INFORMATION SYSTEMS. COMPUTER SCIENCES. ISSUES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
One of the key tasks when working with unstructured data is to find and identify patterns in order to understand them and develop filling patterns. The paper analyzes the rules for the design of bibliographic sources in order to identify common patterns. The existing directions of work with unstructured data and methods of processing unstructured data, in particular, the rules for the design of bibliographic lists of literary sources, are considered. These rules were used to form templates consisting of semantic groups.
The term «unstructured data» means data that is unordered and arbitrary in shape. However, this type of information has a certain structure. Today there is a wide variety of data and, as a result, it is necessary to interpret them. Interpretation tasks include forecasting, classification, clustering, association, sequence search, data visualization, and variance analysis. The difficulty lies in the fact that the data itself can differ not only in terms of format, but also in terms of its structure. One of the key tasks when working with unstructured data is to find and identify patterns in order to understand them and develop filling patterns. The paper analyzes the rules for the design of bibliographic sources in order to identify common patterns. The concepts of structured and unstructured data are touched upon. The existing directions of work with unstructured data and methods of processing unstructured data, in particular, the rules for the design of bibliographic lists of literary sources, are considered. These rules were used to form templates consisting of semantic groups on the basis of examples of the corresponding lists of bibliographic sources. The final comparison of the obtained templates revealed both common features that unite all the considered templates and features that separate them.
MODERN RADIO ENGINEERING AND TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
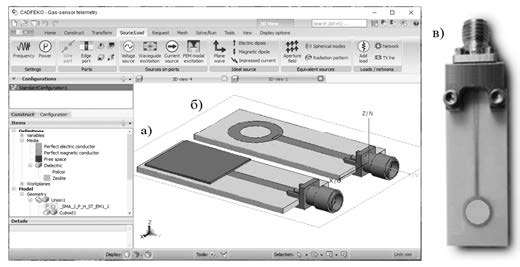
The possibility of using microstrip reflector microwave resonators in solving problems of resonant gas-sensor telemetry on layered dielectric substrates with gas-sensitive sputtering was investigated. The radio-wave principle of the microstrip gas sensor analyzer was formulated. An electrodynamic model of a microstrip gas sensor analyzer in the Altair Feko environment was developed. The transition to the upper microwave frequencies will allow reducing the size of the topology of the microstrip resonator and reducing the effective area of the zeolite deposition, and, consequently, increasing the adsorption rate of the gas-sensitive layer of the active dielectric.
The possibility of using microstrip reflector microwave resonators in solving problems of resonant gas-sensor telemetry on layered dielectric substrates with gas-sensitive sputtering was investigated. It is noted that the use of chemically active sputtering, for example, on the basis of zeolites having a high selective gas adsorbent kinetics in terms of speed, makes it possible to create radiosensor materials capable of changing the dielectric constant in the process of absorbing gases, as well as of sublimated vapors of solid and liquid phases of various compounds. As an alternative approach in the field of dosimetric gas monitoring, a modification of radiosensor applications based on microwave sensors is proposed, which allows using microwave solutions based on microstrip microwave resonators with active gas-sensitive sorption zeolite sputtering on a dielectric substrate to conduct gas analysis in real time. The radio-wave principle of the microstrip gas sensor analyzer was formulated. An electrodynamic model of a microstrip gas sensor analyzer in the Altair Feko environment was developed. An experiment was planned, and gas-sensor telemetry tests of ammonia vapors dissolved in water were carried out. It was established that the amount of sorbed water and ammonia in the zeolite unambiguously conforms both to the absolute value of the reflection coefficient at resonance and to the resonant frequency itself. Using the example of recording hydrogen nitride vapors it was shown that the reflection coefficient and frequency shift in the resonator, which depend on the concentration of the adsorbed gas, correspond to the saturation characteristics of the gas sensor and make it possible to repeatedly measure small concentrations of a gas that can be absorbed by zeolite at a temperature corresponding to the condition of rapid evaporation of controlled gas from the active dielectric layer, which guarantees desorption of the sensor. It was established that in order to increase the speed of the gas sensor response it is advisable to create a microstrip resonator for the resonance region of 8...10 GHz and to use a microstrip sensor substrate material with a high dielectric constant. This is due to the fact that the transition to the upper microwave frequencies will allow reducing the size of the topology of the microstrip resonator and reducing the effective area of the zeolite deposition, and, consequently, increasing the adsorption rate of the gas-sensitive layer of the active dielectric.
