary to provide the technical possibility of organizing inserts of local content signals, such as TV programs of regional broadcasters, as well as information on emergency situations. Broadcast multiplexes of federal TV programs are designed for use within the corresponding time zone (A, B, C, D, M). In each time zone, there are a number of regions, in each of which there are local TV and radio companies that produce local content that must be delivered to the subscribers of the whole subject. The task of embedding/modifying content at each remote transmitting station is performed by an inserter or local content insertion device (ETSI TS 102773). The reliability parameters of the restorable system for organizing terrestrial television broadcasting at a remote station with the content modification were calculated in this article. Tables and a graph of the broadcasting system states are presented, on the basis of which, systems of Kolmogorov differential equations are compiled. It was found that additional redundancy organized by connecting the output stream from the RX1 receiver directly to the transmitting device allows for a 2.5-fold increase in the average operating time between failures, as well as an increase in the availability factor by 5.26 percent. All calculations were performed using the SimInTech software package. The influence of automatic redundancy of the local content inserter and the transmitter on the occurrence of errors in the stream that affect the quality of the output signal is considered. The relationship between the availability factor and the components of the quality of service parameter – SAE, SDE and SIE is determined.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
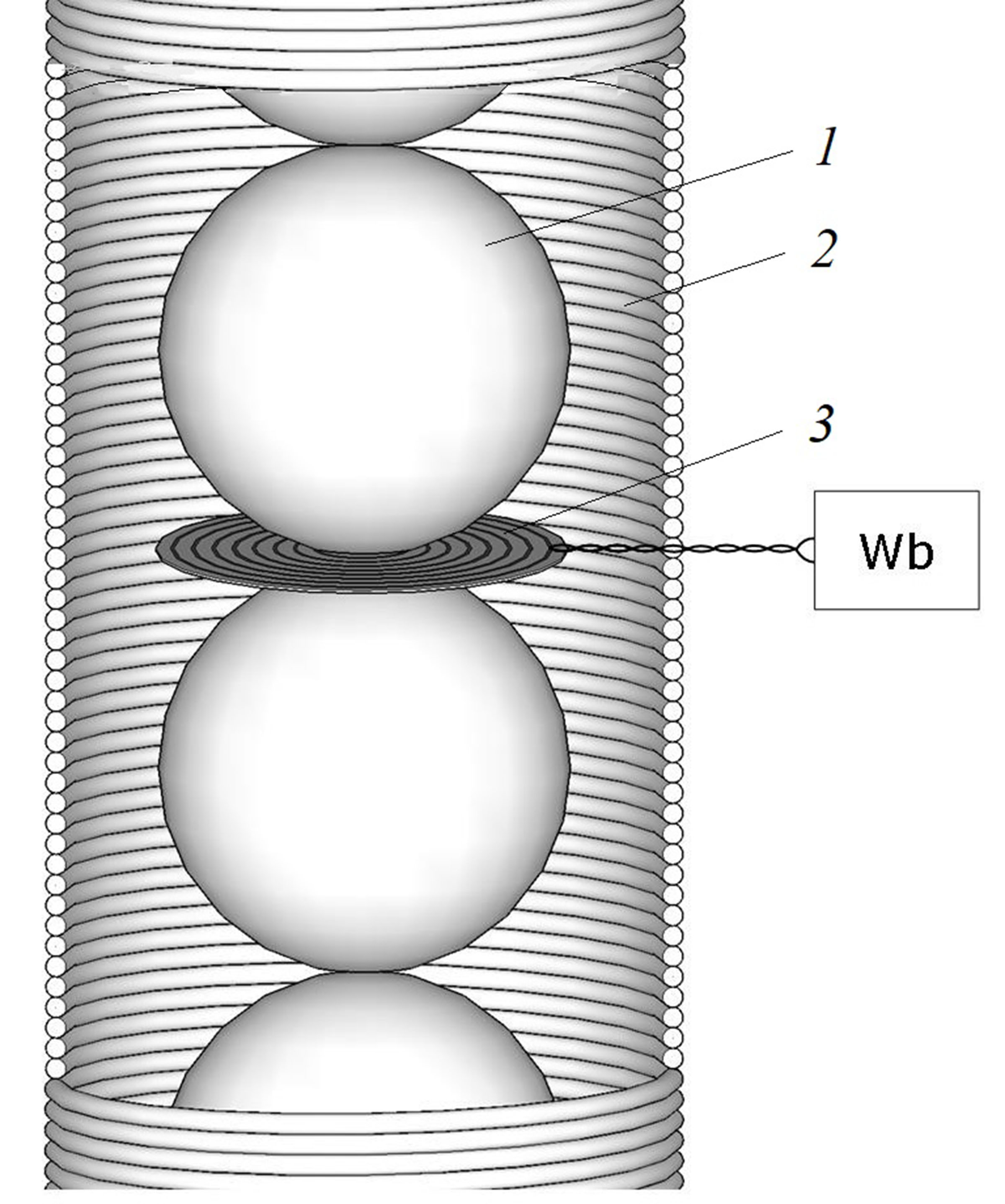
To clarify the magnetic parameters of the conditional cores of a chain of granules-balls, as a physically self-sufficient element of a granular medium, we have made measuring magnetic flux sensors in the core as circuits on thin printed circuit boards (with mounting holes) placed between adjacent balls. Based on the obtained data of the magnetic flux in cores of different radii r (r/R = 0.2–0.9) of a chain of spheres with a radius of R = 20 mm, the magnetic induction B, as well as their magnetic permeability μ, were determined when the chain is magnetized in the solenoid using a field of strength from 4.8 to 54.5 kA/m. It is shown that with formal thickening of the cores, the values of B and μ decrease due to a decrease in the volume of the ferromagnet in the core, and for the chain as a whole, they correspond to the values of B and μ for a poly-ball backfill medium.