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is used for high-speed information transmission in many radio systems and, in particular, in DVB-S and DVB-S2/S2X digital satellite television systems.The paper investigates the influence of amplitude and phase errors in the formation of quadrature oscillations (imbalance of quadratures) on the noise immunity of coherent reception of QAM signals. The amplitude imbalance in a wide range of values practically does not affect the noise immunity. The phase imbalance of quadratures markedly affects the noise immunity of coherent reception of QAM signals.
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is used for high-speed information transmission in many radio systems and, in particular, in DVB-S and DVB-S2/S2X digital satellite television systems. A receiver included as a part of the transmitting equipment of such systems has a block for the formation of quadrature oscillations used as a reference for signal demodulation. Due to hardware instabilities, amplitude and phase errors may occur, which leads to quadratures imbalance. These inaccuracies cause additional errors in the received signal demodulation. This can significantly degrade the noise immunity of the reception. The paper investigates the influence of amplitude and phase errors in the formation of quadrature oscillations (imbalance of quadratures) on the noise immunity of coherent reception of QAM signals. Using the methods of statistical radio engineering the parameters of the distributions of processes in the receiver are obtained, and the probability of a bit error is estimated. The dependences of the bit error probability on the amplitude unbalance factor, on the phase error of quadrature formation and on signal-to-noise ratio are obtained. It is shown that the amplitude imbalance of the quadratures leads to a significant decrease in the noise immunity of QAM signals reception at M ≥ 16. The acceptable amplitude deviation in this case can be considered to be equal to 5%. At M= 4, the amplitude imbalance in a wide range of values practically does not affect the noise immunity. The phase imbalance of quadratures markedly affects the noise immunity of coherent reception of QAM signals. The permissible phase error is no more than 0.05 rad (3 degrees). As the signals positionality increases, this influence also increases.
MICRO- AND NANOELECTRONICS. CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
The methods of the radiometers, photodiodes, filters and multilayer mirrors characteristics measurements are based on the synchrotron radiation absolute spectral characteristics and accelerated electrons number variation. Computer modeling of multi-layer coatings allows us to calculate the optical characteristics of superlattices in the extreme ultraviolet region. The obtained results of measurements of the spectral reflection coefficient of a multilayer coating in the photon energy range of 65–100 ev indicate a resonance reflection character with a max-imum at an energy of 83.5 ev and an energy width at a half-height of about 6.5 ev.
The investigations of multilayer surface nanostructures characteristics was performed with synchrotron radiation sources, characterized by an intensive, calculated continuum. It plays an important role in nanoelectronics metrological base. The main research were carried out at electron storage rings «Siberia-1» (Kurchatov Institute) and MLS (PTB, Berlin) with low electron energy, in a wide wavelength range, including visible range, AUV, VU, EUV and to exclude the X-ray radiation influence. The methods of the radiometers, photodiodes, filters and multilayer mirrors characteristics measurements are based on the synchrotron radiation absolute spectral characteristics and accelerated electrons number variation. The metrological investigations with synchrotron radiation was concentrated on:
– absolute spectral responsivety of silicon photodiodes with multilayer filters for integral radiometers applications;
– spectral transmittances of surface layers of photodiodes in the extreme ultraviolet region;
– spectral reflectance coefficient of superlattice.