In addition to information on the magnetic parameters of inhomogeneous magnetics, in particular, granular magnetics usually studied within the framework of the quasi-continuous medium model, it is of no less interest to obtain information from the standpoint of the model, when the object of study is the characteristic elements of an inhomogeneous magnetic. According to the well-proven model of selective magnetization of a granular medium, the elements that make up this medium are chains of granules – straight and sinuous, always manifesting themselves in the direction of its magnetization. They perform the function of conductor channels of the generated magnetic flux through the granular medium. As a result, it is a kind of branched «bundle» of conductor channels. For any of the chains of granules, for example, granules-balls of radius R, conceptually significant are the magnetic parameters of its conditional cores with radius r ≤ R, and these parameters, first of all, the magnetic permeability of quasi-continuous cores and magnetic induction in them, for different (in r) cores are variable, which requires appropriate magnetic diagnostics. To clarify the magnetic parameters of the conditional cores of a chain of granules-balls, as a physically self-sufficient element of a granular medium (i.e., in accordance with the model of chain-link magnetization of such a medium), it is practical to make measuring magnetic flux sensors in the core as circular sensors surrounding the contact point of granules-balls, however, not as traditional wire loops, but as circuits on thin printed circuit boards (with mounting holes) placed between adjacent balls. Based on the obtained data of the magnetic flux in cores of different radii r (r/R = 0.2–0.9) of a chain of spheres with a radius of R = 20 mm, the values of the magnetic induction B in them, as well as their magnetic permeability μ, were determined when the chain is magnetized in the solenoid by a field of strength from 4.8 to 54.5 kA/m. It is shown that with formal thickening of the cores, the values of B and μ decrease due to a decrease in the volume of the ferromagnet in the core, and for the limiting core (r/R → 1), i.e., for the chain as a whole, they correspond to the values of B and μ for a poly-ball backfill medium.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
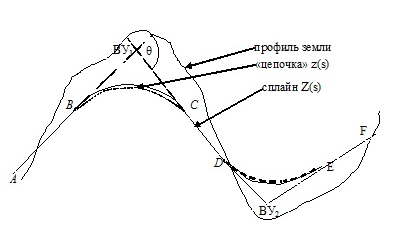
The article proposes a two-stage scheme for spline approximation of a plane curve. At each iteration of the optimization process for the corresponding set of active constraints, a basis is constructed in the null space of the constraint matrix and in the subspace – its complement. This makes it possible to find the direction of descent and solve the problem of excluding constraints from the active set without solving systems of linear equations.