The characteristics of photodiodes and filters on a synchrotron radiation source are measured using a monochromator and a reference detector. The use of a synchrotron radiation channel makes it possible to study the spectral transmittance of thin films and multilayer structures formed in the in situ mode. To form multilayer nanostructures directly on the receiving surface of photodetectors, an ion-plasma sputtering module is used. The optical scheme of the channel provides for the possibility of using monochromators of grazing incidence for the range of photon energies from 25 to 100 ev and normal incidence for the range of photon energies from 4 to 25 ev. At a photon energy of 40 ev, the absolute spectral sensitivity was 70 ma / W for a photodiode with a surface multilayer filter applied. To develop an experimental technique for measuring the spectral reflection coefficient of multilayer mirrors, and to create standard samples, the Mo/Si system was studied. Computer modeling of multi-layer coatings allows us to calculate the optical characteristics of superlattices in the extreme ultraviolet region. The obtained results of measurements of the spectral reflection coefficient of a multilayer coating in the photon energy range of 65–100 ev indicate a resonance reflection character with a max-imum at an energy of 83.5 ev and an energy width at a half-height of about 6.5 ev. The working wave-length of the reflecting mirror corresponds to the calculated one, which confirms the effectiveness of the adopted model.
ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
A promising technology for the production of three-dimensional circuits on plastics, the scope of its current application and prospects for its further development in the radio-electronic industry are considered. A classification is proposed on the basis of the key characteristics of thermoplastics for making a decision when choosing materials on the market, taking into account the application in the radio-electronic industry using 3D-MID technology. The article considers the order of the build process with the application of the LPKF-LDS technology production of three-dimensional circuits on plastics.
A promising technology for the production of three-dimensional circuits on plastics, the scope of its current application and prospects for its further development in the radio-electronic industry are considered. The analysis of current opportunities and limitations is carried out. It is shown that the key component of the technology is the correct choice of thermoplastics with suitable characteristics for the intended object, taking into account the resistance to external factors. An analysis of the international and domestic regulatory framework for thermoplastics was conducted. This allowed to determine the key characteristics for 3D-MID-technology and to make a comparison. A classification is proposed on the basis of the key characteristics of thermoplastics for making a decision when choosing materials on the market, taking into account the application in the radio-electronic industry using 3D-MID technology, which is currently either absent or not fully represented. Methods of testing materials for use in the production technology of three-dimensional circuits on plastics and ensuring the quality of manufacturing of radio engineering products, allowing to confirm the compliance of key parameters of materials are studied. The article considers the order of the build process with the application of the LPKF-LDS technology production of three-dimensional circuits on plastics, which allows building a sequence of processes with particular implementation as an example. The considered LPKF-LDS technology as part of the 3D-MID line is planned in the new laboratory “Threedimensional circuits on plastics and flexible media” at the Department of Design and Production of Radioelectronic Devices of the Institute of Radio Engineering and Telecommunications Systems of MIREA – Russian Technological University.
This paper shows the need for effective technology to control the electromagnetic radiation created in the surrounding space, both by subsystems of aircraft and by the whole object. A method for visualizing 3D electromagnetic field both in space and in time is considered.
The space industry has always set ambitious tasks to create unique equipment, including control equipment. Ensuring electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of such systems is carried out at all stages of the life cycle of an aircraft (AC), starting from its development, including testing and stages of operation. Digital technology is characterized by high noise immunity. However, any modern technical system in the aggregate contains sensors, communication lines and receiving antennas sensitive to the effects of external interfering signals that propagate both through wires and over the air. Hence, the relevance of ensuring the EMC of integrated technical systems that perform the functions of measurement, data processing and the formation of control actions, both digital and analog, is obvious. The electromagnetic compatibility of a sophisticated aircraft or spaceship technical system with other systems is a prerequisite for their sustainable operation. Aerospace technology, where both highly sensitive measurements and energetic control effects are closely combined in the dense layout of an aircraft, requires a solution to the EMC problem. This paper shows the need for effective technology to control the electromagnetic radiation created in the surrounding space, both by subsystems of aircraft and by the whole object. A method for visualizing 3D electromagnetic field both in space and in time is considered.