In the article, computer design of routes of linear structures is considered as a spline approximation problem. A fundamental feature of the corresponding design tasks is that the plan and longitudinal profile of the route consist of elements of a given type. Depending on the type of linear structure, line segments, arcs of circles, parabolas of the second degree, clothoids, etc. are used. In any case, the design result is a curve consisting of the required sequence of elements of a given type. At the points of conjugation, the elements have a common tangent, and in the most difficult case, a common curvature. Such curves are usually called splines. In contrast to other applications of splines in the design of routes of linear structures, it is necessary to take into account numerous restrictions on the parameters of spline elements arising from the need to comply with technical standards in order to ensure the normal operation of the future structure. Technical constraints are formalized as a system of inequalities. The main distinguishing feature of the considered design problems is that the number of elements of the required spline is usually unknown and must be determined in the process of solving the problem. This circumstance fundamentally complicates the problem and does not allow using mathematical models and nonlinear programming algorithms to solve it, since the dimension of the problem is unknown. The article proposes a two-stage scheme for spline approximation of a plane curve. The curve is given by a sequence of points, and the number of spline elements is unknown. At the first stage, the number of spline elements and an approximate solution to the approximation problem are determined. The method of dynamic programming with minimization of the sum of squares of deviations at the initial points is used. At the second stage, the parameters of the spline element are optimized. The algorithms of nonlinear programming are used. They were developed taking into account the peculiarities of the system of constraints. Moreover, at each iteration of the optimization process for the corresponding set of active constraints, a basis is constructed in the null space of the constraint matrix and in the subspace – its complement. This makes it possible to find the direction of descent and solve the problem of excluding constraints from the active set without solving systems of linear equations. As an objective function, along with the traditionally used sum of squares of the deviations of the initial points from the spline, the article proposes other functions taking into account the specificity of a particular project task.
The paper presents a numerical analysis of evaporation from the surface of a water droplet subjected to forced convection in the gas phase. Forced convection compatible with the symmetry conditions are represented by flows directed downward along the axis of the system and diverging along the sides near the drop and the substrate. It is found that the evaporation rate does not change in the presence of forced convection flows, which contradicts most of the experimental works. The reason for the discrepancies is supposed to be the appearance of nonequilibrium conditions at the boundary of the condensed phase: under these conditions, the evaporation regime ceases to be diffusional.
Experiments on measuring the rate of evaporation of liquid sessile droplets into air show that the rate of evaporation increases in the presence of forced convection flows. However, data on the effect of convection on evaporation are often contradictory and should be clarified. The paper presents a numerical analysis of evaporation from the surface of a water droplet subjected to forced convection in the gas phase. The drop is located on a smooth horizontal isothermal substrate; the mode with constant contact angle is considered. The shape of the drop has axial symmetry, the same for the velocities and pressure. Forced convection compatible with the symmetry conditions are represented by flows directed downward along the axis of the system and diverging along the sides near the drop and the substrate. The mathematical model is constructed for evaporation controlled by diffusion in the gas phase and takes into account surface tension, gravity, and viscosity in both media, buoyancy and Marangoni convection. The results indicate the existence of the mutual influence of liquid and gaseous media. Thus, a drop vibrates under the influence of movements in the atmosphere, which generates a density wave in the gas: the drop «sounds». The magnitude of the velocity in a liquid is 50 times less than the characteristic velocity in air. It is found that the evaporation rate does not change in the presence of forced convection flows, which contradicts most of the experimental works. The reason for the discrepancies is supposed to be the appearance of nonequilibrium conditions at the boundary of the condensed phase: under these conditions, the evaporation regime ceases to be diffusional.
In this article, using game-theoretic approaches, the human community was modeled as a dynamic system, and the influence of such ethical norms of behavior as egoism, altruism, and morality. Using the case of a game model of social choice, it was shown that communities, among whose representatives a predominantly egoistic worldview prevails, were less likely to innovate and abandon outdated norms of behavior. Conversely, those communities whose representatives share basic ethical principles are more confident and quickly moving to advanced and progressive norms.
In this article, using game-theoretic approaches, the human community is modeled as a dynamic system, and the influence of such ethical norms of behavior as egoism and altruism, morality (on the example of the Kant imperative or the Golden Rule of Morality) on the state of this system is investigated, as well as the question of determining the effectiveness of the community depending on the prevailing worldview of its representatives. Using the example of a game model of social choice between two norms of behavior – one generally accepted, but outdated, and another, new, not yet widespread, but more advanced and progressive – it is shown that communities, among whose representatives a predominantly egoistic worldview prevails, are less likely to innovate and abandon outdated norms of behavior. Conversely, those communities whose representatives share basic ethical principles are more confident and quickly moving to advanced and progressive norms. In conclusion, the paper examines the question of what advantages a society acquires in which purposeful educational and educational activities are conducted, designed to increase the level of morality and morality among its representatives. The results obtained can be used, firstly, as an integral part of the course on the mathematical base of ethics, which could perform the functions of educational work in higher and secondary educational institutions; and, secondly, for the purposes of evaluating the effectiveness of educational work and state planning in this area.
The study is devoted to the evolution of the rotational motion of a planet in the central Newtonian field of forces. The planet is modeled by a body consisting of a solid core and a viscoelastic shell rigidly attached to it. The mass center of the planet moves along a given Keplerian elliptical orbit. The equations of motion are derived via a system of Routh equations using the canonical Andoyer variables, which are “action-angle” variables in the unperturbed problem. It is shown that in stationary motion, the angular momentum vector is orthogonal to the orbital plane, and the limiting value of the modulus of this vector depends on the eccentricity of the elliptical orbit.
The work is devoted to the study of the evolution of the rotational motion of a planet in the central Newtonian field of forces. The planet is modeled by a body consisting of a solid core and a viscoelastic shell rigidly attached to it. A limited formulation of the problem is considered, when the center of mass of the planet moves along a given Keplerian elliptical orbit. The equations of motion are derived in the form of a system of Routh equations using the canonical Andoyer variables, which are “action-angle” variables in the unperturbed problem and have the form of integro-differential equations with partial derivatives. The technique developed by V.G. Vilke is used for mechanical systems with an infinite number of degrees of freedom. A system of ordinary differential equations is obtained by the method of separation of motions. The system describes the rotational motion of the planet taking into account the perturbations caused by elasticity and dissipation. An evolutionary system of equations for the “action” variables and slow angular variables is obtained by the averaging method. A phase portrait is constructed that describes the mutual change in the modulus of the angular momentum vector G of the rotational motion and the cosine of the angle between this vector and the normal to the orbital plane of the planet’s center of mass. A stationary solution of the evolutionary system of equations is found, which is asymptotically stable. It is shown that in stationary motion, the angular momentum vector G is orthogonal to the orbital plane, and the limiting value of the modulus of this vector depends on the eccentricity of the elliptical orbit. The constructed mathematical model can be used to study the tidal evolution of the rotational motion of planets and satellites. The results obtained in this work are consistent with the results of previous studies in this area.
PHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS OF TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY
The article is devoted to the consideration of the theoretical aspects of the influence of the humanitarian environment in a technical educational institution on improving the quality of training specialists, increasing their competitiveness in the labor market. The analysis of special literature and generalization of different points of view on the subject of research act as research methods.
The article is devoted to the consideration of the theoretical aspects of the influence of the organization of the humanitarian environment in a technical educational institution on improving the quality of training specialists, increasing their competitiveness in the labor market. The analysis of special literature and generalization of different points of view on the subject of research act as research methods. The humanitarian environment represents a certain content orientation of the educational system of curricula and work programs of disciplines that include the unity of material and spiritual values that are responsible for the formation of students’ personality. Each teacher considers this problem in his own way, so the points of view have their own specifics. The humanitarian environment of the university includes a specially organized training system in which a set of specially selected methods and technologies is used to «nurture» a competitive specialist with a set of not only professional, but also personal competencies. The training of specialists in a technical university has its own characteristics related to the further professional implementation of graduates. Students at the stage of training must master special competencies, develop personal qualities, be motivated to study disciplines and master new types of activities. The organization of the humanitarian environment in the organization should be implemented at all levels: university, faculty, at each specific lesson in the study of disciplines, both provided for in the curriculum and extracurricular according to the plan of educational work. For this purpose, it is necessary to maintain and control the interaction of students with all components of the educational environment of a higher educational institution using methods such as: humanitarian technologies, mentoring, organizing a positive psychological climate in the institution, introducing additional educational programs, using active and innovative teaching methods.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)