Before direct exposure to a human organism, the medical equipment is tested on specialized mock-ups of human tissue – phantoms. The aim of this work is to create a phantom that clearly demonstrates the distribution of the thermal field in the volume during heating while maintaining the heating pattern for several hours. Animal tissue (pig liver) and plant tissue (potatoes) were used as biological tissue simulators. The most suitable imitator turned out to be potatoes, because the electrophysical parameters of potatoes are close to those of the human parenchymal organs. As a result, volumetric changes in the structure of plant tissue appear at the place of heating, which makes it possible to evaluate the results of thermal exposure.
Medical equipment, due to its specificity, requires precise adjustment and testing. Therefore, before direct exposure to a human organism, the equipment is tested on specialized mock-ups of human tissue – phantoms. The physicochemical characteristics of phantoms should be close to the characteristics of the selected biological tissue. Depending on the task at hand, the design of the phantom itself and its properties will be different. The aim of this work is to create a phantom that clearly demonstrates the distribution of the thermal field in the volume during heating while maintaining the heating pattern for several hours. The studies were carried out on an experimental stand, which contained a device for radio frequency ablation of tissues “METATOM-3” with a set of electrodes, a thermal imager, and a tripod for fixing the electrodes. Animal tissue (pig liver) and plant tissue (potatoes) were used as biological tissue simulators. The most suitable imitator turned out to be potatoes, because the electrophysical parameters of potatoes are close to those of the human parenchymal organs. Thermal exposure of potatoes at 58–62°C leads to changes in the starch characteristics: the appearance of a fine-crystalline structure filled with water from the surrounding space is observed. As a result, volumetric changes in the structure of plant tissue appear at the place of heating, which makes it possible to evaluate the results of thermal exposure. To form a clearer thermogram, part of the potato is cut off. In general, potatoes have a narrow temperature range of reaction in the range of 58–62°C, which conveniently coincides with the temperature of cell death (60°C). The experiments carried out show the effectiveness of such a phantom. The obtained pictures of thermal field are reliable and persist for several hours. Experimental studies of various singleelectrode and multi-electrode systems provide ground for recommending this phantom for the practice of developing radio-frequency and microwave ablation systems.
MATHEMATICAL MODELING
The peculiarities of light beam expansion in plasma upon irradiation of condensed targets with a powerful UV laser pulse are studied with the help of mathematical modeling. It was shown on the basis of experimental and calculated data that selffocusing of the laser beam developed in the plasma. As a result, hot spots were produced in vicinity of the plasma critical density, and fast (superthermal) electron flows were generated. The parameters of dangerous modes of laser beam perturbations were estimated.
The peculiarities of light beam expansion in plasma upon irradiation of condensed targets with a powerful UV laser pulse are studied with the help of mathematical modeling. Experiments were carried out at the Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences with the use of GARPUN installation: a powerful KrF laser that irradiated two-layer targets consisting of aluminum foil and a plexiglass layer. Channels stretched along the direction of incidence of the laser beam were found at the bottom of the crater. It was shown on the basis of experimental and calculated data that selffocusing of the laser beam developed in the plasma. As a result, hot spots were produced in vicinity of the plasma critical density, and fast (superthermal) electron flows were generated. The electron flows could produce the channels in the plexiglas. In order to describe the self-focusing effect a physicalmathematical model was developed, and “FOCUS” program was created at the Russian Technological University (MIREA). Numerical simulations were carried out on the gas-dynamic profiles (linear and exponential). It was shown that thermal self-focusing could develop at the conditions of “GARPUN” experiments (~ 1 mm longitudinal plasma, moderate radiation intensity: 1011–1012(W/cm2) × µm2). The parameters of dangerous modes of laser beam perturbations were estimated. The interest in the experimental and mathematical modelling results is related to the laser thermonuclear fusion (LTF) research. Although Nd glass lasers are the basic installations for LTF research, UV gas eximer lasers have some advantages as drivers for future thermonuclear fusion reactors. The interaction of UV laser radiation with plasma has some peculiarities. Thus, developing physical-mathematical models and creating new programs required for the interpretation of modern UV laser – plasma coupling experiments and for the design of large scale facilities based on eximer drivers is a topical problem.
ISSN 2500-316X (Online)